PhD in Philological Science,
associate professor Aliseienko O.N., PhD in Technical Science, associate
professor Kotlova L.M., Chepynoga K.G.
Dnipropetrovsk National
University named after O. Honchar
COMPANY
FINANCIAL STRATEGY DEVELOPMENT
WITHIN ITS
LIFE CYCLE
The conditions of uncertainty, which are the
characteristic feature of today’s economic relations, are making contemporary
businesses develop their strategy. The
conditions of this kind are characterized by the high level of competition and
risks.
The
definition of the strategy, its functional advantages and main principals of
its creation has deep historical background and is connected, uppermost, with
the development of military strategy. Thus, the first authors of the treatises
about the strategy were the Chinese philosopher Sun Tzu and the German military
writer Carl von Clausewitz. According to the researchers, strategy is a general
plan of actions according to which the goal is likely to be achieved.
Nowadays
there are plenty of scientific papers
that explore the essence of the company’s general and financial strategy as the
part of its overall development plan. The authors of these papers are both
national and Russian researchers of financial management. Blank I.O., Stoyanova
E.S., Kovalenko O.L., Remenieva L.M., Podderegin A.M., Ansoff I. are among them
as well as the international scientists, notably H.
Mintzberg, R. Ackoff, D. Kliland, P. Druker, etc.
The
scientists offered the most appropriate definition of the financial strategy.
It is considered to be a perspective tool of the company’s finance activity
administration, goal-oriented in terms of its overall development under the
conditions of permanent macroeconomic indexes change together with the system
of market processes state regulation, economic situation on the financial
market and related to these processes uncertainty.
While
developing the company’s financial strategy, the understanding of its
importance as the core component of an overall corporate strategy is vital. In
its turn, the corporate strategy presupposes the realization of company’s
mission and consists of the sum total of functional strategies the quantity of
which depends on the functioning peculiarities of each particular enterprise.
Financial management theorist Blank I.O. is the founder of this theory.
The
fact that the essence of finance strategy depends on both external and internal
factors should necessarily be taken into account. Thus, external factors
include the following macroeconomic indexes: branch and market segment where
the company is, market economic situation, legislation, taxation policy,
exchange rate policy, the volume of company economic cooperation with foreign
partners and clients, etc. The internal factors include the enterprise’s
patterns of ownership, its financial position, the structure of equity and loan
capital, enterprise life cycle stage and other characteristics of its activity.
Taking
into account the fact that each company develops and functions under the
influence of micro and macro indexes, it is essential to elaborate a flexible
strategy, efficient for a particular company, which belongs to a particular
branch. The scientists in the field of financial strategic management in the
network of their research are trying to create particular classifications of
external and internal factors which create the necessity to develop the
financial strategies.
In
accordance with the classification proposed by Kovalenko O.L. and Remenieva
L.M., there are three types of financial strategy, i.e. the strategy to
overcome the unstable financial system of an enterprise, the strategy to
support the financial stability of the enterprise or stabilization of an
enterprise and the strategy of steady growth. The classification proposed by
Blank I.O. outlines the following strategies: the strategy of enterprise
financial resources formation, investment strategy, the strategy which
guarantees financial accountability and stability for the enterprise and the
strategy of financial activity administration.
Ukrainian
economist and researcher in the field of risk management Tereshenko O.O. has
proposed four types of strategies directed to combat the financial crises at an
enterprise, i.e. active strategy, the strategy of delegating authorities, the
strategy of compromises and consensuses and the defensive strategy. All
strategies listed are realized under conditions of deep financial instability
and presuppose the transformation of a company structure. Moreover, while
realizing each strategy, the developed algorithm of actions must be flexible to
the external market conditions and have to be based on the results of the
preliminary carried out analysis of the finance state of an enterprise.
The listed financial strategies can be grouped within the
company life cycle in the proper succession.
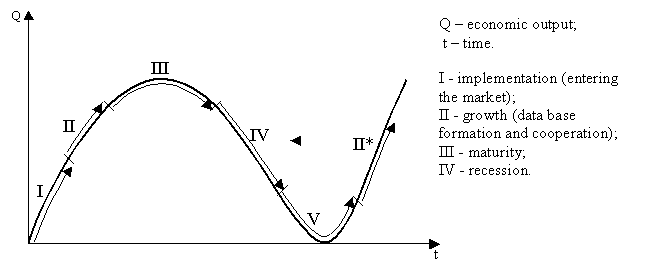

Ill. 2 Stages of an enterprise life cycle
Thus,
the given graph shows four stages of the enterprise development and its
functioning on the market. As shown, the fourth stage is not the last one. The
consecutive fifth position is the result of not only the production output
decline but also the other negative tendencies, which can be observed at an
enterprise. Accordingly, stage V represents the recession (financial and
manufacturing). The next step after the recession is the recovery of an
enterprise (stage II*). It is worth paying attention to the fact that if the
wrong strategy is realized at the fifth stage, there exists high possibility
that the company will not move through the life cycle stages to the next
position of recovery and the only possible result would be the bankruptcy of an
enterprise.
In that
way, with a view to organizing the enterprise stage by stage gradual
development various financial strategies are to be implemented in the company.
These strategies must be realized in a strict succession and should coincide
with life cycle stages of an enterprise.
