Omarov
Kazbek Altynsarovich, Dr. of
engineering sciences., professor, Kungurov Aslan Rahmetullayevich, Candidate of engineering sciences., docent (PhD doctor)
(Astana city, Eurasian National
University named
by Gumilyov L.N ),
(Almaty city, KazNTU named by Satpayev K. I.)
DETERMINATION THE OPTIMAL MODEL OF
BRAKE MECHANISMS
As is
known, the task of optimal designing in the traditional formulation reduces to
the generalized task of nonlinear programming:
it’s necessary to determine the optimal
parameters ![]() =
=![]() ,
which extremalize the function of object
,
which extremalize the function of object
extn F![]() =F
=F![]() (1)
(1)
![]()
where
closed area ![]() define as follows:
define as follows:
![]() :
: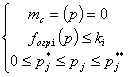
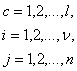
![]()
Here ![]() – description of model behavior in the form of equations;
– description of model behavior in the form of equations; ![]() - functional constraints on a model behavior;
- functional constraints on a model behavior; ![]() - constants;
- constants; ![]() - boundaries of parameter variations.
- boundaries of parameter variations.
Numerous
works are devoted to the
decision of the given task. The result of the decision depends as on the task area ![]() and, in particular, restrictions [1],
and from
the search
method
and, in particular, restrictions [1],
and from
the search
method ![]() .
.
It should be
noted that at the stage of outline design of brake mechanisms such a statement of the problem
in most cases is unacceptable: no information on the reasoned purpose of constants ![]() ;
;
The area of
the task parameters is often significantly more than area of defining models;
due to the
lack of data on the possibilities of projected demand model ![]() , applicable to the projected model, are contradictory; no clear idea of
what should be considered functional limitations, and what is the quality criteria,
etc..
, applicable to the projected model, are contradictory; no clear idea of
what should be considered functional limitations, and what is the quality criteria,
etc..
Lack of
information on projected model of brake mechanism and the impossibility of
complete formalization of requirements essentially led to the fact that in most
cases, the projector refuses to solving the problem of mathematical programming
[1]÷ [3].
Let's
consider a new approach [1,4] to determine the optimal model of brake
mechanism, based on the analysis of the parameter space and making decisions
based on the results of this analysis.
Requirements
for the projected model of brake mechanism, defined as ![]() of functional limitations. Last should be divided into two groups:
of functional limitations. Last should be divided into two groups:![]() of functional limitations, which constants
of functional limitations, which constants ![]() assign "tough" and
their variation is unacceptable;
assign "tough" and
their variation is unacceptable; ![]() functional limitations, which constants
functional limitations, which constants ![]() can be in some field of admittance (as by constructive reasons, and by standard data
). This admittance field sets in some cases, and in
other cases is determined only by solving the task.
can be in some field of admittance (as by constructive reasons, and by standard data
). This admittance field sets in some cases, and in
other cases is determined only by solving the task.
It
should be noted that in the first and second cases, the choice of the constants
is not a priori realized, to solve the task.
Consider
the way to solve formalized task determining the optimal model of brake
mechanism.
1. ![]() functional limitations transmitted to quality criteria:
functional limitations transmitted to quality criteria:
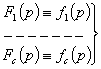
![]() (5)
(5)
2. ![]() – dimensional space
– dimensional space ![]()
![]() by functional limitations it is probed by uniformly distributed
sequence of points
by functional limitations it is probed by uniformly distributed
sequence of points ![]() as the projector on the stage of outline designing does not give preference
to any part of the space [4].
as the projector on the stage of outline designing does not give preference
to any part of the space [4].
3. In each
point ![]() identifying all object functions
identifying all object functions ![]() , where
, where ![]() , and selected
, and selected ![]() models
models ![]() , satisfying
, satisfying ![]() functional limitations.
functional limitations.
4. Based on
the analysis ![]() models of quality
criteria are transmitted into the category of restrictions that should be
called criterial constraints:
models of quality
criteria are transmitted into the category of restrictions that should be
called criterial constraints:
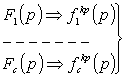
![]() (6)
(6)
or
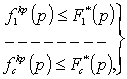 , (7)
, (7)
where ![]() - boundaries of permissible values of quality criteria, defined by
projector on the analysis basis
- boundaries of permissible values of quality criteria, defined by
projector on the analysis basis ![]() models of brake mechanisms.
models of brake mechanisms.
