ABOUT DEUTERIUM
DEPLETED WATER INFLUENCE ON INDICATORS OF PROOXIDE-ANTIOXIDE SYSTEM AT LABORATORY ANIMALS
Barishev M.G., Basov A.A.,
Bolotin S.N., Dzhimak S.S., Dolgov M.A.,
Fedosov S.R., Shashkov D.I.
By nuclear magnetic
resonance spectroscopy established decrease in the maintenance of deuterium in
blood plasma, erythrocytes and homogenate of hearts at the laboratory rats
infected Staphylococcus aureus, using
deuterium depleted water within a month. At rats also infected Staphylococcus
aureus, using the usual water, any changes of isotope structure it is not
revealed. By method EPR spectroscopy it is defined that the quantity of the
paramagnetic centers heart and a liver of the rats took deuterium depleted
water after lyophilization, has decreased in 4 times in comparison with control
group that is testifies about reduction of quantity of free radicals and
favorable influence of deuterium depleted water on animals organism.
Deuterium depleted water, NMR spectroscopy, EPR
spectroscopy, free radicals, oxidative
stress
This work is executed with
financial support of the Russian fund of basic researches, the project
¹11-04-96523-r_south_c.
In modern preventive medicine the great attention is given to the correction of metabolic infringements in organism on nonclinic stage for the purpose of the prevention of
development of proof complications. One of nonspecific protective systems of
the organism is antioxide system (ÀÎS) [1].
It is known that antioxidants regulated normal activity of a human body,
in particular processes of lipids oxidation, fibers and nucleinic acids in which result in cages highly active substances of oxygen
and free radicals are formed[2,3]. In physiological conditions free radicals are
necessary for normal breath, metabolism
and destruction of alien bacteria.
At
the same time at superfluous strengthening of uncontrollable reactions free
radicals oxidations the typical pathological process characterized by
strengthened formation of primary radicals (superoxide anion-radical, nitrogen oxide), jet molecules (singlet
oxygen, a hydrogen peroxide, hydroperoxides), secondary radicals hydroxyl
radical, alkils, alkoxiles, peroxiles) against oppression fermental
(superoxidazmutaza can develop, the catalase, glutathione reductase) and non
fermental (vitamins, thiols, polyphenols) links of antioxidå systems (ÀÎS) that is accompanied by
disbalance of functioning
protective organism systems and
decrease in its nonspecific resistance to pathological processes [4].
The
food is one of the environment factor,
essentially influencing to the health, working
capacity and life expectancy of the person. Now, besides an optimum parity of
food components and mineral substances
in a diet, the great attention is given to
the influence nutrients to the
indicators endogen antioxidå system and level free radicals oxidations in an organism that can
promote increase in duration of active ability to live and preventive
maintenance of complications of some diseases, in pantogenesis which the
essential role is played by the phenomena of oxidizing stress (diabetes, an
atherosclerosis, a bronchial asthma, tumoral and inflammatory diseases of
various localization, etc.).
The greatest interest is represente the revealing possibility antioxide
means, specifically operating on concrete links of processes free radicals of
oxidation, and, except that, products interfering superfluous formation
peroxide oxidation and the last eliminating toxic effects [5].
Important selection for the further tests of such substances which at
introduction in clinical practice, along with high efficiency antioxide
actions, would show a minimum
by-effects represented.
The water
with the lowered maintenance of a deuterium is one of the possible factor that
raising working of the OAS.
It is known that the person in
physiological conditions consumes 2-3 liters of liquid in a day,
therefore changes of structure of a food by the expense of water with the lower
maintenance of a deuterium can influence indicators ÀÎS. Biological effects of water with the
lower maintenance of a deuterium are described in this article [6].
The
purpose of this research is studying influence of water with the lower
maintenance of a deuterium (concerning natural level) on indicators
prooxide-antioxide system and the quantitative maintenance of a deuterium in
fabrics of laboratory rats in one-monthly experiment [7].
Reception gomogenate fabrics carried out by the mechanical crushing of bodies
(heart, liver, kidneys) before
reception of homogeneous weight with the subsequent in centrifuge at 3000 rpm within 20 minutes. The supernatant received took away by means of a
micropipette in volume of 2 ml.
For definition of the quantitative maintenance of free radicals by
method EPR spectroscopy in heart, liver and their kidneys subjected liophilic
to drying (the device: a dryer
liophilic LS-1000).
