Экономические науки/ Банки
и банковская система
Arunyants G.G.,
doctor of technical sciences, professor
Badeyan
A.R. PhD student
Kaliningrad State
Technical University
ANALYSIS OF KEY ASPECTS AND FEATURES OF BANKING RISK MANAGEMENT
WHYLE CREDITING OF ENTERPISES
Under current conditionsthere is an increase and expansion, and also structuring
of banks clients probablycan increase risk component in their activity. The
subject of risk management becomes more and more essential.
Risk management based on the concept of acceptable risk and possibility
of impact on an initial risk level for the purpose of finishing this level to
acceptable value. At the heart of methodology of the concept of acceptable risk
is differentiation of risk levels at various stages of manifestations:
–Yнis initial level
of risk whichisunidentified andunvalued, butvery high due to the unavailability
of the organization's managers, decision-makers to the emergence of risk
situations;
– Ycismeasuredlevelofrisktaking
into account actions for identification, the analysis and a risk assessment. The
value Yc represents a real assessment of a risk level which is the risk of
lower level than Yн;
– Yоis residual risk
leveltaking into account the developed and executed actions for decrease in an
initial risk level;
– Yкis final (acceptable) risk level of
risk that is acceptable in terms of risk criteria.
The mathematical model can be presented the concept of acceptable risk
in the form of the following dependences:
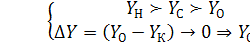 .
.
The received assessment of an acceptable risk level can significantly
change opinion concerning "riskiness".
Management strategy is development of the directions and ways for achievement of the goal
based on long-term forecasting and strategic planning. A certain set of rules
and restrictions for decision-making is developed. Asiswellknownthestrategyis predeterminetactics [1].
The problem of tactics of
management consists in a choice from all decisions which are not
contradicting strategy, the most optimum decision and the methods most
acceptable in this situation and methods of management.Effectiveness of risk
management depends largely on the ability to use fully all the methods and
techniques to reduce risks.
Taking into consideration the risk level can significantly change during
the certain period of time under the influence of internal and external
factors, the bank develops the management system (MS) of risks for ensuring the
maximum safety of own means, minimization negative influence of external and
internal factors, increase the liability to customers, counterparties and
investors.
Banking risks represent a set of risks, the
amount of which increases as the complexity of banking products, used computer
systems and data storage [2].
Ensuring stability of functioning of commercial banks causes the
necessity of development of strategy of development by them and mechanisms of
its realization. Strategy of management is realized in the course of adoption
of administrative decisions, ways of achievement of goals, and also in the
general direction of using means [3, 4]. Consecutive achievement of the purpose
– the maximum profit at preservation of an acceptable
risk level – assumes continuous search of new opportunities of further growth,
increase of profitability and more effective planning and control.
In management sense the concept "strategy" is directly
connected with definition of such characteristics as terms of implementation of
this or that complex of actions, various indicators (liquidity, profitability,
etc.) and necessary to be guided in implementation of the specified actions.
The conceptual component of strategy of bank is much more difficult formalized
concept and generally it represents a complex of the purposes formulated in
general which achievement the bank considers the task.
Currently very limited number of banks develops the strategy with
obligatory presence of a conceptual component. The majority of banks focused
first of all by achievement of short-term objectives [5]. In this case
efficiency and stability of development sharply decreases. Traditionally
strategic risk management is realized by the special management system (MS) covering
levels of strategic management and organizational divisions. The system
approach becomes objective necessity considering impossibility of consideration
of separate elements, the phenomena or problems without the subsequent
interactions with other elements. Definition of optimum strategy of behavior of
bank is connected with a problem of the correct assessment of risk.
Effectiveness of bank risk management system (RMS) is evaluated
according to the criteria: Income (loss) from operations risk, quantitative
risk indicators, quality adaptation subsystem, and the feasibility of using
regulatory mechanisms of risk accepted by the bank.
