Экономические
науки /13. Региональная экономика
Candidate of Economic Sciences,
associate professor Smagulova G.S.
al-Farabi Kazakh National
university, Kazakhstan
State
regulation of regional development
The aggravation of
differentiation of economic and social development of the regions became the
most important problem which faced Kazakhstan during the period of reforming. One
of the ways of eradicating of regional contradictions is the state regulation
of the regional development which contents is consisted in the system of the
organizational legal mechanisms which are really influencing processes of
territorial development in the interest of regions.
The regions
(Concerning Kazakhstan it is regions, the large and small cities, rural areas) should
be considered from two positions. First of all, it is the territory where
economic activity is carried out in compliance with the production
specialization which is gathered the population with the same interest of
regional reproduction. Secondly, the region is part of the general
socio-economic system of the state which development is fully depends on the
general regularities of process reproduction [1].
The
degree of integrity of the general socio-economic system in many respects
depends on the level of territorial differentiation. If natural territorial
distinctions are considered useful and don't break unity of space as its bring
dynamism in placement of places of the appendix of work, in structure of
economy of the region and the system of settlements, abnormally high
progressing differentiation of regions negatively influences its integrity and
a sustainable development.
One of the most
important key indicators characterizing an economic component of regional
systems is the gross regional product (GRP) per capita. The comparing of this
indicator on regions gives the chance to estimate the degree of heterogeneity
of economic space of the country that finally influences the efficiency and the
stability of economy of the regions.
For descriptive
reasons it is brought the data by us (figure 1), testifying pronounced
territorial differentiation of regions of Kazakhstan.
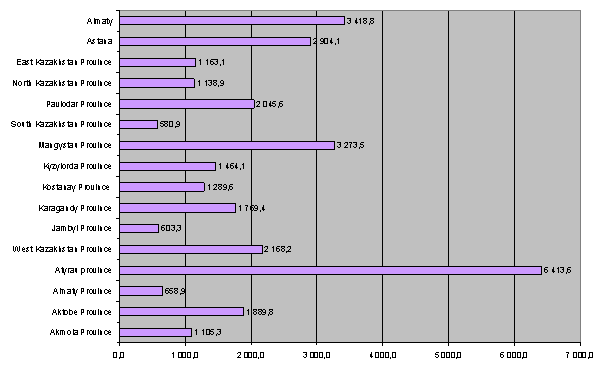
Picture 1.
Gross regional product
per capita in 2011
(A chart is constructed
by author on a basis of the data of Agency of Statistics of Republic of
Kazakhstan)
The break among regions on a
gross regional product per capita was 11 times in 2011. As we see, the break
among the regions of Kazakhstan is huge despite the carried-out measures in a
framework realized these years. If we compare we see that differentiation among
regions in Switzerland makes 2,2 times, in Canada - 1,8 times. The received
values show about insufficient efficiency of undertaken measures for situation
change.
The
leaders among the regions on this indicator are Atyrau, Mangistau provinces, Almaty
and Astana in 2011. The Southern Kazakhstan and Zhambul provinces have the
smallest values. These positions of the regions remain year by year.
First of all, these
distinctions are influenced by volumes of poured-in investments, an industry
level of development and specifics of developed branches.
The analysis of tendencies of
socio- economic development of the country for the last decade allows to reveal
and to state the existence of the following situations:
- Regional differentiation in
adapting to the market;
- Essential distinctions
between leading regions and regions outsiders and, as a result, increase in the
number of problematic territories;
- rupture of economic
communications and weakening of economic relations in the country.
The main reasons for increasing territorial
distinctions are:
- Removal of leveling mechanisms of administrative
management by territories of the country, in particular the mechanisms such as planned alignment of the prices,
establishment of territorial coefficients and extra charges to a salary in the
remote, desert, ecologically adverse regions, the organized set of labor for the
development of new areas, etc.;
- Different
levels of adaptation of regions to market reforms;
- The
strengthened development of the extracting raw materials and export-oriented
regions absorbing the most part of the investment and other resources;
- Weakness
of mechanisms of regional policy which is not as much stimulated development of
regions, as many were directed on their self-survival and independence [2].
Meanwhile
social and economic differentiation of regions is typical practically
for all large countries. Moreover, it is impossible to overcome a difference
socio-economic situation of regions totally. In that
process it is important to determine mechanisms of state regulation on reduction of
interregional distinctions.
Scientists of
Institute of Economy of Kazakhstan allocates various levels of interregional
differentiation: weak, average and
strong.
Table 1. The mechanism of the state regulation of the
interregional differentiations
|
The
level of interregional differentiation |
The
types of government support |
Result |
|
The weak level of differentiation |
Assumes
more delicate approaches which consider situations in those regions as much
as possible where the situation is the worst, but at the same time, areas
preferably needing the state support should manage to pick up reasonable
levers of assignment. In that process, when government resources are
available, which are enough for improving impulses of business activity and
economic activity of weak regions, the lagging of weak regions from strong regions
is minimized. |
The lag
growth is minimized |
|
The average level of differentiation |
the state
support is given in such measure in order to stop the rising of gap in a levels of development of regions and at
the same time to stimulate market activity in weak regions to strong level, that is to promote creation of business
climate in the territory, specifically forming here institutes of market infrastructure
(with the help of the states,
local authorities and
businessmen). |
Preventing
of rising of gap in the levels of
development |
|
The strong level of differentiation |
The
state creates opportunities to weak regions to develop quicker, than the strong
regions developing without support |
The
achievement of regional balance |
|
Made by
author on a basis of source [1] |
||
The offered mechanism of state
regulation of interregional differentiation is directed to provide conditions
for development of regions. According to the Expected scheme of territorial and
spatial development of the country till 2020 assumed that the “providing of
polarized development of the country through stimulating the territorial
concentration of industrial and manpower in “growth points” and in areas
economically perspective and favorable for activity”.
Based on the drawn
conclusions, it is necessary to believe that the purposes of state regulation
of regional development have to be: creation of conditions for emergence of state
and significant "growth points"; stimulation of development of the
territories which are not capable to develop independently.
Literature:
1. Brimbetova N. Zh. The modernization of
territorial and industrial development Kazakhstan: methodology and priorities. Monography. –Almaty: MES RK. -2011.-229p.
2. Nurlanova N.К. Regional paradigm
of a sustainable development of Kazakhstan: theory and practice problems. –
Almaty: Economy institute KN МES RК, 2009. - 328 p.