The definition
of the concentration of a deuterium in
biological liquids and gomogenat fabrics have been spent on a pulse nuclear
magnetic resonance spectrometer JEOL JNM-ECA 400MHz. Shooting of spectra was spent on
corresponding resonant frequency of kernels of a deuterium – 61.4 MHz. Shooting
parameters: 6.7 with (acquisition time), 20 with (relaxation delay), 5.6 mks
(x-pulse), 0.15 Hz (resolution). Shooting temperature – 25 ◦C, thus
accuracy of stabilization 0.2 ◦C. Measurements were spent with the using of an ampoule of 5 mm in
which has been strictly fixed soldered a capillary containing kolibration in the defined concentration
scale mix deuterium and non deuterium of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), giving 2D
a nuclear magnetic resonance a signal in the field of 3,4 m.p. (rather (ÑD3)4Si),while 2D
a nuclear magnetic resonance signal HDO is in area of 4,7 m.p. (Rather (ÑD3)4Si).
Peaks of received signals are displayed
in a picture 1.
Handling of the received spectra consisted in determination of a ratio
integral intensity 2D a nuclear magnetic resonance of signal HDO,
containing in the researched sample rather 2D a nuclear magnetic
resonance of signal DMSO-D1 which intensity, in turn, has been
defined under the same conditions concerning standards – samples of water with
precisely certain content of deuterium (3,7 ppm, 51 ppm, 150 ppm). Measurements
of each sample were led repeatedly for reduction of errors of experiment. Thus
accuracy of determination of the
content of deuterium in biological samples
is 2± ppm.
Picture 1.- Relation of the integral intensity 2D a nuclear magnetic resonance of signal
HDO, rather 2D a nuclear magnetic resonance of signal DMSO-D1
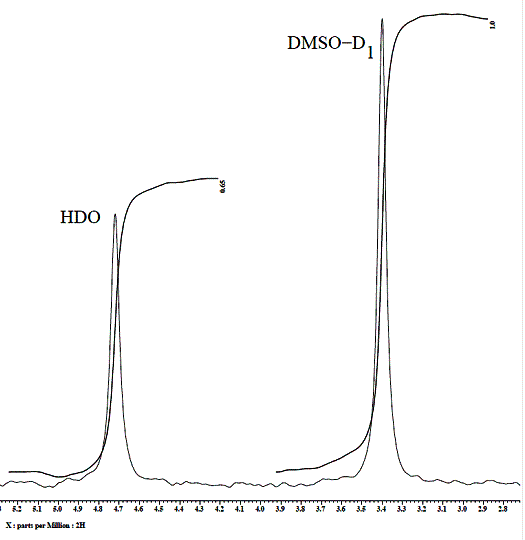
The measurement of
spectra EPR spent at ambient temperature on spectrometer JES FA300 (JEOL,
Japan) in a X-range. The measurement conditions: the microwave oven capacity 1
mW, frequency of microwave radiation of 9144 MHz, amplitude of high-pitched
modulation 0,1 ìÒ. Samples measured in a quartz ampoule (5 mm), the weight of a hinge
plate in a resonator zone is 0,0300 g.
Concentration of the paramagnetic centres in samples defined by comparison with a standard sample signal (TEMPOL). Integral signal strength
EPR in investigated samples defined by a double numerical integration on a
method of rectangles [8].
In thirty days,
after the beginning of carrying out of experiment in skilled and control groups
watched exterior differences. The animals in skilled group outwardly looked
healthy, without any deviations. In a check group watched organic violations on
ears, to a nose. Biopsy research has shown that some rats in a check group had
a formation of the Nevus of Bekker – pigmentary hair epidermal a nevus to an inflammation. CODE ÌÊB: CODE D23.3 Other good-quality new growths of a skin.
By
this researches it is installed that indexes
antioxide activity at animals in I group have made plasmas of
blood 1287,3±11,6. And in animals of II group indexes ÀÎS were above on 9,2 % in comparing by
group I (p <0,05) that testifies to increase at them activity ÀÎS and allows to speak about improving of
system operation of nonspecific protection of an organism. At rats of II group
indexes free radical oxidation have
been lowered on 24,8 % in comparison with group I that specifies in reduction
of processes of formation of the free radicals at usage of water with the
lowered content of deuterium. Such changes prooxide-antioxide with
prevalence antioxide potential at system level should be
considered systems as the factor of increase of nonspecific protection of an
organism.