The development of strategy of risk
management has a number of consecutive stages. First of all the factors
influencing a concrete type of risk at implementation of certain bank
operations identified. Factors are analyzed from the point of view of force of risk
impact. At the following stage defined an assessment of zones of a concrete
type of risk. Assumptions are made concerning possible sources of losses and
the risk situations yielding losses and predicting thelevel of future losses.
The central problem of this stage is quantitative measurement of risk.
Usually the measurement of risk is
carried out in two main directions. Firstly, determine the probability
distribution of the causal event, or at least some quantitative indicators of
the distribution (mathematical expectation, confidence interval, etc.). Secondly, reveal
dependence of size of a negative event on the size of a causal event.
Indicators such dependence are the elasticity coefficient determination,
correlationand etc. First direction indicators are called probabilistic, the
second - scaled. Two areas are complement each other, and on their basis it is
possible to receive complex estimates of risk which is popular recent appraisal
VaR (Value-at-Risk) [ 5].
Research of uncertainty and risk can be carried out on the basis of
alternative options – scenarios according to which succession of events is
possible. Each scenariois quantitatively measured (quantified) that is
necessary for an assessment and risk management. Thus it is necessary to
consider that there are the reasons limiting possibilities of implementation of
reliable and full calculations. Control of risks assumes coordination of
actions of all divisions and bank services on situation tracking during the
whole period of existence of risk, and also monitoring (tracking only key types
of risk) and risk restriction through system of limits (a maximum permissible
risk level). The combination of strategic objectives and operational tasks,
strategic and routine planning allow commercial banks to minimize risk.
In the Russia a leading place on the emergence frequency (about 60%) and
volume of losses (more than 80%) occupied by risks of liquidity and credit
risks.
Credit risk refers
to the risk that a borrower will default on
any type of debt by failing to make required payments and can be considered as
the largest, inherent in bank activity [6, 7]. And such types of risks belong
to credit risks as [8]: risk of a default
of the credit, risk of delay of payments (liquidity), risk of providing credit;
risk of solvency of the borrower.
The accounting of credit and liquidity risks is
an obligatory information basis of decision-making process in the development
of practical measures for safety of specific banking operations and
transactions [9]. It determines substantially an originality of methodology of
management by credit risks. Bank, before granting credit,should define the
overall risk for each borrower.
Credit risk management can be defined as organized
influence of the subject of management (bank officers who are carrying out
activity on crediting of borrowers and the leading personnel) to object of
management (credit risk and activity of the employees involved into the credit
operations) for the purpose of maintenance at admissible level of credit risk indicators
of bank [10]. The special relation to credit risk is explained by that the
credits are one of main types of bank assets and at competent management of
credit operations bring in to bank the considerable income [11]. Credit risk
management is an essential part of the strategy and tactics of survival and
development of any commercial bank.
Effective identification of risk factors, the
analysis and calculation, monitoring of the current open positions is
impossible without using formal systems of decision-making support. The credit
risk depends on external and internal factors. Possibilities of external
factors management are limited although the bank can mitigate their impact and
prevent major losses. Nevertheless the main control levers of credit risk are
in the sphere of domestic policy of bank. Eventually, ability to operate risk
depends on competence of the bank management and a skill level of its ordinary
structure. Efficiency of optimization of banking risks can be reached only on
the assumption of system approach when all aspects of bankactivity become as
object of analysis, all carried out operations considered in interrelation and interdependence
[12].
Recently on all segments of national economy
distribute the implementation of the risk management system which means [13]: risk management is a purposeful search and
organization of work for decrease riskdegree, art of receiving and increasing income
in an uncertainty situation.In this situation special relevance is gained by
the researches directed on development of approaches and methods, reducing
liquidity and credit risks in banking activity taking into account their multifactorial
nature and scale.
The hierarchy of credit risk types has
three-level structure. In the bottom (basic) level the credit risk is presented
by the transaction risk, which connected with variability of solvency of
borrowers. This risk expressed in variability of a cash flow of the
enterprises. Risks located in the following level connected with
"behavior" of big groups of the credits, united in the “united big
credit", called portfolio. Such
metacredit is characterized by the parameters, allowing estimating portfolio
risk. The third level is presented by allocation credit risk which caused by
distribution of bank assets on branches, regionsand bank products.
