Pedagogics
and psychology
Increasing of tne educational
processes effectivness
with the help of students collective
intellectual activity
G.A. Yessenbayeva
I. Introduction
In the work [1] we have examined the
group of students as a totality of the “non-interacted objects”. Using the
methods of statistic unequal thermodynamics we have got the expression for the
effectiveness of educational information acquisition as a function of the
number of students. It was shown that in such
model the effectiveness of acquiring educational information comes down
with the growth of students number and the optimal number of students in the
group is about 5-6 persons. It is actual for the first year of studying when
the students are not acquainted quite well and the approaching of the
“non-interacted objects” may take place. Thus, at the very beginning of
studying, in the first year and in the first term, the academic group should be
divided into subgroups consisting of 5-6 students.
II. Settings of
objectives
In this very work we will focus our
attention on the effects connected with the collective intellectual activity of
the students. But we will not touch the psychological structure of this
activity, that is thoroughly expounded, for example, in work [2], and we will
use the methods of mathematical modeling, mechanical analogy and
thermodynamical approach, developed in work [1].
First let us consider some qualitive
aspects of the connection between the members of any students, group.
Let the members of the group communicate in different ways, for example,
orally, or in the written form or even by using gestures. Means of
communication used by students create a web of connection for the group. In
this case the web is a count, the tops of this count coincide with the members
of this group, and the sides (the channels of connection) mean the possibility
of direct connection of the group’s members.
The approximate count (pic.1) shows
the possibility of connection between some students, coinciding the tops, while
the arrows show the direction of possible transmission of information. The
matrix of the tops of this count has the type as follows:
 . (1)
. (1)
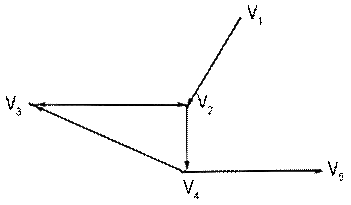
Picture
1. The approximate count that shows the connection among some students of the
group.
Imagine that there is a great number
of top’s connections (directly through the arcs or indirectly through the ways)
in the web of interrelation, that is essential condition in order to organize
the connection among the students. And there is a question – weather the task
about the students’ interaction can be solved with the help of such
web. As a rule, there are different ways to change the interaction of the
students. And each way of changing the interaction coincides with some
structure of the web. The structure of it can be optimal by some criterion, for
example if we take to consideration the minimum of the whole continuation of
some task solving. In our next work we will discuss the approach using some
qualities of the connection channels and one of them have been already defined
in work [1]. But here we will define other quality characteristics using the
mechanical model.
III.
Results
Let us consider the students of the group as the totality of harmonical
oscillators using the potential of the pair interaction with some quantity C,
that characterize the “power” of this interaction. So, the classical theory
gives for the frequency of vibration of such system the expression as follows:
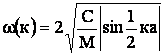 ,
(2)
,
(2)
where M is the oscillator mass, a is the distance
between these masses.
According to the terminology and
denomination of work 1, where we consider that E ~ ω, K ~ N, a ~Δ
ε, M =1, we get the next correlation for the effectiveness of acquiring
information; here E – is the effectiveness of the information acquisition, N –
the number of students, Δ ε –destruction of intellect (deviation of
the student’s intellect in comparison with the average in the group).
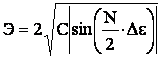 . (3)
. (3)
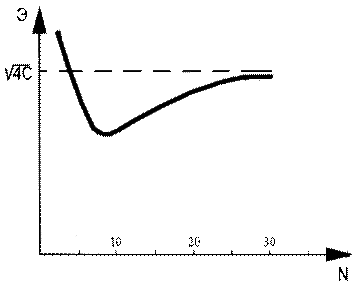
The graph of this interrelation is
shown on the picture 2. On the basis of this picture and formula 2 we come to 2
conclusions:
-
the maximum value of the
effectiveness of acquiring depends on the “power” of the students, interaction,
exactly:
![]() ; (4)
; (4)
-
the maximum number of students in the
group depends on the quantity of the destruction of students’ intellect, exactly:
![]() . (5)
. (5)
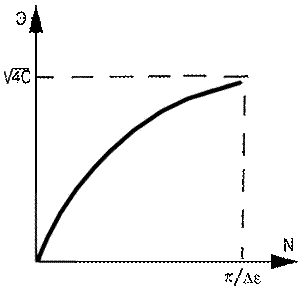
Picture 2. Dependence of the acquiring effectiveness
on the number of students in the group.
As it follows from work [1] the optimal value Δε≈0,1 and
then Nmax≈30 students in a group.
So, unlike the totality of
non-interacting students where the number of students in the group must be 5-6
people; by interacting and slight intellect divergence (~10%) the optimal
amount in the group is 30 people. This makes quite definite limits on the
formation of academic groups’ number at the initial and next stages of the
educational process.
In case of the account of the
fact that not all students (sometimes according to objective reasons)
participate in the collective intellectual activity, generalized dependence of
acquisition efficiency will have such form shown on picture 3. And in this case
the optimal amount of students in the group will consist of about 30 people.
Picture 3. Generalized dependence of acquisition efficiency from the
number of students in the group
If a teacher works with the stream (100-150
students) but using the active methods of education leading to the collective
intellectual activity the stream divides into some groups of 30 people each,
having different acquisition efficiency. This situation is shown on picture 4
as a scheme.
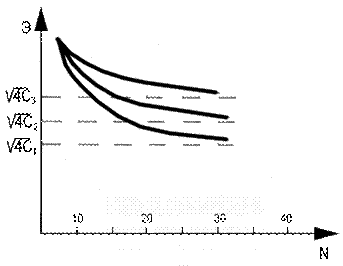
Picture 4. Acquisition efficiency dependence in case of the stream
education
IV. Conclusions
In conclusion we should point that all the data
can be expressed in numbers. Exactly, the value Δ ε in (5) can be
defined with the help of well-known psychological tests [4]. Acquiring
effectiveness can also be defined by using tests. All the prior experiments of
investigating of the freshers’ environment, that were made by us, show that
when there is no interaction the effectiveness of acquiring educational
material is no more than 10-15%.
The list ob books.
1.
Yessenbayeva G.A., Yurov V.M.
“Thermodynamics and studying process in higher educational establishment
Scientific work, Almaty, KazSU.
2005, p. 144.
2.
Dzhakupov S.M. “Psychological
structure of the educational process”
Almaty 2004, 312 p.
3.
Selevko G.K. “Modern educational
technologies” 1982, 256 p.
- Anastazy
A., Urbina S. “Psychological test”
2003, 688 p.
Summary
Using methods of mathematical modelling, the
mechanical analogies and non-equilibrium statistical thermodynamics are
reviewed problems of digestion efficiency of the information by students. A
number of the formulas permitting to conduct the analysis of organization of
educational process is obtained there are shown the possibilities of efficiency
strengthening.
Key words:
collective intellectual activity, thermodynamical approach, acquisition
efficiency
Review
on an article of Yessenbayeva G.
Increasing of tne educational
processes effectivness
with the help of students
collective intellectual activity