Abdykerova G.Zh.
EKSTU
Decision taking effectiveness in the
project management
One of the most
important questions in the innovative projects management is the determination
of its quality level under modern conditions.
By innovative
project quality as a management object we will mean those characteristics
relating to the results capacity of the projects and its realization process to
satisfy the requirements to the innovative products competitiveness and their
innovative attractiveness for investors.
It is rather
difficult to assess the project quality on the beginning stage of R&D due to the uncertainty in the technical and economic indices but the new development
analysis on this stage is of a great interest.
On the basis of certain criteria we offer a technique of
innovative projects expertise on the beginning stage. The technique is based on the model of
American scientist McKinsey [1].
In the development
of this technique a methodological approach based on the expert assessment of
innovative project competitiveness and innovative attractiveness has been
applied. The adequacy of the criteria used in the relation to the complex index
is formed due to the implementation of weighing coefficient to each criterion
and the application of additive-multiplicative computing technique.
The assessment of
an innovative project with the application of McKinsey’s model is better to
realizes by 3 stages: à) selection of
optimal criteria; b) determination of weighing coefficients; c)projects positioning in a
matrix.
From the point of
view of the market, innovative projects are the objects of its two interacting
segments: science and business. That is why it is advisable to formalize them
as two dimensional objects: competitiveness and innovative attractiveness. The
peculiarity of these indices is in the dependence on many criteria. Below there are criteria that have the greatest impact on
these indices.
Criteria of competitiveness:
1) The sales market availability and the possibility to commercialize the results of the project;
2) The level of competitive advantage of R&D results and the possibility of their long maintenance;
3) Conformity with the existing distribution
channels;
4) Patentability (possibility to
protect the project by a patent);
5) The availability of the intellectual
property object;
6) The availability
scientific and technological background;
7) The scopes and the spectrum of
the technologies practical application;
8) The provision with the modern
level of innovations management (project management techniques);
9) The level of project development;
10)
The availability of the qualified team and work experience in the projects
implementation;
11)
The perspectives of attracting private funds (investment attractiveness);
12)
The possibility to perform future R&D on the basis of the given
project and new technologies.
Criteria of
innovative attractiveness:
1) The compliance of the project with the priority directions of industrial and innovative strategy;
2) The actuality of the research and product uniqueness (absence of analogies);
3) Scientific and
technological level of the project;
4) The scientific
novelty of
the suggested in the project solutions;
5) Technological level
of the project (technology transfer, new technology);
6) Technical
feasibility of the project;
7) The cost of the
project;
8) The project payback period;
9) The project
advantages in comparison with the existing analogies in the world;
10)The
cost-effectiveness of the project
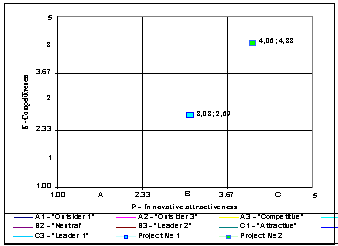
Ðèñ.1. McKincey’s matrix (innovative projects,
absolute positioning)
It is important to note that the sectors names of McKincey’s matrix in our case differ
from the classical ones [7].
So, in the given
matrix (Fig. 1) we defined 3 spheres: 1) «leaders»; 2) «outsiders», 3) «bordering».
The projects which after positioning are in the sphere of “leaders” have the best or average index values of innovative attractiveness and competitiveness and are of higher priority,
they can be implemented right now.
Projects that are in 3 sectors in the lower left corner of the matrix (“outsiders”) have low values on
many criteria. These projects are problematic – they have more weaknesses than
advantages.
3 sectors located along the main diagonal
going from the lower left to the upper right edge of the matrix have the
classical name “bordering”: they are competitive sector (in case of low
attractiveness), attractive sector (in case of low competitiveness) and neutral
sector. These projects are rather perspective and need further development.
As a solution we
will take that alternative (project), where regulated assessment of the
vector is located in sector “Leader 1”. Project ¹2 might be
considered to be such an alternative which is of higher priority according to
the experts’ assessment and is ready for the implementation.
Project ¹1 takes a neutral
position in the matrix, is a perspective but has certain disadvantages which
should be worked out.
On the bass of the
received criteria model and criteria weight assessment the requirements and
techniques have been developed for the innovative projects expertise. It can be
applied in projects assessment in HEI, enterprises, development institutes,
etc.
References:
[1]
I.Ansoff, Strategic management,
Moscow, Economics, p. 99-103, 1989.
[2]
V.S. Efremov,
Business strategy and planning techniques, Economics and
statistics, p. 89-92, 1998.
[3]
S.V. Valdaitsev, O.V. Motovilov, Research, developments and innovative
projects, Saint-Petesburg, Economics, p. 68-74, 2004.
[4]
S.I. Shelobayev, Mathematical methods and models in the economics,
finance, business: textbook for the universities. - Ìoscow: UNITI-DANA, 2001. – p. 367.
[5]
R.A. Fatkhutdinov, The development of management solution, Textbook for HEI,
2d ed.,
- Ìoscow: “Intel-Syntez” Business school, 1998. - 272 p.
[6]
G.Ya. Goldshtein, Management principles, Taganrog: TRTU, 2003.
[7]
A.A. Thompson, A.J. Strickled, Strategic management: The art of strategy development
and realization,Textbook for HEI/Moscow, Banks and bourses, UNITÈ, 1998.-578p.