The basis of transaction credit risk management
systemis score which is fast, exact,
objective and steady procedure of an assessment of the credit risk [14]. There are
many scoring models for the solution of the same problem. Each of them has
individual algorithm, uses the set of the factors characterizing risk,
connected with thecrediting of borrower, and as a result receives a threshold
assessment which allows dividing borrowers on "bad" and
"good".Score is the automatic or automated procedure classifying
borrowers required quantity of classes. In the simple case there are two classes:
first- borrowers who can grant the credit, second - whom it "is strictly
contraindicated". Using score the bank has an opportunity of decrease the
quantity of "bad" credits by filtration of client credit applications.
The most known isa model by Edward I. Altman [14] for an assessment of
the large companies solvency. The uniting moment for all three types of models
is equality:
![]() ,
,
where Zisascoreassessmentvalue;ak — the weight
coefficients characterizing the importance of risk factors;Xk — the risk factors defining solvency of the
borrower.
Such (or similar) formula is "kernel" of any score system.
In the Edward I. Altmanmodel itis:
![]()
where coefficients
of model are the scales defining the importance of risk factors; A, B, Csymbols are risk factors. For
exampleАis relation of working capital to total assets; В is relation of
retained earnings to total assets; С is profit
relation before payment of percent and taxes to total assets; D is relation of market funds to the
overall balance cost of debts; Е –
relation of volume of realization to total assets.This model of scoreunited the
general characteristic - multidimensionality. Finally the model of score "search",
using statistics of earlier processed credits.
The analysis of various approaches to formation of models of statistical
scoreconclude that using above mentioned model becomes the most powerful risk
factor of credit assessment which in
risk management called model risk. The set of the variables
forming an assessment of score, can eventually change and «border" between
analyzed groups can be not linear, have significantly more difficult form which
will not be able to be described by the formula of elementary model by Edward I.
Altman. Practical offers for expansion of logical model of score are presented
in paper [14].
Considering three levels of credit riskshierarchy, for management two
more complexes of models are necessary. The first is forportfolio credit riskmanagement,
and the second for support of administrative decisions regarding an allocation
of credit capital and productsof bank. Besides, even in the transactional level
it is insufficiently to classify borrowers on "good" and
"bad". It is necessary a number of functions without which the
application of the score will not give satisfactory results.
Modern risk management system is
based on a powerful information-analytical system.Integrated IT risk management
system should solve problems all types of financial risks management.
Implementation of IT risk management system will allow the bank: minimize
losses; improve the efficiency and profitability of operations; increase the
volume and reduce the cost of financing business; improve the stability and
attractiveness to investors; improve position in the market; make reasonable decisions
about reservation and allocation of capital; cover costs of risk management as
soon as possible.
The General
structure of the IT risk management solutions are presented in Fig. 1.
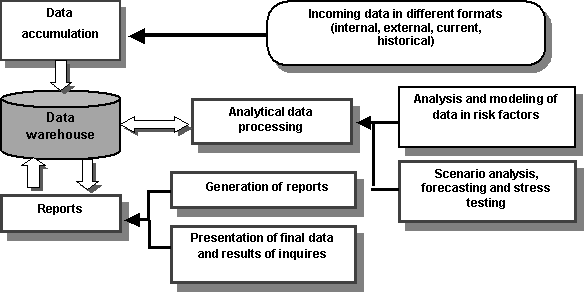
Fig. 1. General architecture of IT
solutions of the risk management
Implementation of IT risk management system is
closely connected with other large IT projects, firstly with the introduction
of the Data Warehouse, introduction of front-office systems, ABC ...;
implementation of CRM-systems.
The integrated architecture and functionality of the credit risk management
decision is presented in Fig. 2.
