Математика/5. Математическое
моделирование
cand. tech. sci. Semakhin A.M.
student Batalov I. S.
Kurgan State University,
Russia
MATHEMATICAL
MODEL OF OPTIMIZATION OF STRUCTURE OF THE ELECTROASSEMBLY PANEL OF A CONTROL
SYSTEM
Increase of efficiency of designing of electroassembly panels is an
actual problem. Mathematical modelling allows to raise efficiency of designing
of electroassembly panels of control systems of the process equipment.
The open joint-stock company (Open Society) “Kurganhimash” - one of the
leading Russian enterprises on designing and manufacture of the process
equipment for oil and gas extraction, chemical, power, nuclear, metallurgical,
machine-building, medical, food and other industries /1/.
Let's develop mathematical model of optimization of structure of an
electroassembly diagram of a control system of the modular compressor station
which is let out by the enterprise “Kurganhimash”.
Statement of a problem. From among the nomenclature of the blocks
offered by firms on a commodity market forming structure to choose the blocks
defining the optimum plan with the least cost.
Let ![]() - the firms offering
accessories for electroassembly panels,
- the firms offering
accessories for electroassembly panels, ![]() ;
; ![]() - the name of completing products,
- the name of completing products,
![]() ;
; ![]() - the blocks forming an electroassembly panel of a control system by
modular compressor station,
- the blocks forming an electroassembly panel of a control system by
modular compressor station, ![]() ;
; ![]() - quantity of blocks j names
- quantity of blocks j names ![]() ;
; ![]() - cost of the block of j-th name;
- cost of the block of j-th name;
![]() - required variable (binary).
- required variable (binary). ![]() =1 - if the block j names i firms is established on an electroassembly
panel,
=1 - if the block j names i firms is established on an electroassembly
panel, ![]() =0 - if the block j names i
firms is not established on an electroassembly panel.
=0 - if the block j names i
firms is not established on an electroassembly panel.
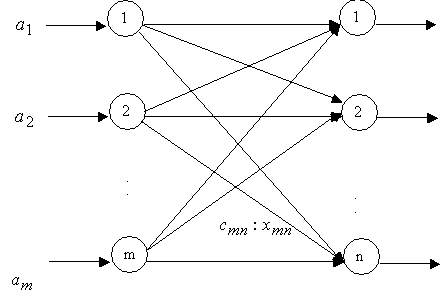
The network model of a problem of optimization of structure of an
electroassembly panel is presented on fig.1.
blocks quantity
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Fig. 1 Network model of optimization of structure of an electroassembly
panel
The mathematical model of optimization of structure of an
electroassembly panel of a control system of modular compressor station looks
like
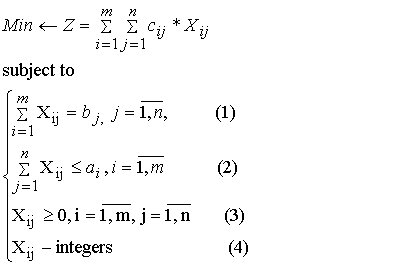 (1)
(1)
Restriction 1 provides a choice j the block i firms.
Restriction 2 provides a choice i the firm delivering j the block.
Restriction 3 imposes unnegativity on required variables.
Restriction 4 imposes step-type behaviour on required variables.
The initial given problems enter the name in the form of the
distributive table (table 1).
Table 1
The distributive
table of a problem of optimization
|
Firms |
Blocks |
Quantity of blocks |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
… |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
… |
|
|
||||||
|
… |
… |
… |
… |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
… |
|
|
||||||
|
Need for blocks |
|
|
… |
|
|
||||||
Algorithm of the decision of a problem of optimization
1. Definition of the basic plan of a problem of optimization.
2. Check of the received distribution of blocks on an optimality.
3. If distribution is not optimum, blocks are redistributed, reducing
value of criterion function.
4. Repeated check of an optimality of the received distribution of
blocks /2/.
Iterative process repeats until the optimum decision will be received.
Application of algorithm demands performance of conditions:
1. Costs ![]() of blocks of j-th name are
presented,
of blocks of j-th name are
presented, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
2. Quantity ![]() of blocks j-th names are
presented,
of blocks j-th names are
presented, ![]() .
.
3. Names ![]() of completing products are
presented,
of completing products are
presented, ![]() .
.
4. The general need for blocks is equal to the general offer: 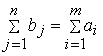 .
.
The general need for blocks less than the general offer,  .
.
The open model will be transformed in closed by introduction of the
fictitious block ![]() .
.
The need of the block pays off under the formula
 (2)
(2)
Methods of the decision of a problem
1. A distributive method.
2. A method of potentials.
Results of the lead researches have allowed to draw conclusions.
1. The mathematical model of optimization of structure of an
electroassembly panel of a control system is developed by the modular
compressor station which is let out by the enterprise “Kurganhimash”.
2. The mathematical model allows to reduce expenses and terms of
designing of an electroassembly panel. To raise validity of accepted decisions.
References:
2. Hamdy A Taha
Operations Research: An Introduction. Seven Edition - М.: Publishing house "Williams", 2005 - 912 p.