Stud . Borodina O.O.,
c.b.s. Lych I.V.
National University of
Food Technologies
COLOSTRUM’S ABZYMES AS IMMUNOSTIMULATORS FOR IMMUNE
CELLS
In
the late 40s of the 20th century, L. Pauling studied properties of enzymes and
antibodies. During research scientist noted that antibodies are much like
enzymes, namely by capability of binding to ligands, and may catalyze different
chemical compounds. Based on this concept, came the idea of
obtaining catalytic antibodies by immunization of animals with
hapten, which have already immobilized on a carrier. Obtained antibodies were
able to accelerate in 1000 times hydrolysis of esters and named
"abzymes" [1].
Today,
abzymology is rapidly developing, promising and relevant science that studies
the catalytically active antibodies and combines elements of immunology,
enzymology, molecular biology, organic chemistry. Catalytic immunoglobulins have
biological functions of antibodies and present in colostrum, which secrets in
mammals to provide passive immunity against invading pathogens. The specificity
of the natural antibodies found in cows’ colostrum and milk displays a wide
range of antigens with which the animal has faced in the past. Since 1980, a
wide range of clinical studies have shown that immune drugs based on milk’s immunoglobulins
not only prevent diseases of humans and animals caused by various pathogens, e.g.
rotavirus, Escherichia coli, Candida albicans,
Clostridium difficile, Shigella flexneri, Streptococcus mutans, Cryptosporidium
parvum and Helicobacter pylori
[2], but also strengthen health and immunity. Search of such biologically
active proteins are huge interest for scientists around the world.
Based
on present researches, found that abzymes IgG and sIgA from cows colostrum are
able to not only communicate with pathogenic bacteria and viruses, but also
hydrolyze their DNA and RNA [3], which is an important component of newborn’s
humoral immunity. The hydrolysis process of bacterial and viral DNA, and
homologous oligoribonucleotides and oligodeoxyribonucleotides occurs by Fab
fragments of antibodies. Thus, due to specific functional properties, catalytic
antibodies of cows colostrum are showing outstanding commercial and scientific
interest right now.
The aim of our study was
to explore the influence of abzymes and proteins mixture in cows’ colostrum on immunocompetent
human cells in vitro.
Materials and methods.
Mixture of proteins and abzymes obtained from cows milk and colostrum. Samples
of colostrum were taken during the first 7 days right after cow’s calving and
purified by the method, which shown in Fig. 1.
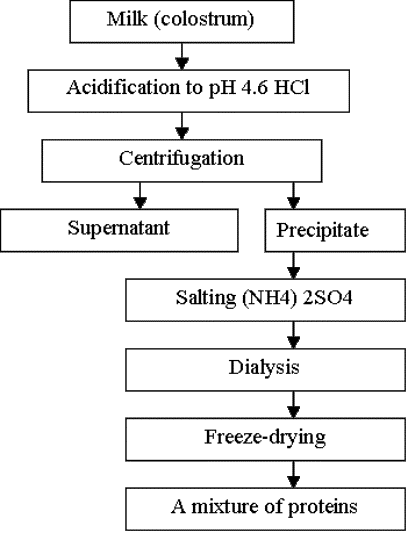
Fig. 1. Method of isolation and purification of
proteins and abzymes mixture received from cows colostrum
Obtained
lyophilized samples of protein dissolved in saline to a concentration of 1 mg
protein/ml. In experiments were used a mixture of proteins and abzymes in
concentrations 1.0 mg/ml and 0.1 mg/ml respectively. In research, we studied
the effect of a colostrums proteins-abzymes mixture on functional activity of
immune defense cells in vitro. To
study the immunostimulatory effects used lymphoid blood cells of healthy
donors, such as lymphocytes (Lph), monocytes (MC), neutrophil granulocytes (NG)
and natural killer cells (NK cells).
Percentage
of phagocytic cells (neutrophils and monocytes) was determined by absorption of
latex particles (d = 1,0 - 1,3 mm) with phagocytosis percentage calculation.
The intensity of their oxygen-dependent
metabolism studied in NBTR-test (the percentage of NBTR-positive cells and the
cytochemical coefficient). By cytochemical coefficient (CCC) conducted a peroxidase
activity efficiency. To determine rosettecreating/soccetcreating cells used
method of the rosettecreation/soccetcreation with particles, which were previously
coated with monoclonal antibodies.
Results and discussion.
