Ïåäàãîãè÷åñêèå íàóêè/5.Ñîâðåìåííûå ìåòîäû ïðåïîäàâàíèÿ
V. Novikov,
associate professor
of HAC;
G.Kalakova,
a senior lecturer of computer science and
mathematics of Kostanay State University named by A.Baitursynov;
B.Kalakov,
assistant professor
of physics and GTD Kostanay State Pedagogical Institute
Pseudodecisions
of tasks on physics
In
methodical literature it is accepted PseudoDecisions to count such decisions
that at seeming loyalty, result in incorrect results. Such decisions are mostly
made by students in considering of combined non-standard tasks, especially the
tasks of increased difficulty, offered to them on different competitions,
Olympiads of different levels.
Consider
the following examples said.
Task 1 Two sources of EMF with 5V
and 3V and internal resistance of 1 ohm and 3 ohm respectively are connected in series and close the external
resistance at 12 ohms. Determine the
potential difference across the first source.
Decision of student
Ohm¢s law for a clozed
circuit
I=E/(R + r), (1)
Where E = E1 + E2
– EMF sources connected in series;
r = r1 + r2 – their general internal
resistance.
We find the numerical values of these quantities and put them in a
formula(1) : we get
I = 0,5 A.
Sought
after difference of potentials
U1 = Ir1
= 0,5 A*1 Îì = 0,5 V.
And answer to the task - 4,5 V.
Student isn’t defined sought value, and the voltage drop within the
first current source (work performed shock - or rather, an electric field to
move a unit of positive charge inside it).
Potential difference between the first source, that is, voltage at its
terminals (in other words, the voltage in the external circuit of the first
source)
U1 = E1 – Ir1 = 5Â – 0,5Â = 4,5V.
Task 2 For the test of equipment under conditions of
weightlessness a container up is thrown upwards by a pneumatic piston device,
located at the bottom of the mine evacuated. The piston acts on container
during the time Δt with a force F = nmg, where m - mass of the container with the equipment. How long does the
container will fall to the bottom of the mine? During what time does last the
state of weightlessness for an equipment, if ∆t = 0,04 with, and n =
125?
We will show a
decision resulting in a right answer at once, paying attention to the mistakes
assumed by students.
During a given
time, ![]() the equipment was moving with
acceleration
the equipment was moving with
acceleration
![]() (1)
(1)
And acquired speed
![]() (2),
(2),
rising to a height
![]() (3)
(3)
 To this part of the
decision pupils make the mistake, assuming that the container is moving with
the equipment only under the force
To this part of the
decision pupils make the mistake, assuming that the container is moving with
the equipment only under the force ![]() and therefore acceleration
and therefore acceleration![]() . And therefore,
. And therefore,![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
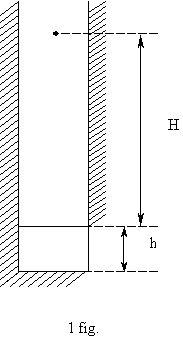
The container moves under the action only of gravity,
and rises to a height H (see fig. 1)
![]() (4)
(4)
Lifting time ![]() of the container to
this height is determined from the equation:
of the container to
this height is determined from the equation:
![]() (5)
(5)
And
time of descent to the bottom of the mine container (also under the influence
of gravity only) from the equation:
![]() (6)
(6)
Many
students here believe that, assuming that the piston does not return to its
original position (on the bottom level of the mine)
From
equalization(6) we have: ![]() .And taking into account equalizations (3) (4) we get:
.And taking into account equalizations (3) (4) we get: ![]()
The time during
which the state of weightlessness lasts for an equipment, equal:
![]()
And all the time
motions of container :
![]()
The decisions of
these two problems have occurred due to the substitution mistakes of physical
quantities.
Task 3. Pile weight of 100
kg is driven into the ground pile-driver, whose mass is 400 kg. Pile-driver
falls freely from a height of 5 m, and at each stroke pile descends to a depth
of 5 cm. Determine the average force of resistance of the soil.
True answer is 325
kN, students received – 405kN