Сельское хозяйство /
5.Растениеводство, селекция, семеноводство
УДК
633.63:631.816.1
Candidate of agricultural sciences Ionitsoy Y.S.
Institute of bioenergetics cultures and sugar beets NAAS of Ukraine
Removal
of nutrients by sugar beets depending
on
fertilizer dose
In modern conditions together with positive effect from crops capacity,
the degradation of soil fertility in agro ecological systems is observed [1, 4]. The analysis of soils condition in Ukraine concerning humus dynamic in
crop rotation indicates its negative balance. If after cereals in some years
the humus balance was positive, than after technical, feed crops, potato and
vegetables its balance is negative. [6].
The lack of organic material in the soil that is not refilled by plant
remains is necessary to be compensated by application of organic and mineral
fertilizers [7] that is the most effective
resource facility to increase productivity of agriculture production and
reserve soil fertility [6]. Sugar
beets occupy leading position among technical crops, the potential productivity
of which can amount to 90–95 t/ha [2].
As it is known, yield indexes of this crop are directly depend on
fertilizers, especially on mineral one. That is why fertilizers rate, applied
for the crop, should satisfy its needs in nutrients without decrease of humus
content in the soil, after the harvest alienate the nutrients. The intensity of
soil nutrient elements usage is determined by removal index of nutrients [3] that is calculated in the basis of fertilizers rate for
agriculture crops [5].
In this connection, the aim of the research was to determine the removal of
nutrients by sugar beet plants of domestic, foreign and joint breeding
depending on fertilizers rate.
Researches were
conducted on breeding plot of diagnostics and feeding optimization laboratory
of Institute of bioenergetics cultures and sugar beets NAAS of Ukraine in
2001–2003 years. The vessel of Vagner was
used with the volume 14,5 kg of air-dried soil for the vessel, which was
filled by typical alkaline black soil
with the following agrochemical characteristics: humus – 3,8–4,0%, salt
pH – 6,4–6,6, Hr – 1,4–1,6 mg/equivalent for 100 g of soil, mobile phosphorus
and potassium exchanged according to Chirikov 184–197 and 81–89 mg/kg of soil,
alkaline hydrolyzed nitrogen 159–163 mg/kg of soil (according to Cornfild).
Four options were
analyzed: no fertilizers, 1,5; 3,0 and 6,0 g of active ingredient/NPK vessel.
Ammonium nitrate was used as nitrogen fertilizer (34 %), phosphate – simple
granular superphosphate (19,5 %), potassium – potassium chloride (60,0 %). Soil
moisture maintained at 60 % of the maximum field capacity of the soil by
watering in vessels by weight. Seeds of sugar beets planted in late April to
early May, the crop harvested – in early October. Removal of nutrients by
plants of sugar beet were determined at harvest time. Repetition of the
experiment is 7 times.
The content of total nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium,
sodium, calcium and magnesium in sugar beet plants was determined in a
navazhtsi after wet ashing by C. Ginzburg with further determination of
nitrogen – Kjeldahl method, phosphorus – in Denizhe a modification Buvatye.
It is found that version
control of sugar beet hybrids of different origin are characterized by unequal
biological removal of nitrogen during the growing season. The maximum figure
showed sugar beet hybrid KW Zbruch – 0,60 g/vessel, Extra and Ukrainian ChS 70
are inferior for 13,3 and 33,3 % respectively. In the structure of nitrogen
removal by leaves and root crops the advantage belonged to the underground part
56,7–60,0%. Removal of phosphorus in this embodiment was within 0,10–0,14
g/vessel with a maximum in sugar beet hybrid KW Zbruch and a minimum of in
Ukrainian ChS 70. The share of the aerial part removal was 30,0–35,7 %.
Sugar beet in the process of growth and development accumulate a lot of
carbohydrates and therefore require significant amounts of potassium. Thus, the
removal of this nutrient by Ukrainian ChS hybrid plants was at the level of 0,64, Extra – 0,75 and KW Zbruch 0,82 g/vessel. The roots of sugar beet
contained 48,8–56,0 % or 0,37–0,42 g/potassium a vessel. The removal of sodium
and magnesium by sugar beet plants of the investigated hybrids was identified
within 0,10–0,19, calcium – 0,42–0,58 g / a vessel. At the same time
sodium (70,0–75,0 %) and magnesium (52,9–63,6 %) more than half contained in
the leaves, and calcium (51,1–57,1 %) in the underground part (tabl. 1).