During our research we found that the percentage of phagocytized neutrophils,
who seized latex particles during processing with proteins mixture of 1.0 mg/ml
concentration of was above 14%, while processing with concentration of 0.1 mg/ml the values decreased twice
(6%), compared to the control. Similar studies were conducted on monocytes. Obtained
results revealed that monocytes showing resistant to treatment with a mixture
of proteins-abzymes. Exploring intensity of oxygen-dependent metabolism of
neutrophils, a mixture of proteins and abzymes with 1.0 mg/ml concentration had
a stimulating effect on the number of NBTR-positive
cells - 31%, while processing the cells with a proteins mixture at
concentration of 0.1 mg/ml showed none
stimulating effect on the number of NBTR-positive
cells. This suggests that greater concentration of the catalytic antibodies
mixture are showing positive effect on oxygen-dependent metabolic activity of neutrophilic
granulocytes (NG). Although, processing monocytes with mixture of proteins-abzymes
at 0.1 mg/ml concentration displays the percentage of NBTR-positive monocytes
and CCC increased by 11% and 32% respectively. Thus, the results can testify
that the proteins and abzymes mixture can act as a trigger in some redox
reactions in monocytes, due to its specific physical and chemical properties.
The
next stage of research was to study the spontaneous cytotoxicity (SC), and
antibody- cell cytotoxicity (ABCC) NK cells under the influence of proteins-abzymes
mixture. From received data, it is worth noting that processing cells with
mixture 1.0 mg/ml concentration values of ABCC and SC close to control values
- 31% and 44% respectively (control - 29% and 40% respectively),
while processing a mixture 0.1 mg/ml concentration increases activity of NK
cells almost in 2 times (SC - 60%, ABCC - 75%).
The
third stage of the research was to identify the impact of proteins-abzymes
mixture on receptors expression level on peripheral blood’s Lph: T- Lph (CD3
+), B- Lph (CD22+) and their individual subsets (CD4+ and CD8+). For this
purpose, the method of Lph’s rosettecreation
with particles that are coated with mAb against CD3+ (T- Lph), CD4+ (T-helper)
and CD8+ (T cytotoxic/effector Lph). To determine the density level of
receptors on B- Lph used erythrocytes coated with mAb against CD22+ after
treatment Lph with different concentrations of proteins-abzymes mixture.
In
the study, we found that by adding the proteins-abzymes mixture of 0.1 mg/ml concentration,
number of receptors to CD3+ cells decreased by 8% compared to the control,
while number of receptors for CD22+ conversely increased by 4%. Under the
influence of proteins-abzymes mixture at 1.0 mg/ml concentrations, number of
receptors CD3+ cells increased by 20%, but the CD22+ cells were shown reduction
by 14%. While studying the influence of catalytic immunoglobulins mixture on the
rosettecreation process of T-lymphocytes subpopulations found, that while
processing cells with the mixture of proteins at 1.0 and 0.1 mg/ml
concentrations showed an increase in CD4+ subpopulation of 25% and 15%
respectively. In determination of CD8+ (T-cytotoxic/effector lymphocytes)
observed inhibitory effect of proteins-abzymes complex at 0.1 mg/ml concentrations
to 44%, while after processing with mixture at concentration of 1.0 mg/ml an
increase showing in the expression of receptors for CD8+ by 15%. By studying
changes in the expression of receptors for SE coated with monoclonal
antibodies to the CD4+ and CD8+ after lymphocytes’ incubation with proteins-abzymes
mixture of different concentrations, should be noted following. Lph processed
by proteins-abzyms mixture in concentrations 1.0 and 0.1 mg mg/ml shows an increase in CD4+ by 26% and 24%
respectively (control - 22%), for CD8+ an increase to 27% (control - 24%) when
processing a protein mixture 1.0 mg/ml concentration.
Therefore,
proteins-abzymes complex had a significant impact on rozettecreation ability
not for only T- Lph (CD3+), B- Lph (CD22+), but for their individual subsets
(CD4+ and CD8+). Moreover, the efficiency of receptor expression was dependent
on the concentration of the protein-abzymes complex, which was used.
Conclusions.
Hence, in the study found that the proteins-abzymes mixture in certain
concentrations has both stimulating and inhibitory effects on non-specific
immune cells in vitro. This gives a
impulse to the creation of antiviral and antibacterial drugs, which would have
find their purpose in medical practice.
References:
1. ʳò Þ.ß., Ñòîéêà Ð.Ñ. Êàòàë³òè÷íî
àêòèâí³ àíòèò³ëà (àáçèìè) ìîëîêà ëþäèíè //. – Ë.: Óêð.
á³îõ³ì. æóðí. – 2007. – Ò.79. ¹2.– Ñ. 5-16.
2. Korhonen H. J. Production and properties of health-promoting proteins
and peptides from bovine colostrums and milk. //Cell. Mol. Biol. – ¹59 (1). – 2013. – Ð. 12-24.
3. Stepaniak L.
Isolation and partial characterization of catalytic
antibodies with oligonuclease activity from bovine colostrums //Prep. Biochem. & Biotechnol. –
¹ 32(1).
– 2002. – Ð. 17-28.