Master of Economics and Business Bissenova R.A.
Kyzylorda State University
Korkyt Ata, Kazakhstan
The infrastructure of the Financial
Market
and its constitutive elements in Kazakhstan
Financial Market -
a system of redistribution mechanisms of capital between lenders and borrowers
through intermediaries in the form of supply and demand for capital.
The main functions
of the Financial Market:
- Regulatory - is
the regulation of the market, whether by public authorities, and by the
self-regulatory organizations
- Information,
which implies ensuring equal and adequate access to information for all
participants in the financial market
- Distributing -
converting of financial market instruments provides an overflow of funds from
one economic sector to another;
- Commercial,
implying that the transactions carried out in the financial market brings
income to all participants of the transaction;
- Pricing - the
price of the financial instruments in the market formed under the influence of
supply and demand in conditions of free competition
Buyers and sellers in the Financial Markets:
- Households
(individuals);
- Business entities
regardless of their form of ownership;
- State governments
Factors
contributing the function of the Financial Market:
• To minimize the
role of government in the redistribution of financial resources;
• Complete
independence of economic entities under all forms of ownership in order to
promote competition and limiting monopolies;
• Ceasing the Use
of Loan Fund of the Central Bank of the country to finance the budget deficit;
• Constant increase
cash income from businesses and the public, which may be invested in
securities.
According to the
established order of the Republic of Kazakhstan in financial reporting by
public regulation, the structure of the financial market of Kazakhstan is
presented in Figure 1.
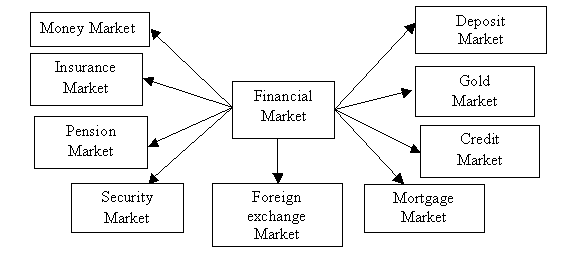

Figure 1. The
structure of the financial market of Kazakhstan
Money Market - a
market in the circulation of cash and serves a short-term means of payment
(bills, checks, etc.).
Credit Market - the
market of short-term and long-term bank loans.
The Securities
Market - a market that is issued, the securities, as well as their substitutes
(certificates, coupons, etc.)
Foreign Exchange
Market - a market in which goods are objects that have a monetary value:
• foreign currency;
• securities;
• precious metals.
The subjects are
the foreign exchange market, stock exchanges, exporters and importers,
financial and investment institutions, governmental organizations.
The Gold Market -
is the sphere of economic relations associated with the purchase and sale of
gold, both for savings and replenish the gold reserves of the country, and for
the organization of business and consumer industrial production.
Capital Markets, in
turn is divided into the money market
and the market equity securities. This division expresses the nature of the
relationship between purchasers of goods (financial instruments) sold in this
market, and issuers of financial instruments.
On the capital
market traded long-term financial instruments, provided the conditions of
maturity, repayment and payment.
Individual securities and their substitutes
(certificates, coupons, etc.) are produced, traded and consumed in the
securities market. For most world economists it is characterized by the
inclusion of the financial market structure to the insurance market, pension
and mortgage markets.
Insurance, Pension
and Mortgage markets - are the emerging markets with its financial instruments
and institutions - savings institutions operating on a contractual basis.
Need for the
provision of Mortgage Markets in the capital markets, which is characteristic
for developed countries, due to a number of circumstances. Firstly, mortgage
loans are always provided with real guarantee in the form of land or buildings.
Secondly, mortgage loans are not standard parameters and therefore it is
difficult to implement in the secondary market. Thirdly, - mortgage markets is
strictly regulated by special government agencies in contrast to other
long-term capital markets in developed countries.
Literature
1. Искаков У.М. Рузиева Э. Бохаев Д.Т. Финансовые
рынки и посредники. Алматы-Экономика ,2005.
2. Международные валютно-кредитные и финансовые
отношения: Учебник / Под ред. Л.Н.Красавиной.-Москва
3.
«О Национальном
банке РК» Закон РК от 30.03.1995 г.
4.
«О банках и банковской деятельности в РК» Закон РК от 31.08.1995 г.