Bioscience/5. Molecular biology
Candidate
of Agriculture Beyshova I.S.
The 4th year student
of Agrarian faculty of biology Mylnikova E.A.
Kostanay State University named after A.Baytursynov,
Republic of Kazakhstan
The definition fungal pathogens using the reactions of polymerization
chain mode R-time
On the territory of the Republic of
Kazakhstan, as in many other countries, Septoria especially dangerous diseases
of grain crops. The disease called mushrooms Septoria tritici and Septoria
nodorum. This disease is one of the most dangerous. In the initial stage on
leaves you notice tightened veins,then lamina edges become twisted, gradually
leaves dry up and fall off, leading to the destruction of plants. More than
other crops leaf curl subject paniculate Phlox. To overcome this disease
impossible, infected plants should be destroyed. When the disease appear on the
leaves are light orange stain spreading across the surface of leaf plate. With
the development of Septoria leaves gradually die. Septoria is widespread and
harmful disease of cereal crops. In the last 30 years, it took a firm place in
the list of economically important diseases. Weather-climatic conditions are
favorable for the development and distribution of Septoria disease, reducing
the profitability of grain production. According to the governmental order of
Republic of Kazakhstan from December 10, 2002 Godea ¹ 1295 "About approving the list of quarantine
objects and especially dangerous harmful organisms" (with changes and
additions from 23. 11. 2005), in the List of specially dangerous pests and
diseases of agricultural plants" was included in Septoria diseases of
grain crops.
The annual damage caused by pests and diseases of
agricultural crops, according to the organization of food and agriculture (FAO), is approximately 20-25% of the
potential of the world harvest of food crops. That is why, the role of plant
protection in increasing production and conservation of agricultural products
is wide [1].
Adopted in the Republic of
Kazakhstan the system of monitoring and protection of plants against especially
dangerous diseases uses imperfect methodology of field surveys with visual
diagnosis and does not cover even half of the arable land, which leads to wrong
diagnoses and reduction of profitability of grain production. There are a
number of biotic and abiotic diseases with the same signs.
Traditional methods of complex
diagnostics, including the selection of species in pure culture, selection
environments and cultivation conditions, obtaining monoporosa isolates and
microscopy are long, time-consuming and ineffective. Immune-enzyme analysis
method takes a few hours, however, developed on the basis of the methodology of
species-specific, predictive and quantification S. tritici and S. nodorum in
the leaves and seeds of wheat insensitive do not always provide a clear
identification of these species.
The introduction of express methods
of diagnostics of Septoria leaf blotch on the basis of the polymerase chain
reaction (PCR) in modifications of Real-Time lets quickly and accurately
diagnose the disease.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
compared to the ELISA technique is the more sensitive and specific, and its
modification in the format of Real Time using hybridization probe with a
fluorescent tag allows you to quickly analyze the results, without
electrophoresis. The principal feature of real-time PCR is also monitoring and
quantitative analysis of accumulation of PCR products, automatic registration
and interpretation of results. Saving of production areas, reducing the number
of staff and vostrebovannosti quantitative determination of DNA/RNA this method
in recent years has been successfully used in major diagnostic and research
centers of developed countries.
Studies of this nature are relevant
and globally, for example, in the United States of America has conducted
research on the identification and mapping of microsatellite loci from the
database EST Septoria tritici, pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola [2], a group
of scientists examined the specificity and sensitivity of PCR diagnostics
Septoria musiva, S. populicola and S. Populi [3], in China together with the
U.S. conducted research on designing PCR primers for the diagnosis of plant
pathogenic fungi. [4]
The current system of monitoring
and protection of plants against especially dangerous diseases primarily uses
techniques of field surveys with visual diagnosis of signs of disease
development, including Septoria. The first signs of infection by fungi of the
genus Septoria on plant leaves are manifested through a considerable time,
until the pathogen is in the incubation period, and diagnose the presence of
him in a seemingly healthy plant visually impossible [5].
The
aim of the scientific work is
definition and diagnosis of septoriosis crops based on the polymerase chain
reaction (PCR) using R-time.
To achieve this goal it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
-
The
selection of strains of the causative agents of Septoria leaf blotch and a
study of their basic biological properties;
-
The
testing and selection of optimal methods of DNA isolation Septoria;
-
The
obtaining of high purity DNA mushrooms Septoria;
-
The
diagnosis of Septoria PCR mode R-time.