According to the
research, fertilizers application in a rate 1,5 g/vessel caused the increase of
nutrients removal in 2,0–4,0 times comparing to the control. In this
embodiment, the nitrogen content at harvest period in hybrid plants Ukrainian
sugar beet breeding was 1,55; German – 1,81 and joint 0 1,93 g/vessel, among
which roots contained 0,93–1,17 g. The biological removal of phosphorus, sodium
and magnesium increased from 0,37 to 0,47 g/vessel. Thus most of the sodium
endured aerial part (71,7–72,1%), phosphorus – roots (64,9–73,3 %) and magnesium
almost identical proportions aerial part (52,3–55,6 % ) and roots (44,4–47,7
%). In general version without fertilizer and a half dose of fertilizer in
descending order of removal of the nutrients during the growing season hybrids
can be placed as follows: KW Zbruch – Extra – Ukrainian ChS
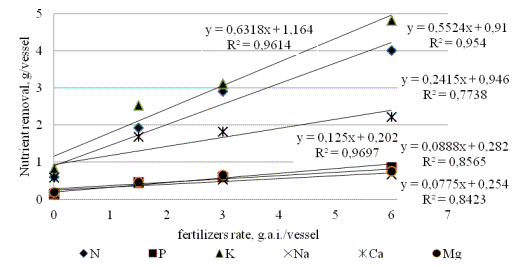
Pic. 1. Nutrients removal by the plants of sugar beet hybrid KW Zbruch depending on fertilizers doze
The use of optimal dose (3,0 g
a.i./vessel) contributed to the improvement of plants nutrition and therefore
further increase of the biological removal of nutrients by sugar beets, which
exceeded the indexes in the variant without fertilizers in 3,2–6,0 times and in the form of 1,5 g a.i./vessel NPK in 1,1–1,7
times. In this embodiment, the
total nitrogen removal plants was within 2,28–3,06 g/vessel with a maximum of Extra hybrid and minimum for hybrid
Ukrainian ChS 70. Share of leaves inferior roots in removal of nutrients and was
36,6–39,0% (tabl. 1). The highest removal of phosphorus in oprimal fertilizers
dose was observed in hybrid Extra 0,72 g/vessel, while others inferior to him
0,11–0,16 g. Among studied hybrids, third part of elements removal (27,8–29,8 %) belongs to over ground part a and the rest – to the roots. On the background of
optimal doses of fertilizers significant absorption of potassium was observed
and its removal by the culture was 3,03–3,79 g/vessel. Share of
underground and ground plant parts in the removal of potassium remained the same
as in the form of half-dose of fertilizer. Sodium
and magnesium content has reached 0,48–0,58 and 0,60–0,65
g/vessel, respectively, and calcium was within 1,47–1,97 g/vessel.
Table 1
Nutrients removal by the plants of different sugar
beet hybrids, g/vessel
|
Hybrids |
Nutrients |
||||||||||||
|
N |
P2O5 |
K2O |
Na |
Ca |
Mg |
||||||||
|
leaves |
roots |
leaves |
roots |
leaves |
roots |
leaves |
roots |
leaves |
roots |
leaves |
roots |
||
|
No
fertilizers (control) |
|||||||||||||
|
Ukrainian ChS 70 |
0,16 |
0,24 |
0,03 |
0,07 |
0,27 |
0,37 |
0,07 |
0,03 |
0,18 |
0,24 |
0,07 |
0,04 |
|
|
Extra |
0,22 |
0,30 |
0,04 |
0,08 |
0,33 |
0,42 |
0,11 |
0,04 |
0,24 |
0,32 |
0,09 |
0,08 |
|
|
KW Zbruch |
0,26 |
0,34 |
0,05 |
0,09 |
0,42 |
0,40 |
0,12 |
0,04 |
0,27 |
0,31 |
0,12 |
0,07 |
|
|
1,5
g a.i./vessel NPK |
|||||||||||||
|
Ukrainian ChS 70 |
0,60 |
0,93 |
0,13 |
0,24 |
0,98 |
1,24 |
0,28 |
0,11 |
0,64 |
0,71 |
0,23 |
0,28 |
|
|
Extra |
0,64 |
1,17 |
0,12 |
0,33 |
0,93 |
1,46 |
0,31 |
0,12 |
0,65 |
0,85 |
0,25 |
0,20 |
|
|
KW Zbruch |
0,76 |
1,17 |
0,14 |
0,31 |
1,17 |
1,36 |
0,33 |
0,13 |
0,85 |
0,84 |
0,25 |
0,22 |
|
|
3,0
g a.i./vessel NPK |
|||||||||||||
|
Ukrainian ChS 70 |
0,89 |
1,40 |
0,17 |
0,40 |
1,18 |
1,85 |
0,34 |
0,14 |
0,66 |
0,81 |
0,37 |
0,26 |
|
|
Extra |
1,12 |
1,94 |
0,20 |
0,52 |
1,41 |
2,38 |
0,40 |
0,18 |
0,96 |
1,01 |
0,36 |
0,24 |
|
|
KW Zbruch |
1,06 |
1,84 |
0,18 |
0,43 |
1,33 |
1,79 |
0,36 |
0,18 |
0,85 |
0,98 |
0,35 |
0,30 |
|
|
6,0
g a.i./vessel
NPK |
|||||||||||||
|
Ukrainian ChS 70 |
1,54 |
2,14 |
0,28 |
0,59 |
1,73 |
2,68 |
0,47 |
0,18 |
1,13 |
0,95 |
0,48 |
0,26 |
|
|
Extra |
1,33 |
2,20 |
0,26 |
0,57 |
1,66 |
3,00 |
0,43 |
0,20 |
1,02 |
1,09 |
0,36 |
0,22 |
|
|
KW Zbruch |
1,63 |
2,38 |
0,26 |
0,66 |
1,94 |
2,88 |
0,43 |
0,24 |
1,13 |
1,09 |
0,45 |
0,30 |
|
|
НІР05 А (hybrids) В (fertilizers) АВ (total) |
