Technical science
Zhussupova
B.T., Chromushina Ì.Å.
A.Baitursynov Kostanay State University
POSSIBILITY TO REALIZE THE MODULE OF FUZZY-NEURAL
CONTROL USING FUZZY LOGIC TOOLBOX
Abstract
In
our days there is a need for systems that can not only be performed once
programmed sequence of actions with pre-defined data but also able to analyze
incoming information, search and find patterns to make predictions, etc. In
this area of application in the best way proved neural network. This area explores the intelligent methods to
solve various tasks used in various areas, including in industry, economy,
medicine, and other. The intelligent computing systems (ICS), representing an
association of neural networks, genetic algorithms and fuzzy systems, allow to
solve various tasks, but the most important thing - they become a universal
tool for information processing.
Key words: neural
networks, fuzzy system, membership function, forecasting.
I. Introduction
Thanks to the development and publications of L. Zadeh, E. Mamdani, M,
Sugeno has identified a range of possible applications of fuzzy set theory (
FST) for practical tasks, in which the object and terms of its functioning
poorly understood, the model of the object and purpose of management of poorly
formalized. Using traditional approaches, it is difficult to get adequate model
of the processes, taking into account the available expert knowledge [1]. Note
that often we come to the conclusion, acting on the basis of linguistic rules,
in which is concentrated theoretical knowledge and personal experience of
management. To turn such expert rules in the mathematical model is conveniently
using FST. It is possible to implement
such model with the help of means of “Fuzzy Logic Toolbox” of “Matlab” package.
II. Task Statement
Let's
say, we will call predicted criterion number ![]() . Many different factors influence this criterion. Designate them
through
. Many different factors influence this criterion. Designate them
through ![]() , then the model of this criterion will represent functional display of
a look:
, then the model of this criterion will represent functional display of
a look: ![]() , where
, where ![]() - vector of influencing factors. At a large number of factors it is
convenient to classify their influence in the form of a hierarchical tree of a
logical conclusion. Elements of a tree it is interpreted so: tree root –
criterion
- vector of influencing factors. At a large number of factors it is
convenient to classify their influence in the form of a hierarchical tree of a
logical conclusion. Elements of a tree it is interpreted so: tree root –
criterion ![]() ; terminal tops – private influencing factors of influence (
; terminal tops – private influencing factors of influence (![]() ); non-terminal tops – parcels of influencing factors; arcs of the graph
out of non-terminal tops – enlarged influencing factors (
); non-terminal tops – parcels of influencing factors; arcs of the graph
out of non-terminal tops – enlarged influencing factors (![]() ).
).
Rollups ![]() and
and ![]() are implemented through the
logical conclusion of the fuzzy knowledge bases. Values of factors are
expressed as a deviation (in percent) from average indicators. For modeling of
the integrated influencing factors expert fuzzy knowledge bases type Mamdani are used. Elements of
antecedents of indistinct rules communicate logical operation And. For modeling
of considered criterion the fuzzy knowledge base type Sugeno is offered. Each
rule of this knowledge base models one type of marketing. The coefficients in
the conclusions of the rules define the sensitivity criterion for the relevant
factors. The coefficients are selected expertly by the method of paired
comparisons Saati.
are implemented through the
logical conclusion of the fuzzy knowledge bases. Values of factors are
expressed as a deviation (in percent) from average indicators. For modeling of
the integrated influencing factors expert fuzzy knowledge bases type Mamdani are used. Elements of
antecedents of indistinct rules communicate logical operation And. For modeling
of considered criterion the fuzzy knowledge base type Sugeno is offered. Each
rule of this knowledge base models one type of marketing. The coefficients in
the conclusions of the rules define the sensitivity criterion for the relevant
factors. The coefficients are selected expertly by the method of paired
comparisons Saati.
For getting the graphs of the membership
functions of fuzzy therms "Low" (L), Medium (M) and High (H) is used
membership function of Gauss. ![]() , where
, where ![]() – the membership function of the
factor
– the membership function of the
factor ![]() to the fuzzy number
to the fuzzy number ![]() ;
; ![]() and
and ![]() – the parameters of the membership function: the coordinate of the
maximum and the coefficient of concentration.
– the parameters of the membership function: the coordinate of the
maximum and the coefficient of concentration.
In a clear case the extent of membership is calculated by substituting
the current value of the variable in the formula for calculating ![]() . When we have fuzzy source data it is necessary to determine the extent
of membership of one of fuzzy set
. When we have fuzzy source data it is necessary to determine the extent
of membership of one of fuzzy set ![]() – the values of the input variable, to another fuzzy set
– the values of the input variable, to another fuzzy set ![]() – to the therm from the
knowledge base, which is equal to the height of the intersection of these fuzzy
sets. When creating a fuzzy model of the considered criteria systems of fuzzy
output for each factor are implemented in the Fuzzy Logic Toolbox of Matlab
package.
– to the therm from the
knowledge base, which is equal to the height of the intersection of these fuzzy
sets. When creating a fuzzy model of the considered criteria systems of fuzzy
output for each factor are implemented in the Fuzzy Logic Toolbox of Matlab
package.
III.
Results
For the
implementation of the fuzzy model of competitiveness of the University are use
four systems of fuzzy conclusion [3, c.255-276]:
y1_Quality.fis – fuzzy
modeling system of quality of the University (y1).
y2_Image.fis
- fuzzy modeling system of the image of
the University (y2).
y3_Service.fis
- modeling system of the Service (y3).
Q_Competitive
Strength Index.fis - fuzzy system of
forecasting of competitiveness of the University (Q).
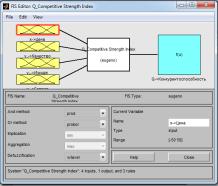
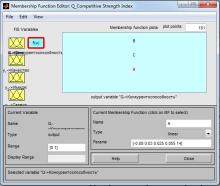
Picture 1 – Membership functions of competitiveness
The
interface of model is realize using a system GUI. When you click to “Rate
competitiveness” is a function conc.m. call.
IV. Conclusions
This interface is simple, intuitive and
does not require much explanation: the source data are entered in the text
boxes according to the legend (L - low, BA - below average, A - average, UM -
upper-middle, UI - upper intermediate)
Literature:
1. Ëóêàñ Â.À. Ââåäåíèå â Fuzzy-ðåãóëèðîâàíèå. – Åêàòåðèíáóðã: Èçä-âî
ÓÒÃÃÀ, 1997. – 36 ñ.
2. http://matlab.exponenta.ru.
3. Ãîðáàíü À.Í. Íåéðîííûå ñåòè íà ïåðñîíàëüíîì
êîìïüþòåðå. / À. Ãîðáàíü, Ä. Ðîññèåâ. –
Íîâîñèáèðñê.: Íàóêà, 1996. – C. 255-276.