5. Analyzed
the multitude, consist of ![]() brake mechanisms models,
simultaneously satisfy all criterial constraints. From a given set by integral
estimates determines the optimal model of brake mechanism.
brake mechanisms models,
simultaneously satisfy all criterial constraints. From a given set by integral
estimates determines the optimal model of brake mechanism.
For the
analysis of a set consisting of ![]() brake mechanism models,
introduced two types of complementary comparative evaluations denoted respectively
brake mechanism models,
introduced two types of complementary comparative evaluations denoted respectively ![]() and
and ![]() . Estimations
. Estimations ![]() characterize the models in terms of
their proximity to the best result for each criteria (assume that all criteria should
be minimized). For calculation
characterize the models in terms of
their proximity to the best result for each criteria (assume that all criteria should
be minimized). For calculation ![]() used ratio
used ratio
![]()
![]() (8)
(8)
where ![]() - the smallest value,
- the smallest value, ![]() - from all obtained from the
calculations; it belongs to one of the
- from all obtained from the
calculations; it belongs to one of the ![]() models, for
models, for ![]() . It should be noted that the same model is generally not the best on all
counts
. It should be noted that the same model is generally not the best on all
counts ![]() ; therefore, in order to find a compromise variant must be set admittance for deviation
; therefore, in order to find a compromise variant must be set admittance for deviation ![]() îò
îò ![]() (or
(or ![]() îò 1) , hereinafter referred to as
criterial admittance and designated
îò 1) , hereinafter referred to as
criterial admittance and designated ![]() . We believe that
. We believe that ![]() brake mechanism models
simultaneously satisfy all conditions (7)
brake mechanism models
simultaneously satisfy all conditions (7)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (9)
(9)
Complex
criterion ![]() is used as an integrated
estimation
is used as an integrated
estimation ![]() for brake mechanism
models by all quality criteria
for brake mechanism
models by all quality criteria
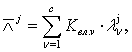
![]() (10)
(10)
where ![]() – Moisture coefficient
– Moisture coefficient
In the case, when ![]() =1
=1
![]()
![]()
where ![]() .
.
The set ![]()
![]() always has a lower limit
always has a lower limit ![]() ; the brake mechanism model
should have such estimation, in which all the criteria are minimal.
Consequently, because of the antagonism of the criteria
; the brake mechanism model
should have such estimation, in which all the criteria are minimal.
Consequently, because of the antagonism of the criteria ![]() .
.
The optimal model of brake mechanism ![]() on the set
on the set ![]() models is as follows:
models is as follows:
![]() (11)
(11)
If there is
information about the moisture coefficients ![]() of optimal model of a brake mechanism corresponds an estimation
of optimal model of a brake mechanism corresponds an estimation
![]() (12)
(12)
Constructive
formation depending ![]() finally depends on concrete
requirements, required to projected brake mechanism models and its related to
operations research sphere [3].
finally depends on concrete
requirements, required to projected brake mechanism models and its related to
operations research sphere [3].
In
case, if any of brake mechanism models doesn't meet requirements, it makes
decision on increase number of tests, changes in formulation of the task or on
transition to other block scheme of a brake mechanism.
Conclusions.
Statement of optimal projecting task of brake mechanism on the stage of outline projecting in most cases is
unacceptable. The proposed approach to the determination of the optimal model
of the brake mechanism is based on the transition from a one-criterion nonlinear programming task to the multicriteria task. The algorithm of the decision
includes research of space parameters, introduction criterial restrictions and
an estimation of models by complex (integrated) criteria.
Literature
1.
I. I. Artobolevsky, M.D Genkin, G.V. Kreinin and etc. Search of
compromise decision in choosing the machine parameters.- DAN , USSR, 1984,
t.218, ¹ 1, p. 78-82.
2.
A. I. Birger. Strength analysis.- M: Mechanical Engineering, 1986, 340 p.
3.
Y.B. Germeyer. Introduction to
operations research theory. - M., Science, 1981, 287 p.
4.
I. M. Sobol, R. B. Statnikov LP- search and optimal design / / Coll. "Problems of
random search - Riga: Knowledge, ¹ 1, 1992, 28-33 p.