0,15 0,11 0,30 |
0,11 0,08 0,22 |
0,03 0,03 0,07 |
0,06 0,04 0,11 |
0,22 0,17 0,45 |
0,20 0,15 0,40 |
0,06 0,05 0,13 |
0,02 0,02 0,04 |
0,15 0,11 0,30 |
0,14 0,11 0,28 |
0,08 0,06 0,17 |
0,27 0,21 0,55 |
|
The highest removal of nutrient elements is observed in the form of a
double dose of fertilizer (6,0 g
a.i./vessel NPK), nitrogen 3,53–4,01; phosphorus 0,83–0,92; potassium 4,41–4,82; sodium 0,63–0,67,
calcium and magnesium 2,08–2,22 and 0,58–0,75
g/vessel. These figures were higher than no fertilizers
background for the removal of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in 5,9–9,2
times in sodium, calcium and magnesium in 3,4–6,6 times. Comparing the maximum
removal of nutrients in the experiment that was over half (1,5 g a.i./vessel)
doses of fertilizers, it is clear that the advantage is 1,3–2,4 times. The
difference in removal of nutrients by sugar beets between double and optimal
doses of fertilizer in sugar beet hybrids Ukrainian ChS 70 and KV
Zbruch is 13,3–38,0 %, and hybrid Extra – 3,4–18,7 %. The proportion of leaves and roots in the structure removal of nutrients
is remained the same as in the form of the optimal dose of fertilizer.
The results of the researches proved the dependence between dose of
fertilizers and the removal of nutrients by sugar beet hybrids of different
origin. An analytical dependence enable to predict the value of
nutrients removal by hybrid of sugar beets, which was studied in the
experiment, depending on the dose of fertilizer introduced (Fig. 1).
In all investigated variants of fertilization the maximum removal of
nutrients during the growing season was provided by sugar beet hybrid KW
Zbruch except variant of the optimal dose of fertilizer, when Extra hybrid was
a leader. By increasing the dose of fertilizer nutrients
removal of sugar beet plants was growing, as evidenced by analytical equations
that make it possible to predict the removal of nutrients, depending on the
dose of fertilizer. On average for the optimal dose of fertilizer sugar beet
hybrids Ukrainian ChS 70, Extra and KW Zbruch removed respectively nitrogen
2,28; 3,06 and 2,90, 0,57 phosphorus; 0,72 and 0,61, 3,03 potassium; 3,79 and
3,12 g/vessel. Share of aboveground plant organs in removal of nutrients is:
nitrogen 35–43 %, phosphorus, 27–36, potassium 36–51, sodium, 64–75, calcium
43–54 and magnesium 52–66 %, and the rest is made by underground parts of
plants.
Literature
1.
Булигін С.Ю. Гумусовий стан чорноземів України /
С.Ю. Булигін, В.В. Дегтярьов, С.В. Крохін // Вісник аграрної науки. –
2007. – № 2. – С 13–16.
2.
Вишневська Л.В. Вплив тривалого застосування добрив у
сівозміні на родючість чорнозему опідзоленого правобережного Лісостепу та
продуктивність гібридів буряка цукрового: автореф. дис. на здобуття наук.
ступеня канд. с.-г. наук: спец. 06.01.04 "Агрохімія" / Л.В.
Вишневська. – Харків, 2009. – 24 с.
3.
Гринів С.М. Удосконалення основних агротехнічних прийомів
вирощування цукрових буряків сучасних гібридів у лівобережній частині Лісостепу
України: автореф. дис. на здобуття наук. ступеня канд. с.-г. наук: спец.
06.01.09 "Рослинництво" / С.М. Гринів. – Київ, 2010. – 18 с.
4.
Медведев
В.В. Мониторинг почв Украины. Концепция, предварительные результаты, задачи. /
В.В. Медведев – Харьков: ПФ Антиква, 2002. – 428 с.
5.
Сазоненко
О.П. Динамика потребления и вынос фосфора и калия растениями сахарной свеклы
при применении разных доз фосфорных и калийных удобрений / О.П. Сазоненко, И.В.
Чечёткина // Сельскохозяйственная экология. – 2013. – №4. – С. 82–88.
6.
Сінченко В.М. Вплив гумусу та елементів живлення при
вирощуванні сільськогосподарських культур / В.М. Сінченко // Цукрові буряки. – 2013. – № 1. – С. 9–11.
7.
Цвей Я.П. Наукове обґрунтування відтворення родючості
ґрунтів та підвищення продуктивності зерно-бурякових сівозмін Лісостепу
України: дис. …доктора с.-г. наук: 06.01.01/ Цвей Ярослав Петрович. – К., 2010.
– 425 с.