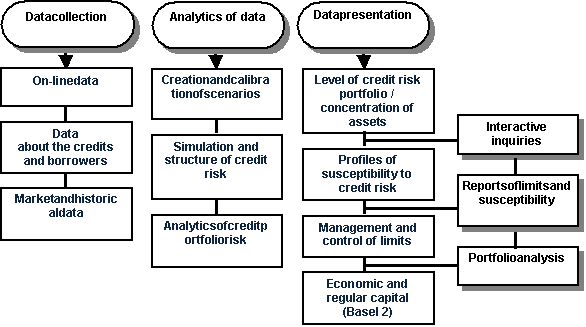
Fig. 2.Architecture and
functionality of the decision of credit risk management
Conclusion:
Successful functioning of the credit organization in the conditions of
risk is possiblewith developmentof special decision-making mechanism, allowing to determine the value of potential losseswhich the credit organization is able to
accept, and also estimate, how expected profitability justified risk. This
problem is solved by creation of the automated by risk management system,
allowing to reveal, localize, measure and control particular risk and minimize impact.
Bibliography:
1.
Руководство
по риск-менеджменту / Д. А. Марцынковский, А. В. Владимирцев, О. А.
Марцынковский; Ассоциация по сертификации «Русский Регистр». Санкт-Петербург:
Береста, 2007.
2.
Иода Е.
В., Мешкова Л. Л., Болотина Е. Н. Классификация банковских рисков и их оптимизация
/ под общ. ред. проф. Е. В. Иода. 2-е изд., испр., перераб. Тамбов: Изд-во
Тамб. гос. техн. ун-та, 2002. – С. 11-12.
3.
Арунянц
Г.Г., Дзестелова К.Г., Алиханов Д.В. Оптимальное управление ресурсами
коммерческого банка с использованием информационных технологий. В кн.
«»Материалы V
Международной конференции: Устойчивое развитие горных территорий – проблемы и
перспективы интеграции науки и образования, Владикавказ, сентябрь 2004, с19-22.
4.
Арунянц
Г.Г., Дзестелова К.Г., Алиханов Д.В. Ресурсы коммерческого банка как объект
оптимального управления. В кн. «Труды 5 Международной конференции молодых
ученых и студентов – актуальные проблемы современной науки», Самара, сентябрь
2004.
5.
Арунянц
Г.Г., Мнацаканян А.Г. Распределение ресурсов банка с использованием оптимальной
стратегии управления рисками при кредитовании: Монография. - Калининград,
Балтийский институт экономики и финансов, 2009. - 167 с.
6.
Осипенко
Т. В. О системе рисков банковской деятельности // Деньги и кредит. 2000. № 4.
С. 28 – 30.
7.
Банковское
дело: Учебник для вузов / Под.ред. В.И. Колесникова, Л.П. Кроливецкой. – М.:
Финансы и статистика, 2005. – 476 с.
8.
Банковское
дело: Учебник для вузов по экономическим специальностям / О.И. Лаврушин, И.Д.
Мамонова, Н.И. Валенцева и др.: Под.ред. О.И. Лаврушина. – М.: Финансы и
статистика, 2005. – 573 с.
9.
Белоглазова
Б.Н., Толоконцева Г.В. Денежное обращение и банки. – М.: Финансы и статистика,
2006. – 355 с.
10.
Гамидов
Г. Н. Банковское и кредитное дело. - Москва: ЮНИТИ, Банки и биржи, 2005. - 315
с.
11.
Бэррел,
Т. Банковское дело: стратегическое руководство. - М.: Консалтбанкир, 2006. -
367 с.
12.
Уварычева
Е.С. Особенности управления банковскими рисками // Международной заочной научно-практической конференции студентов,
аспирантов и молодых ученых «Современные проблемы управления риском», 20
октября 2010 г., Пермь
13.
Синки
Дж. Финансовый менеджмент в коммерческом банке и индустрии финансовых услуг/
Джозеф Синки-мл.; Пер. с англ. М.: Альпина Бизнес Букс, 2007.1018 с.
14.
Черкашенко В.Н.,
М.: «Банковское
кредитование», №4,
2012 г.