Economic
THE ROLE OF VALUE ADDED TAX AND LEVY
Imanbayev T.B.
Magistrant of the Kazakh Academy of Finance and
Economic
Baluanov. J.K.
PhD in Economics the Kazakh Academy of Finance and
Economic
 Value added tax (VAT) is
a part of the contributions to the budget value of taxable sales turnover,
added in the process of production and circulation of goods (works, services),
as well as contributions to import goods into the territory of the Republic of
Kazakhstan.
Value added tax (VAT) is
a part of the contributions to the budget value of taxable sales turnover,
added in the process of production and circulation of goods (works, services),
as well as contributions to import goods into the territory of the Republic of
Kazakhstan.
VAT payable to
the tax on taxable turnover, defined as the difference between the amount of
VAT charged for the sale of goods (works, services) and the amount of VAT
payable for goods (works, services), ie the difference between the purchased
and sold VAT.One of the first compulsory payments, the introduction of the tax
in December 1991, was the value added tax (VAT). Introduction of VAT is a
logical step and the key to improving the tax system of Kazakhstan.
Over the years, he firmly established in the
tax system in Kazakhstan. Currently VAT - one of the major taxes. The
basis of his collection, as the name suggests, is the value added of all stages
of production and distribution of goods. This tax is traditionally classified
as universal indirect taxes in the form of original premiums charged by
including in the price of goods, carrying the main burden of taxation on the final
consumers of products and services.
VAT as the most
significant indirect tax has two complementary functions: fiscal and
regulatory. The first (main), in particular, is to mobilize significant
revenues from this tax to the budget at the expense of ease of collection and
sustainable base of taxation. In turn, the regulating function is shown to
stimulate capital formation and strengthening of control over terms of
promoting products and their quality.
As you know, the
VAT is one of the most important taxes paid by enterprises and organizations.
During the existence of the value added tax operating mechanism of calculation
and collection has undergone significant changes. Questions calculation
and payment attract attention of many local economists and widely discussed in
the periodical press.
VAT as the most
significant indirect tax has two complementary functions: fiscal and
regulatory. The first (main), in particular, is to mobilize significant
revenues from this tax to the budget at the expense of ease of collection and
sustainable base of taxation. In turn, the control function is shown to
stimulate capital formation and strengthening of control over terms of
promoting products and their quality.Under the Treaty of October 6, 2007,
signed in the capital of the Republic of Tajikistan - Dushanbe, was established
Customs Union (CU).Single EurAsEC Customs Union at the moment is a combination
of trade and economic relations between the three countries: Russia, Belarus
and Kazakhstan.This organization EurAsEC Customs Union was to create a single
customs territory, consisting of several states where canceled all customs
duties for the products in between. Within the limits of the customs union has
a common customs tariff and uniform requirements for regulation of trade
relations with other countries.The changes in the customs legislation,
particularly with regard to customs duties on a number of imports, causing the
society to interpretation essence goals of the Customs Union.
Opposition
parties and movements indicated a negative perception of Kazakhstan's accession
to the Customs Union, and in many speeches and statements noticeable tendency
to present the ongoing process of economic integration as a partial loss of
sovereignty of our country.In reality, the decision on the establishment of the
Customs Union, adopted by the heads of states of the Eurasian Economic
Community in August 2006, is aimed at creating a more favorable environment for
economic development of the Community and the CIS. Customs union, by definition,
is a higher level of economic integration, and, of course, that the Union is a
transfer of national powers of the state, forming the Customs Union, in
specific areas of trade regulation.Treaty on the Customs Union Commission,
signed by the heads of Kazakhstan, Russia and Belarus in October 2007, provides
for a unified standing regulatory body - the Commission of the Customs Union,
responsible for implementing the decisions of the supreme body of the Customs
Union - EurAsEC Interstate Council.In the member countries of the Customs Union
are different rates of value added tax, in Kazakhstan - 12%, Russia 18%,
Belarus - 20%, which significantly complicates the export of Kazakh businessmen
(Diagram 1).
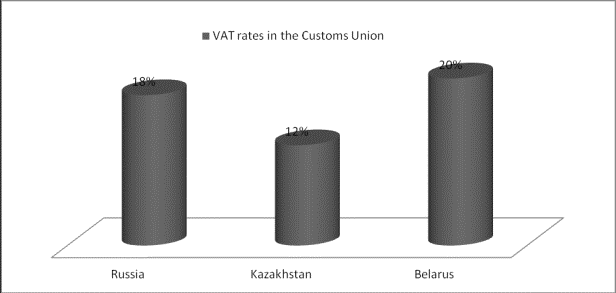
Diagram 1. VAT
rates in the Customs Union.
The Treaty
provides that the decisions taken by the Commission, will be binding on
enforcement in the territories of the Parties, which is aimed at improving the
functioning of the Customs Union.[2].
