Ýêîíîìè÷åñêèå íàóêè/ 6.Ìàðêåòèíã è ìåíåäæìåíò.
Postgraduate student: Shapovalova
E.,
Scientific supervisor: Yerysh
L
Donetsk National University of Tugan-Baranovsky, Ukraine
Features of the
development of international marketing
The key
difference between domestic marketing and marketing on an international scale
is the multidimensionality and complexity of the many foreign country markets a
company may operate in. An international manager needs a knowledge and
awareness of these complexities and the implications they have for
international marketing management.
International
marketing involves the firm in making one or more marketing mix decisions
across national boundaries. At its most complex, it involves the firm in
establishing manufacturing/processing facilities around the world and
coordinating marketing strategies across the globe. At one extreme there are
firms that opt for ‘international marketing’ simply by signing a distribution
agreement with a foreign agent who then takes on the responsibility for
pricing, promotion, distribution and market development. At the other extreme,
there are huge global companies such as Ford with an integrated network of
manufacturing plants worldwide and who operate in some 150 country markets.
Thus, at its most complex, international marketing becomes a process of
managing on a global scale. These different levels of marketing can be
expressed in the following terms: Domestic marketing, which involves the
company manipulating a series of controllable variables such as price,
advertising, distribution and the product/service attributes in a largely
uncontrollable external environment that is made up of different economic
structures, competitors, cultural values and legal infrastructure within
specific political or geographic country boundaries. International marketing,
which involves operating across a number of foreign country markets in which
not only do the uncontrollable variables differ significantly between one
market and another, but the controllable factors in the form of cost and price
structures, opportunities for advertising and distributive infrastructure are
also likely to differ significantly. It is these sorts of differences that lead
to the complexities of international marketing. Global marketing management,which
is a larger and more complex international operation. Here a company
coordinates, integrates and controls a whole series of marketing programmes
into a substantial global effort. Here the primary objective of the company is
to achieve a degree of synergy in the overall operation so that by taking
advantage of different exchange rates, tax rates, labour rates, skill levels
and market opportunities, the organisation as a whole will be greater than the
sum of its parts. This type of strategy calls for managers who are capable of
operating as international marketing managers in the truest sense, a task which
is far broader and more complex than that of operating either in a specific
foreign country or in the domestic market.
How
international marketing is defined and interpreted depends on the level of
involvement of the company in the international marketplace. International
marketing could therefore be: Export marketing, in which case the firm markets
its goods and/or services across national/political boundaries. International
marketing, where the marketing activities of an organization include
activities, interests or operations in more than one country and where there is
some kind of influence or control of marketing activities from outside the country
in which the goods or services will actually be sold. Sometimes markets are
typically perceived to be independent and a profit centre in their own right,
in which case the term multinational or multidomestic marketing is often used.
Global marketing, in which the whole organisation focuses on the selection and
exploitation of global marketing opportunities and marshals resources around
the globe with the objective of achieving a global competitive advantage.
International
Business conducts business transactions all over the world. These transactions
include the transfer of goods, services, technology, managerial knowledge, and
capital to other countries. International business involves exports and
imports.
International Business is also
known, called or referred as a Global Business or an International
Marketing . An international business has many options for
doing business, it includes,
1.
Exporting goods and
services.
2.
Giving license to produce goods in the host country.
3.
Starting a joint venture with a company.
4.
Opening a branch for producing & distributing goods in the host
country.
5.
Providing managerial services to companies in the host country.
The nature and characteristics
or features of international business are:-
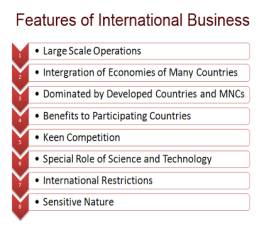
Illustration
1.
1.
Large scale operations : In international
business, all the operations are conducted on a very huge scale. Production and
marketing activities are conducted on a large scale. It first sells its goods
in the local market. Then the surplus goods are exported.
2.
Intergration of economies : International
business integrates (combines) the economies of many countries. This is because
it uses finance from one country, labour from another country, and
infrastructure from another country. It designs the product in one country,
produces its parts in many different countries and assembles the product in
another country. It sells the product in many countries, i.e. in the
international market.
3.
Dominated by developed countries
and MNCs : International business is dominated by developed countries and their
multinational corporations (MNCs). At present, MNCs from USA, Europe and Japan
dominate (fully control) foreign trade. This is because they have large
financial and other resources. They also have the best technology and research
and development (R & D). They have highly skilled employees and managers
because they give very high salaries and other benefits. Therefore, they
produce good quality goods and services at low prices. This helps them to
capture and dominate the world market.
4.
Benefits to participating countries : International
business gives benefits to all participating countries. However, the developed
(rich) countries get the maximum benefits. The developing (poor) countries also
get benefits. They get foreign capital and technology. They get rapid
industrial development. They get more employment opportunities. All this
results in economic development of the developing countries. Therefore, developing
countries open up their economies through liberal economic policies.
5.
Keen competition : International
business has to face keen (too much) competition in the world market. The
competition is between unequal partners i.e. developed and developing countries.
In this keen competition, developed countries and their MNCs are in a
favourable position because they produce superior quality goods and services at
very low prices. Developed countries also have many contacts in the world
market. So, developing countries find it very difficult to face competition
from developed countries.
6.
Special role of science and
technology : International business gives a lot of importance to science and
technology. Science and Technology (S & T) help the business to have large-scale
production. Developed countries use high technologies. Therefore, they dominate
global business. International business helps them to transfer such top
high-end technologies to the developing countries.
7.
International restrictions : International
business faces many restrictions on the inflow and outflow of capital,
technology and goods. Many governments do not allow international businesses to
enter their countries. They have many trade blocks, tariff barriers, foreign
exchange restrictions, etc. All this is
harmful to international business.
8.
Sensitive nature : The
international business is very sensitive in nature. Any changes in the economic
policies, technology, political environment, etc. has a huge impact on it.
Therefore, international business must conduct marketing research to find out
and study these changes. They must adjust their business activities and adapt
accordingly to survive changes.
The new quality of international marketing complexity allowed the researchers to speak on the nomination of the marketing concept to a higher level,
the emergence of a global, multinational,
etc. marketing.
Bibliography:
1.
http://www.cengagebrain.co.nz/content/doole07630_1844807630_02.01_chapter01.pdf
2.
http://www.skema.edu/programs/masters-of-science/msc-international-marketing-and-business-development
3.
http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/2011/09/what-is-international-business-meaning.html
4.
http://www.marketing.spb.ru/
5.
http://marketing.onset.ru/