Mgr Patrycja Kokot-Stępień
Technical University of Czestochowa
Faculty of Management
Department of Finance, Banking and Management
Accountancy
IMPACT OF THE ECONOMIC
ENVIRONMENT ON ENTERPRISE‘S INVESTMENT ACTIVITY
The economic enterprise environment includes phenomena’s
and economic processes which appear as a result of conscious and aimed economic
activities of physical persons, economic subjects and also authorities. Its structure
represents resources and their utilisation in national and international scale.
Processes that accompany resources usage because of technological changes and
multiple styles of economical cooperation and internationalisation are
increasingly complicated. Economic activity that is perused by enterprises
reaches high level in areas which give hope for development while it’s decreases
in other areas which aren’t very prospective[1].
Economic environment is
shaped through a large range of subjects those results in legal regulations
which influences on investment decision making. Prospecting and complex analysis
of economic information is a prerequisite for determining enterprise’s
investment opportunities. By identifying the strengths and risks for investment
project, businesses can build alternative investment options. Omission of critical information or misinterpretation
can cause incorrect or delayed investment decisions[2].
Multiple factors of economic
environment cause changes in demand resulting in concurrence amongst economic
subjects. Significant factor influencing on economic subject’s investing
activity is purchasing power of consumers to buy products offered by
enterprises. Purchasing power depends
on financial status of the individual consumer and enterprise to buy
interesting products. The higher financial status of consumers they are able to
buy more divers range of products and at higher quality[3] that demands additional production lines built based on the investment
project of the enterprise.
The economic environment of
enterprise is assigned via economic condition.
It is possible to use many indicators to assess it. The most important
from investing project perspective are as below.
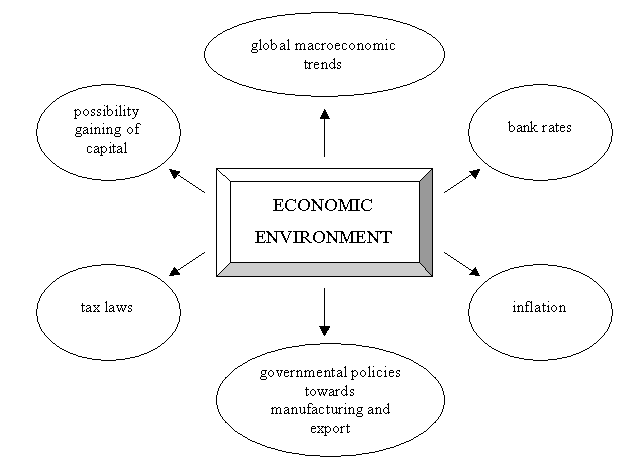

Picture. 1 Main
factors of economical environment important for enterprise’s investment
activities
Source: elaborated on the basis of: K. Marcinek: Ryzyko projektów inwestycyjnych. Wydawnictwo AE w Katowicach, Katowice 2001, p. 62-64.
Growth
rate has direct influence on size and character of strength and risks. Economic
growth cause increase of expenses around investment and consumption and it has
dynamic impact on scale of demand for products. This in turn creates
opportunity to develop economic subjects and leads to weaken concurrence within
industry. Recession in economy results in negative impact to projects. Hence it
is important to analyze trends in these matters while planning on investment
strategies[4]. It is necessary
to identify trends in economy, within the country or the region where the
project would be completed or investment would be economically linked to.
While
assessing the developing trends in economy, one should factor for changes that
happens cyclically including its frequency and intensity. Depending on the
enterprise specifics, economic boom can have stronger or weaker influence on
the enterprise situation and effectiveness of some projects can change the
influence of the boom phase. Implication of economic globalization are stronger
relations between boom in global and local markets giving new opportunities for
enterprise growth in a large scale and in some cases enables not only growth
but also survival[5]. Knowledge at least main economic indicators referring
to world and country economy which are especially interesting for particular
enterprises and observation changes of these indicators is used during decision
making in diverse areas of economic subject’s functioning.
Irresponsible
actions of investing enterprise activity impacts the level of society’s
savings. Their growth resulting in decrease of expenses on current consumption
impacts sales of produced articles. All these factors can result in preventing
traders from investing again. Production, employment and salary levels would
come down[6].
The functioning and development of a company are
significantly influenced by its connections with financial institutions.
