Change
the hydrogen factor of water, as a result of phase turning the first sort.
Dmitry M. Kuznetsov, Vladimir
L. Gaponov,
Irina A. Luganskaya, Victoria V. Aliluykina
Novocherkassk Reclamation Engineering Institute named
affer A. K. Kortunova FGBOU VPO "Don" State Agrarion University
The characteristic so named melting
water is dedicated to it is enough much publications in scientifically-popular
literature and relatively little especially scientific [1].
At destruction gipsogonalny
structures, the crystalline structure ice and as a result of phase
turning the first sort is seldom changed
structure material. The crystalline structure ice decays quicker, than reforms
in firm balance condition, formed from it net stable, melting water.
Unikalinosti phase transition ice-water is concluded in that ice and water
consist of one molecules (Í2Î), but
in ice they balance, but in water no. In melting water concentration ion of the
hydrogen and hydroxyl certain time save in not balance and such, what it was in
ice. Then in a curtain time concentration ion in water takes its usual balance
importance. As of [2,3] concentrations ion H+ and ÎÍ- in ice forms 1,4-5,0*10-10 mol/l,
but in water balance concentration under 0°Ñ -
0,35*10-7 mol/l, i.e. on three orders more.
Reaction dissociation the water:
Í2Î⇆ H+ + ÎÍ-
Requires the significant expenses,
energy and runs much slowly. The constant to velocities to this reactions forms
whole 2,5*10-10 ñ-1 about 20°Ñ. So period to relaxations of melting water
before balance of the condition theoretically must be is several hours. However
speakers of the change to concentrations ion H+ does not happen to.
In connection with above stated by
purpose persisting work was shown study, change the hydrogen factor of melting
water at time, as well as determination of the influence of this factor on the
characteristic of water. The measurement to concentrations ion H+ was realized by means
of ðÍ- metre ÀÒÒ-3507,
but study characteristic melting water was conducted by studies of the
phenomena to acoustic emission under flowing homogeneous chemical reaction in
fluid ambience [4].
It is installed that concentration
proton in melting water and purely distilled water noticeably differ. And if in
the course of time hydrogen factor ðÍ purely distilled water practically remained unchangeable, that
characteristic of melting water, first, differ from characteristic usual
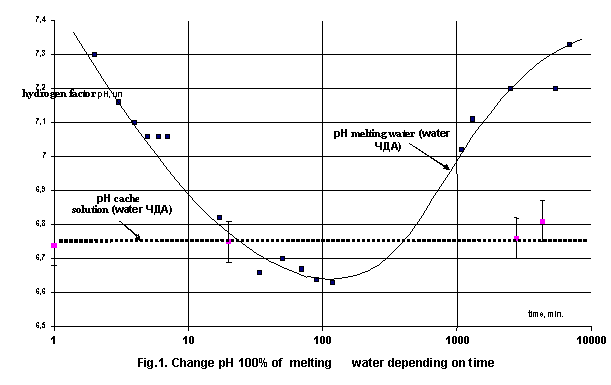
distilled, but, secondly, greatly change at time (fig.1). As far as axis of the
abscissas is shown by logarithmic scale, that becomes obvious that kinetics of
these change different. Observation after change exceed the level to inaccuracy
(±0,03 ðÍ) and are
reliable. In conducted experiment not to manage to define the time domain,
under which hydrogen factor ðÍ of melting water amount with factor of simple distilled water though
this follows to expect in view of that melting water also is distilled water.
From presented graphics is seen that such interval exceeds the level several
groups of ten hours.

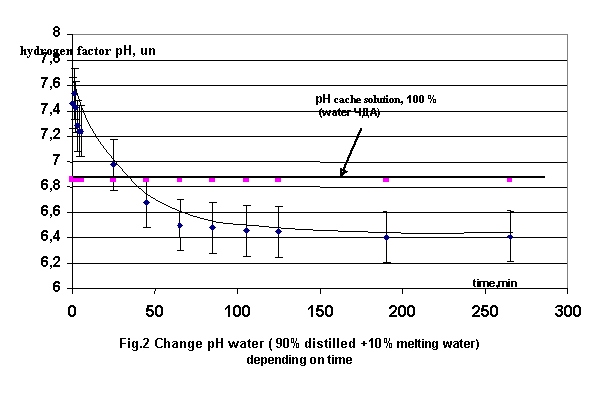
Similar change were fixed and for
distilled water, containing10 and 20% weighting amount melting water (fig.2). On presented fig.2 are
shown initial stage of the change the hydrogen factor mixture, containing 90%
distilled water and 10% melting water at observation concurrence first five
hours after mix.

The fact not balance conditions of
melting water is confirmed by direct measurements of the move chemical reaction
different reagent in usual distilled water and melting water. The measurements
were conducted by means of acoustics-emission complex A-line 32D and
teplovision equipments. As object of the study well studied reaction solvatation
by concentrated chamois of the acid in water. Established that in the case of
solvatation by concentrated chamois of the acid in melting water, amount
inductionialy acoustic signal increases in a hundreds once. The growing to
acoustic emission to homogeneous chemical reaction of the dissolution reflects
exotermition nature of the process as a whole. It is known that most idle time
way experimental determination enthalpy solvatation consists in direct
measurement of the heat effect of the dissolution. In this instance at
dissolution by chamois of the acid in water measurement heat effect was
conducted with use teplovision SAT HOTFIND.
Fig.3 Thermogramma process solvatation by concentrated chamois of the acid in
usual distilled water and melting water.
On the fig.3 are
presented teplovision of the scene to capacities with solution by chamois
of the acid. It is seen that in the case of dissolution by chamois of the acid in melting water exotermic
nature of the process is expressed vastly more brightly. The separation to heat
energy at solvatation brings about change of density of the solution that in
turn causes the generation of the waves to bounce of the material of the
ambience – an acoustic emission.
The findings.
After study of the hydrogen factor of distilled
water and melting water is installed that after appearance ice melting water
certain time is found in not balance condition that is reflected on its
characteristic, shown in particular idle time solvatation.
Literature.
1. D.M.Kuznecov, A.N.Smirnov, A.V.Seroeshkin
Acoustic emission under phase conversisons in water ambience// Rus.chemic.g.,
2008, t LII, ¹1, P.114-121.
2 Zacepina G.N. Characteristic and structure water/
M, MGU, 1974. - 168 p.
3.
Eizenberg D.,
Kaucman V. Structure and characteristic
water/ L., Gidrometeoizdat, 1975.- 280 p.