Physics/7. Optics
Zaiets T., Maksymenko D.,
Odarenko E.
Kharkiv National
University of Radio Electronics
V.N. Karazin Kharkiv
National University
Photonic crystals resonance structure for optical
biosensors
Photonic crystals are materials with refractive index
which is spatially periodic modulated. Photonic crystals can be designed to
provide photonic bandgaps, within which light propagation is prohibited for
specific wavelengths [1]. Ñontrol of the light can be achieved by introducing
certain defects in photonic crystals structure. The light is only allowed to
exist within defect region. The photonic crystals structure exhibit significant
confinement of light compared to conventional optical device. This feature allows downsizing of the
device based on photonic crystals structure.
Nowadays there is an
intensive theoretical and experimental research of photonic crystal properties,
methods of analysis and different devices, which include photonic crystal
structures such as channel drop filter, power splitter, light sources etc [2,3]. The studying of optical sensing based on photonic
crystals has become a relevant topicin the recent years. Sensors
based on photonic crystals allow performing a label-free detection based on the
interaction of the evanescent field in the structure to detect changes in the
refractive index induced by the target analytes [4]. The high sensitivity of
photonic crystals-based sensing structures arises from the high confinement of
the optical field in the defect regions designed for sensing purposes, as well
as from the enhancement in the light-matter interaction provoked by the
slow-light effect.
In this work we consider the dispersion
characteristics of biosensors based on usage of photonic crystal resonators.
The photonic crystals kind called a holes-on-dielectric structure is presented.
This type is chosen due to several
factors, including easiness of fabricating and coupling with single mode
optical waveguides. Moreover, this structure allows obtaining wide photonic
bandgaps for the TE polarization. Resonant cavity usually formed within the
photonic crystal structure by changing of the one or some holes sizes.
Principal parameters of the task in this work are holes radius r, the
lattice constant a and permittivities of the photonic crystal ε and
target analyte ε1.
MIT Photonic-Bands (MPB) software is used to examine
spectral properties and calculate dispersion characteristics [5].
In this report, a photonic crystal structure with a
local defect is considered. Fig. 1 shows
a basic configuration of the photonic crystal structure with triangular
symmetry and holes with radius r/a = 0.48.

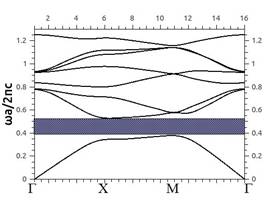
Using package MPB we calculated dispersion
characteristic of the infinite photonic crystal (Fig. 2). Here c – speed of light in vacuum. The
photonic bandgap is shown by shaded zone and has boundaries at ![]() 0.377 and
0.377 and ![]() 0.53. Photonic crystal devices like a resonators and
waveguides are developed for working frequencies within the photonic band
gap.
0.53. Photonic crystal devices like a resonators and
waveguides are developed for working frequencies within the photonic band
gap.
Let's consider the photonic crystal where there is a
hole which has a smaller diameter than other elements of the structure. This
case is illustrated in Fig. 3. This phenomenon is called “the local defect of
the periodic structure” [1]. A resonance frequency of this structure was
calculated on the base of using MPB package. The resonance frequency equals ![]() 0,493607.
0,493607.
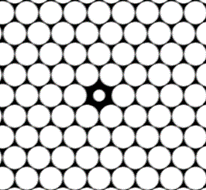
Fig. 3 – Local defect of a periodic structure
The next step of the
investigation is infiltrating
the another dielectric into hollow local defect of the photonic crystal. Fig. 4
shows the dependency of the resonance frequency on the resonator core
permittivity. For example, defect is infiltrated by biological liquid (blood-serum)
with ε = 1.8 [6]. As a result, the resonance frequency shifts from initial
value to value 0.490312. Changing values of the permittivity allows us
calculating the sensitivity of the biosensor, which is defined as the
normalized frequency shift per permittivity unit.
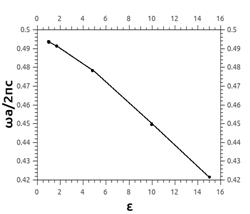
Fig. 4 – Resonance frequency vs permittivity.
In Fig. 5 spatial distribution of the magnetic field
in the resonator is showed. Obviously, in this case the field intensity maximum
forms inside of defect hole. It provides an intensive interaction between an
electromagnetic field and analytes. This leads to an increase of the sensor
sensitivity.
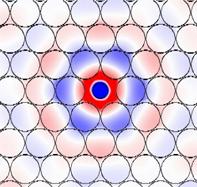
Fig.
5 – Spatial distribution of the magnetic field in the sensor area.
In this work a model of biosensor that bases on the
photonic crystal resonance structure was developed. Resonator is formed on base
of a local defect of PC. Calculations of the resonance frequency for various
values of the permittivity of the infiltrated substances are carried out.
Sensitivity of this sensor structure was defined.
References:
1.
Lourtioz J.M.,Henri Benisty H., et al. Photonic Crystals. – Springer-Verlag, 2008. –
514 p.
2. Joannopoulos J.D., Meade R.D., Winn J.N. Photonic
Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light. – Princeton Univ. Press,
1995. – 137 p.
3.
Skorobogatiy M., Yang J. Fundamentals of Photonic Crystal Guiding. – Cambridge University Press, 2009. – 267 p.
4.
D. Dorfnera, T. Zabela, T. Hürlimanna, Photonic
crystal nanostructures for optical biosensing applications // Biosensors and
Bioelectronics. – 2009. – Vol. 24. – pp. 3688–3692.
5. Johnson S. G., Joannopoulos J. D. Block-iterative
frequency-domain methods for Maxwell's equations in a planewave basis // Optics
Express. – 2001, No. 3. – Ð. 173-190.
6. El-Kashef H., Atia M.A. Wavelength
and temperature dependence properties of human blood-serum // Optics &
Laser Technology. – 1999. –Vol. 31. – pp. 181-189.