On the stage of the company’s
entering the market, the main thing is to form clients’ data base with a view
to receiving profit from sales in future. It is also important to build up
effective partner relationship. Therefore, it should be mentioned that the
majority of the enterprises business plans are supposed to achieve a breakeven
point at the first stages of its activity. The essence of this index lays in
the idea that enterprise initial production and sales costs should be equal to
the received profit after covering all the compulsory payments. Thus, according
to the classification of Blank I.O., the most appropriate strategy that should
be implemented at the first stage of the enterprise life cycle is the strategy
of enterprise resources formation. It means that upon setting up of a new
enterprise and from its startup until the more or less counterbalance of this
system, the definitive period of time should pass. For that time being, the
enterprise has to form the necessary resources both financial and manufacturing
to make further business activity profitable. Considering these theories the
most representative is the breakeven point calculation. It shows the volume of
output to be manufactured at an enterprise to cover the previous costs.
It is
reasonable to conclude that at the first stage of the life cycle upon
realization the financial strategy of the financial resources formation, the
enterprise will not achieve the breakeven point and its expenses will be higher
than the profit received.
According
to the classification proposed by Kovalenko O.L. and Remenieva L.M., within the
second stage of an enterprise life cycle, the financial strategy of growth or
the strategy of steady development should be implemented. In accordance with
Blank’s theory, the most appropriate strategy at this stage is the financial
activity administration strategy. Unification of these two strategies stipulates
the enterprise financial activity administration with a view to achieving and
keeping financial stability of an enterprise. Such a strategy stipulates
dramatic realization of manufacturing policy, making the enterprise assets
liquid and the efficient use of loan and equity capital, etc. As a result, the
company receives an opportunity to increase its economic output and invest a
part of the profit received in new business activity. Having implemented the
strategies proposed, the costs will be totally covered by the profit received.
At the
third stage of an enterprise life cycle in accordance with both classifications
the financial investment strategy should be implemented. At this stage the
company’s revenue exceeds its expenditures. It is also assumed that the margin
will be good enough to finance production both intensively and extensively as
well as to perform investment activity.
The
activity of this kind assumes an implementation of the real investment policy,
financial investments, enterprise investment policy into branch and regional
reserves. But, according to the research done by Blank I.O., due to the
investment activity, the company gets an opportunity to raise its gains as well
as to increase its market price. On the other hand, the company acquires
definite risk portfolio. That is why
together with the investment strategy, the strategy of the financial
accountability and stability that contemplates current assets management,
management of the structure of capital and the implementation of the financial
risks management policy are to be realized.
The
forth stage of company development life cycle is characterized by the
production decrease. The enterprise appears in the situation when it had been
impossible to foresee some external factors in the process of realization and
development of the afore mentioned financial strategy. That is why according to
the research done by Kovalenko O.L. and Remenieva L.M., the financial strategy
directed to the overcoming of the unstable financial system should be implemented.
Under the given strategy, the enterprise receives funds from the external
economic subjects to be able to settle debts with the other subjects of the
market. But the financial situation of this kind is very complicated for the
company because it loses its solvency and acquires an additional risk
portfolio. While redeeming, the company is unable to attract funds to
manufacturing process and, as a result, the enterprise faces the deep financial
crisis.
The
fifth stage of an enterprise life cycle is characterized by the crisis that is
why the strategy proposed by Tereshenko O.O. is to be implemented. As
emphasized, these strategies are gradual strategy, strategy of authority
delegation, the one on compromises and consensuses and defensive strategy. If
being at this stage, the enterprise chooses the wrong strategy, its financial
situation is falling dramatically and the only possible variant is to initiate
the liquidation process. If the management of an enterprise chooses and
realizes a better financial strategy, the company enters the next stage of its
recovery and keeps on functioning on the market of goods or services.
Thus,
the financial strategy should thoroughly coincide with the stages of the
company life cycle. It should look like an algorithm of actions which, in its
turn, should take into account the possibility of the external market factors
appearance, foresee the possible influence of these factors on the financial
activity of the company and possible risks. That is why one of the most important
characteristics of the financial strategy is its flexibility to the external
market. The key issue is to identify the factors that characterize the
productivity of financial strategies implementation depending on the company
market segment and its overall activity.
Literature:
1. Бланк,
И.А. Финансовая стратегия предприятия [Текст]: учебник/ И.А. Бланк. – Киев:
Ника-Центр. – 2004. – 540 с.
2. Гавриленко
Т. В. Механізм розробки та реалізації стратегії в системі стратегічного
управління [Текст] / Т. В. Гавриленко // Вісник Київського національного університету технології та дизайну (КНУТД) :
Збірник наукових праць. - 2006. - № 2. - С. 155-158
3. Гаращенко Н.
М. Стратегічна платформа підприємства [Текст] / Н.М. Гаращенко // Стратегія
економічного розвитку України: Науковий збірник. - К., 2008. - Вип.2-3. - С. 123-131
4. Коваленко,
Л.О. Фінансовий менеджмент [Текст]: навчальний посібник /
Л.О. Коваленко, Л.М. Ременьова. – Київ: Знання. – 2008. – 483 с.
5.
Поддєрьогін, А. М. Фінанси підприємств [Текст]: підручник/ Керівник авт. кол. і
наук. ред. проф. А. М. Поддєрьогін. 3-тє вид., перероб. та доп. — К.: КНЕУ. -
2005. — 535 с.
6. Стоянова,
Е.С. Финансовый менеджмент [Текст]: учебник/ под ред.
проф.. Е.С. Стояновой. 5-е изд., пере раб. и доп.- М.: Перспектива. – 2006. –
656 с.
7. Терещенко
О.О. Антикризове управління підприємством [Текст] / О.О. Терещенко//
Фінанси України. – 2007. - №12. – С. 56-63
8.
Mintzberg H. Strategy Safari: a guided tour through the wilds of strategic
management: [Text] / Henry Minzberg, Bruce Ahlstrand, Joseph Lampel. – New
York: The free press. – 2000