Nakonechnaya T.V., Nikulin A.V.
Application of taksonometric method at planning of mathematical preparation
for students of higher technical institutes
In the modern terms of integration pedagogical
science must be oriented not only on the traditional pedagogical methods of
research, but also to lean and on methods, widespread in many areas of
knowledge. In particular, based on the methods of cluster analysis, it is
possible to create a programmatic cluster and analyze intercommunication
between the structural elements of educational programs. Under a programmatic
cluster the educational-training program structured as a matrix is understood
in the variety of all of its intercommunications. Research of intercommunications between the
different structural elements of educational programs allows lining up the
optimum trajectory of the professional becoming of specialist. In obedience to
curricula, ratified by the department of education and science of Ukraine (before 2005 year),
the aggregate of disciplines, taught in higher technical educational establishments,
is broken up on six cycles (clusters): An is a cycle of humanitarian and socio-economic
disciplines, B is a cycle of fundamental and professionally-oriented disciplines,
C — is a cycle of the professionally-oriented disciplines on the list of the program,
D is a cycle of disciplines of independent choice of higher school, E is a
cycle of disciplines of student free choice, F is a cycle of disciplines on the
professional orientation of specialist. Authors considered expedient to add
another cluster of G — course and diploma planning. In order that to work out a
real plan of continuous mathematical preparation of students of higher technical
institutes a successive clusterization (which was carried out in terms of
matrix of similarity) was conducted. As a measure of similarity of the
indicated clusters descriptions was chosen a size, reflecting that, as far as often
educational disciplines from the indicated cluster use the methods of
mathematical analysis, theories of differential equations or other sections of
mathematics. A
research result is presented by dendrogramm (fig. 1).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
1 0
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
A
![]()
![]()
G
![]()
![]()
![]()
E
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
D
![]()
![]()
![]()
C
![]()
![]()
F
![]()
![]()
B
![]()
Fig. 1
 It should be noted that built dendrogramm
illustrates the difference of higher education in the west (for example, in the
It should be noted that built dendrogramm
illustrates the difference of higher education in the west (for example, in the
However now, in connection with passing to the
two-stage system of education, from curricula was exempted the cycle F — cycle
of disciplines on the professional orientation of specialist. Because of such
simplification of educational process structure there is total reduction of
amount of audience hours, taken on teaching of natural sciences and first turn
on higher mathematics. It means that the far of programmatic material passes on
an independent (but not controlled) study of students (that even if will be
studied — that only by units). Thus, by virtue of the folded situation, knowledge,
«received less» on junior courses, are not compensated and in subsequent time.
Negative changes, conditioned by structures simplification and by the decline
of plenitude of education, showed in changed dendrogramm (fig.2).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
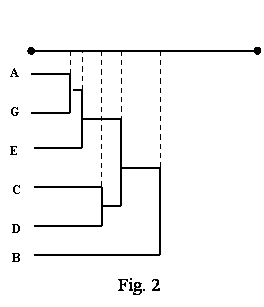 It
is appropriate to quote of L.N.Gumilev, which writes about existence of two
ideal types of the systems: hard and corpuscular, or discrete. In spite of the
fact that he wrote about ethnic systems, the system of higher education with a
complete right it is possible to attribute to the corpuscular systems because
«…in corpuscular systems elements cooperate freely. Easily substituted by analogical,
thus the system does not stop to operate, and it is possible even the loss of
part of elements with a post reduction. If such will not follow, then it will become
the simplification of the system, having its elimination in a limit» [3]. Here
such «simplification, having in the limit elimination» is showed at comparison
of dendrogramms, which are on a fig. 1 and fig 2. Thus the integral index of
compendency falls from 1 to 0,6. Thus, it is necessary to continue work on
adjustment of curricula of engineering directions to increase the integral
coefficient of compendency (to approach him to 1). Otherwise, losing advantage
of preparation on junior courses, we will not purchase him and on elders.
It
is appropriate to quote of L.N.Gumilev, which writes about existence of two
ideal types of the systems: hard and corpuscular, or discrete. In spite of the
fact that he wrote about ethnic systems, the system of higher education with a
complete right it is possible to attribute to the corpuscular systems because
«…in corpuscular systems elements cooperate freely. Easily substituted by analogical,
thus the system does not stop to operate, and it is possible even the loss of
part of elements with a post reduction. If such will not follow, then it will become
the simplification of the system, having its elimination in a limit» [3]. Here
such «simplification, having in the limit elimination» is showed at comparison
of dendrogramms, which are on a fig. 1 and fig 2. Thus the integral index of
compendency falls from 1 to 0,6. Thus, it is necessary to continue work on
adjustment of curricula of engineering directions to increase the integral
coefficient of compendency (to approach him to 1). Otherwise, losing advantage
of preparation on junior courses, we will not purchase him and on elders.
References
1.
Academic science and education: the past,
present and the future // Economy and mathematical methods, 2008, vol. 44, ¹1, p.126-136
2. Didukh
J.P. Modern approach to the classification of biotical objects. — Visn. NAN of
3.
Gumilev L.N. Etnogenez and biosphere
of Earth. - M.: Ayris-press, 2007. — 560 p, ill.