As President
Nursultan Nazarbayev in his address to the nation, "New Decade - New
Economic Growth - New Opportunities for Kazakhstan", the creation of the
Customs Union - a breakthrough for all of Kazakhstan integration initiatives.
To ensure compliance with decisions of the Commission of the Customs Union in
Kazakhstan, the Constitutional Council in November 2009, adopted a normative
judgment that the decision of the Commission, as a general rule, take
precedence over national laws and can be applied directly.
Customs union
involves, in addition to the duty-free trade between the application of a
single trade policy towards third countries outside the Customs Union. The
Customs Union is: a unified customs tariff policy, which includes the common
customs tariff, non-tariff measures uniform, unified customs legislation.
The main element
of the customs and tariff regulation of the Customs Union is the common customs
tariff, which came into force on 1 January 2010.
It should be
noted that by the time of the creation of the Customs Union with Belarus,
Kazakhstan and Russia have common duties for about 40 percent - is about 4500
codes. That is, the fee for a number of items of goods imported from third
countries, were similar in the three countries. Therefore, it was necessary to
unify around 60 per cent customs duty. In this case, the government of
Kazakhstan, Belarus and Russia the following criteria: the presence of its own
production, the structure of imports. In the course of this work on a regular
basis, consult with representatives of local business on changing rates of
import customs duties.[3].
According to the
Agreement on the export of goods from the territory of one state - member of a
customs union on the territory of another country - a member of the customs
union applies to "zero" rate of VAT, subject matter of record
exports. In this case, VAT is charged on such goods in a foreign country - a
member of the customs union on their importation.
The list of
documents to be submitted to the tax authorities to confirm the validity of the
zero rate of VAT is set item 2 of article. 1 of the Protocol. These documents
must be submitted to the tax authorities within 180 days from the date of
shipment. If you are not providing the relevant documents within the specified
time the tax is paid at 18% for the tax period, which accounts for the date of
shipment. In this case, under the date of shipment of the goods means the first
date of the time of the primary accounting document.
In the case of
the taxpayer of the relevant documents, in the later period after 180 days, the
amount previously paid VAT is deductible
It is also
necessary to note that the publicly available information on the Internet is
known that the tax authorities are trying by all means to refuse to refund the
VAT from the budget, so we need to be prepared for tax claims and related
defense costs in a tax dispute on VAT refunds. Here are the main claims, which
are often used for tax motivation failure to refund VAT:
The exporter can
not apply a zero rate of VAT, therefore, to accept tax deductible, unless the
proceeds of the transaction.
Taxes is
important to establish a place where they work or services provided. State -
Customs Union members decided that the performance of work, rendering of
services the company will have to pay VAT in the State in which such services
and activities are implemented. If the place of supply of services will be
Russia, VAT will be calculated according to the rules of Articles[1].
This arrangement
of the customs union is enshrined in paragraph 2 of the Protocol of 11.12.2009
"On the procedure of indirect taxes on the performance of work, rendering
of services in the Customs Union"
Define the place
of supply of services and works
Place of
implementation of works and services, depending on the type of the latter can
be determined by the location of the property, the buyer, the artist, as well
as the place of delivery and the implementation of major works (services).
To confirm the
place of supply will be required:
- A contract for
work or services;
- Documents
confirming the performance of work, rendering of services;
- Other documents
required by the legislation of the Customs Union (Article 3 of the Protocol).
Consider the
place of supply rules for setting details.
The location of
the property. The place of supply of works and services related to real estate,
will be the area where this property is actually located. In practice, this
rule is applied in construction, repair, restoration, and also works on
gardening.
By the way, the
same way define the place of implementation services for renting and hiring of
immovable property. For example, the Kazakh company is building a warehouse in
Moscow. The warehouse is in Russia, so the work of this company are subject to
VAT at rates of the Tax Code.
The location of
the movable property. With movable property is the opposite. The place of
supply and services in this case will be the territory of the country where the
property is located physically (podp.2 paragraph 1 of Art. 3 of the Protocol).
This rule is applied in practice to work and services for installation,
assembly, processing equipment.
Summing up the
work done - you can say the following:
This paper deals
with the VAT - one of the most complex in terms of taxes.
He has a huge
fiscal importance, being a significant source of new revenue.
At the same time,
the value added tax performs a regulatory function by influencing the pricing
mechanism.
The value of VAT
for the domestic economy is difficult to overestimate. VAT applies to state
taxes and is valid on the entire territory of Kazakhstan.
SUMMARY
The concept of the role of the
value-added tax in the Customs Union. Written about the benefits of the customs
Union. Written about the benefits of the customs union and the problems of value added.
List of
sources used
1. Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On taxes and other obligatory
payments to the budget
2. Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On Customs Affairs in the
Republic of Kazakhstan"
3. B.Nurakhmetov // Questions and answers on the legislation of the Customs
Union // seven establishments