Monetary and credit policy becomes a very important factor motivating a company
and creating conditions for the development of innovation and investment
activity. The rules of this policy concern money supply and conditions of
credit providing. Establishing basic interest rate which influences the credit
policy of banks as well as the level of investment activity is vital[7]. The interest rate is the cost of the capital used in financing an
investment project. The level of the interest rate is reflected in financial
efficiency of such a project. Low interest rate means the lower cost of capital
which causes taking credits which results in increasing investments. On the
other hand high interest rate limits company investment activity because the
capital becomes hardy available[8].
The inflation rate which is an important source of
risk for companies has a significant influence on the interest rate. It might
result in difficulties in estimating the value of outlays for implementing an investment
project as well as in forecasting profits from its realization[9]. Problems with estimating actual
profitability of investment projects appear. In the presence of inflation it
has been noticed that the tendency for long-term investments decreases, the
tendency for speculative investments increases and harder to forecast capital
circulation additionally increases economic risk[10].
Government fiscal policy also influences the
investment activity of companies by stimulating or curbing the general level of
economic activity[11]. Moreover unsuitable fiscal policy causing exaggerated inflation
influences directly the success of a particular project because it distorts the
level of estimated investment outlays making them inefficient in respect of
financial issues[12].
A company should consider tax policy instruments
while establishing the strategy of investing. Taxes influence directly the
financial efficiency of an investment. They are included in the revenues of an
undertaking, especially income tax which lowers company revenues generated by
the undertaking. The knowledge and usage of possibilities included in tax
policy concern mainly tax reliefs or temporary income tax exemption or
exemptions in other financial charges which influence the financial success of
a project. Their lack or inability of using them not only lowers the financial
efficiency of an investment but it might be the reason to abandon the
investment as well. The change of tax policy rules during the investment
realization is also an important threat for the project success[13].
Gaining
the capital on profitable conditions has a vital meaning for the success of a
particular undertaking. Therefore a suitably developed bank system, which
conditions efficient functioning of companies to great extent, is necessary. It
also provides the realization of financial obligations between domestic and
foreign business entities and creates the conditions and mechanisms to transfer
and transform investment resources[14]. Moreover a better access to resources which might be invested may
provide the company with the capital market. The high development level of
long-term debts, shares issued by business entities, investment, trust and
pension funds markets influence positively the investment activity of
companies. Government policy regarding production and foreign trade concerning
particularly the analysed effects of a planned project as well as the existence
of pro-investment institutional infrastructure enabling co-financing projects
in particular fields[15].
Biblography
1.
Borowiecki R.
(red.) Efektywność przedsięwzięć rozwojowych. AE,
TNOiK, Kraków-Warszawa 1995
2.
Borowiecki R.
(red.): Zarządzanie wiedzą a procesy restrukturyzacji i rozwój
przedsiębiorstwa. AE-TNOiK, Warszawa-Kraków 2000
3.
Caban W. (red)
Ekonomia. PWE, Warszawa 2001
4.
Gierszewska G.,
Romanowska M.: Analiza strategiczna przedsiębiorstwa PWE, Warszawa 2002
5.
Henzel H. i in.:
Vademecum inwestora: przygotowanie i wykonawstwo inwestycji rzeczowych.
Górnicza Izba Przemysłowo-Handlowa, Katowice, 1996
6. Hill Ch. W., Jones
G.R.: Strategic Management Theory. An Integrated Approach. Houghton Mifflin
Co., Boston 1989
7.
Kardaz J.
Wójcik-Augustyniak M. (red.): Zarządzanie przedsiębiorstwem.
Difin, Warszawa 2008
8.
Marcinek K.:
Finansowa ocena przedsięwzięć inwestycyjnych przedsiębiorstw.
AE Katowice 2002
9.
Marcinek K.:
Przedsiębiorstwo jako podmiot inwestujący [w:] Czynniki inwestowania
w przedsiębiorstwie. AE Katowice 1995
10.
Marcinek K.:
Ryzyko projektów inwestycyjnych. Wydawnictwo AE w Katowicach, Katowice
2001
11.
Nasiłowski
M.: System rynkowy. Podstawy mikro- i makroekonomii. Wydawnictwo Key Text.
Warszawa 2002
12. Rokita J.: Zarządzanie strategiczne. Tworzenie i
utrzymywanie przewagi konkurencyjnej. PWE, Warszawa 2005
13.
Urbanowska-Sojkin
E., Banaszyk P., Witczak H.: Zarządzanie strategiczne przedsiębiorstwem.
PWE, Warszawa 2007
14.
Żurek J.
(red.) Przedsiębiorstwo. Zasady działania, funkcjonowanie,
rozwój. Fundacja Rozwoju Uniwersytetu Gdańskiego, Gdańsk 2007