The result of this research the content of deuterium in blood plasma is
resulted in table ¹1.
Table ¹1 – The deuterium content in blood plasma of rats
|
Sample |
Changes of deuterium content, % |
|
Plasma of blood |
15,2 |
Apparently from table 1, after the use by rats of water with the under
content of deuterium within a month, its concentration in blood plasma has
decreased on 15,2%.
Spectra EPR of samples of heart of laboratory animals contain a
non-isotropic singlet signal, parametres of spin-gamiltoniana (g^ = 2.0074, g֕ = 2.003) correspond to
stable radicals [9,10]. Spectra EPR of
samples of a liver have similar character.
The results of measurement of
concentration of paramagnetic centers (PÌC) in lyophilization fabrics of a liver and heart of
laboratory animals, show that amount PMC in researched fabrics decreases
approximately in 4 times in comparison with a check group that testifies to
favorable influence of water with the under content of deuterium on an organism
of animals.
In lyophilization fabrics of kidneys of differences
between skilled and control groups it is not revealed.
By this way, it is installed that the use of water with the under
content of deuterium concerning natural level HDO, leads to lowering of
concentration of this element in blood plasma, erythrocytes and hearts of
laboratory animals. Such changes in turn, conduct to reduction prooxide
loadings in an organism and to balance recovery of prooxide-antioxide systems that further is accompanied by
increase of immunity to the laboratory animals[11].
Literature
1. Dubinina Å. Å. Some
singularities of functioning fermentative antioxide protection of the person plasma blood / E.E. Dubinin //Biochemistry. – 1993.
–
Ò. 58. – ¹ 2. P. 268–273.
2. Vladimirs U. A. The free radicals
and antioxidants / U.A.Vladimirov// Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Medical
Science. – 1998. – ¹ 7. P.43–51.
3. Gutteridge J. M.C. Copper
salt-dependent hydroxyl radical formation. Damage to proteins acting as
antioxidants / J. M. A C. Gutteridge, S. Wilkins//Biochim. Biophys. Acta. –
1983. – Vol. 758. – P. 38–41.
4. Christen Y. Oxidative stress and
Alzheimer’s disease / Y. Christen//Am. J. Clin. Nutr. – 2000. – Vol. 71. – P.
621–629.
5. Young I. S. Antioxidants in health and disease I. S. Young, J V. Woodside//
J.
Clin. Pathol. – 2001. – Vol. 54. – P. 176–186.
6. Barishev M.G. Electrochemical method of obtaining and
biological properties of water with deuterium depleted water/
M.G. Barishev, S.N. Bolotin, N.S.Vasilev, S.S. Dzhimak, M.A. Dolgov, V.U.
Frolov// Science of Kuban. – 2010. – ¹ 3. P.18–21.
7. Basov A.A. Using analog-digitizer in a part of system of
collection and information processing with chemiluminescence LT-1 / A.A. Basov,
I.I.Pavljuchenko, A. M. Plaksin, S. R. Fedosov// Vestnic new medical technologies. – 2003. – Ò. 10. – ¹ 4. P.67–68.
8. Bachvalov N.S. Chislennye metods /
N.S. Bachvalov, N. P. Zhidkov, G.M.Kobelkov – Ì:
Fizmatlit, 2001. – P.630 .
9. Borovik Å.S. Lectures on magnetism / E.S. Borovik, V.V.
Eremenko,
A.S. Milmer
– Ì: Fizmatlit,
2005. – P. 512.
10. Azhipa J. I. Medical and biologic
aspects the application of the method electro paramagnetic resonance / J.I. Azhipa – Ì: Science, 1983.
– P. 528
.
11. Barishev
M. G. Nmr and epr study of deuterium pepleted water effect on the laborotary animals’
prooksidant-antioksidant system / Barishev M. G., Basov A. A., Bolotin S. N.,
Dzhimak S. S., Kashaev D. V., Fedosov S. R., Frolov V. U., Malishko V. V.,
Vlasov R. V. // Ecological Bulletin of Research Centers of the Black Sea
Economic Cooperation (BSEC). Iss. 3. 2011. P. 16-20.