Pedagogical sciences 5.SModern teaching methods
E.Z.Zharlygasova
Kostanai State
University A.Baitursynov , Kostanai
Professionally
oriented tasks in teaching engineering students mathematics
Serious training in natural sciences, which includes mathematical
training as an essential component, is needed in order to master the
professional knowledge of students.
The present level of development of science and technology makes to
future professionals, using their professional activities in mathematics, high
requirements for knowledge, skills and abilities of mathematical, and as well
of applied nature. Since the 60’s, parallel to the idea of
polytechnic training delineated the process associated with the
birth of the so-called «applied orientation «in the teaching of mathematics.
Theoretical mathematical training does not mean that knowledge is
students’ active stock. It should be ensured that students are able to apply
their knowledge in different situations. This ability can be formed in the
learning process based on extensive disclosure links of mathematics with the
general technical and special disciplines.
One of the means of implementation of interdisciplinary links of the
general technical mathematics with the special disciplines is educating professionally-oriented
tasks’ decision. At the moment theoretical justification of techniques, using
tasks in the process of learning mathematics became particularly relevant.
Task solution is the most important kind of learning activity in
teaching mathematics. In the process of task solving mathematical theory is perceived,
intellectual activity is developed, identity of student is formed.
There is no clear separation of the concepts of professional and applied
orientation in most studies. As a rule, the term " applied orientation
" is used, while at the same time often that means the professional
direction .
However, a course in mathematics for the most part is still isolated
from the technical disciplines. This insulation is so deep that students do not
see they are familiar with mathematical objects in the real world, therefore,
unable to use mathematical tools to describe this situation. At the workshops
addressed the problem of applied orientation this problem is left inattentive, therefore,
as a result of such a process practical skills of students are not formed.
As mentioned above, one of the important directions of forming the applied and professional orientation of
mathematical training of future engineers is the selection and study of
professionally-oriented tasks. Such training can be successful, provided complete
approach to the organization of this process . At all stages of educational
interaction through professionally oriented tasks it is required to use effectively
mathematical apparatus , show its application in the study of technical
disciplines in the future professional activity engineer.
Understanding of mathematics helps future engineers in solving problems
by mathematical modeling . There must be a link between mathematics and the real
world around us - a specific type of model , on the one hand, it can hold
information about a particular subject of investigation , and on the other
hand, is formulated by using standard mathematical concepts and , therefore,
suitable for application of powerful mathematical tools. This is a mathematical
model of the phenomenon under investigation, that serves as a kind of
translation patterns, identified by specific
science, into the strict mathematical language . Construction of a mathematical
model of the test process includes the following steps: 1) the object of study
, 2) functions of the state of the
system , 3) independent variables , 4) coordinate system , 5) the reasons for
the evolution of the system; 6) cause - effect relationship , 7) the input
parameters of the system , 8) the conditions of applicability of the
mathematical model , 9 ), the output parameters of the system .
Let’s consider
the motion of a ballistic missile launched at an angle to the horizon. Movement
of the body will not be straightforward, since it is affected not only by the
force of gravity, downward, but the thrust F,
acting at an angle to the horizon. Position of the missile will be
characterized by a horizontal coordinate x
and vertical coordinate y.
The launching point chosen as the start point. Then function x = x(t) expresses the
distance from the projection point, in which the missile at the moment of time,
on a horizontal plane ( earth's surface
) , to the origin; the function y =
y(t) determines the height of missile above ground. To derive the
equations of motion it is necessary to write Newton's second law in vector form
. In the horizontal direction there will operate the horizontal component of
thrust Fx and vertical -
vertical component of thrust Fy
and weight of P. According to Newton's second law, acceleration of the body in
a horizontal and vertical direction will be proportional to the corresponding
forces. As a result, we obtain the following system of equations of motion: 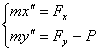
Traction components are calculated according to formulas ![]() , where
, where ![]() - - the angle between the traction and the horizontal axis coordinates. Thus
the equations of motion take the form:
- - the angle between the traction and the horizontal axis coordinates. Thus
the equations of motion take the form: ![]() , where
, where ![]() .
.
Tractive force is valid until until all the fuel burns . Time combustion
t ∗ is assumed known . Then the equality is right 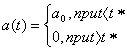 , where a0 the
ratio of the thrust F to missile’s
weight m are the
parameters of the process.
, where a0 the
ratio of the thrust F to missile’s
weight m are the
parameters of the process.
Suppose that at the initial time the rocket is at the origin and at
rest, which corresponds to the initial conditions ![]()
Movement of the rocket goes up to a certain time T , in which it lands ,
which means we will have zero vertical coordinate . Thus arrive at the
condition y(T) = 0 from
which we are to find the landing time T.
A mathematical model parameters are an angle u, generally speaking, the time-dependent , the ratio a0 and the combustion time of fuel t ∗. The mathematical model makes sense only if its
initial vertical acceleration is positive . The initial acceleration in the
vertical direction is equal to ![]() . Thus , we come to the following condition of applicability of the
model
. Thus , we come to the following condition of applicability of the
model ![]() .
.
Thus, systematic and purposeful use of professionally - oriented tasks
in teaching mathematics, based on the technology of visual modeling of
engineering processes and phenomena in the real resource disciplines
interaction leads to increased motivation for learning mathematics background
enhancing professional knowledge and quality of subject knowledge and skills of
engineering students at universities.