Differentiation of
isolates Septoria cultural and morphological characteristics. Description cultural-morphological
characteristics of the isolates was performed on the 20-th (S. nodorum) and 30th
(S. tritici) day, marked the size, the
nature of the structure and color of colonies, and the intensity of sporulation
of the fungus. Most isolates of S. nodorum are developed colony with a
well-developed, porosity, woolly or velvety mycelium and different number of
pycnidia. Sometimes met isolates, whose colonies consist almost one pycnidia
and very rare mycelium. The size of colonies isolates of S. nodorum are reached
80-90 mm in diameter. For isolates of S. tritici in the early development of
the typical yeast colonies of pink, almost entirely consisting of conidia, and
looks very reminiscent of bacteria colonies; later the colonies of some
isolates become mycelial colonies, others remain yeast, but can change color.
The growth of colonies S. tritici occurred much more slowly. After a month
diameter yeast colonies was approximately 5-10 mm; diameter mycelial colonies
was 25-30 mm.
The
main morphological types of colonies isolates of S. nodorum and S. tritici are
presented in tables 1 and 2.
Table
1 - Characteristics of the colonies isolates of S. Nodorum
|
Type colony |
Morphological type |
Characteristic morphological type |
|
|
a |
Pink, granulated, mycelium rare
air, pycnidia lot. |
|
b |
Black, corrugated Yeast (I) |
|
|
c |
Black, corrugated, with pink
edging |
|
|
Dark (II) |
a |
Black, centre yeast, black;edge
of filamentous, black |
|
b |
The centre of yeast, pink; edge
black mycelial |
|
|
c |
Gray; center yeast, pink |
|
|
Mixed (II) |
d |
The centre of filamentous; the
edge of yeast, corrugated, black. |
|
- |
Brown in the middle, light on the periphery, woolly,
pycnidia lot. |
Table 2 - the Characteristic colonies isolates
of S. Tritici
|
Type colony |
Morphological type |
Characteristic morphological type |
|
|
a |
Pink, corrugated surface |
|
b |
Black, corrugated |
|
|
c |
Black,
corrugated, with pink edging |
|
|
Dark (II) |
a |
Black,
centre yeast, black;the edge of filamentous, black |
|
b |
The
centre of yeast, pink; edge black mycelial |
|
|
c |
Gray; center yeast, pink |
|
|
d |
The centre of filamentous; the
edge of yeast, corrugated, black |
|
|
e |
The
same; the edge pink |
|
|
Mixed (II) |
a |
White or gray |
|
b |
Black |
To determine the intensity of sporulation of
the fungus in a nutrient medium cork drill with known sectional area took parts
of the colony, and suffered in suitable containers (chemical beakers, flasks,
test tubes). The most convenient it was a drill with a diameter of 0.7 see as
nodorum sporulate irregularly over the area of the colony took wybicki with
Central, intermediate and peripheral parts and mixed in one sample. Wybicki
flooded precisely measured amount of water, insisted for about 1 hour, then
thoroughly mixed with a glass rod. From the colony S. tritici took one wybuchu
and immediately after sampling were determined sporulation.
The species identification of mushroom
of the genus Septoria. For species
identification mushroom of the genus Septoria were taken from areas affected
leaves, stems, and ears (pycnidia) and placed on the glass slide into a pool of
water. After a few minutes, looking through the drug at low magnification
microscope, found a way out of picospan (figure 1).


Figure 1 - Output pycnidiospores from pycnidia
and S. nodorum, b - S. tritici
In S. nodorum pycnospores came in the form of glued mucus tape, which
then falls apart into separate conidia. They are cylindrical, straight or
slightly curved, with 1 to 3 walls, the size of 12-35 x 2-4 microns. In S.
tritici conidia came out of pycnidia beam; they are filiform, straight or
slightly curved, with 3-5 unclear partitions, 35-90 x 1.8 micron.
Testing and selection
of optimal methods of DNA isolation Septoria. DNA isolation of many plant species is
considered to be a difficult task because of the high concentration of
secondary metabolites, such as polysaccharides and polyphenols, and also
because of the presence of proteins, fats and inhibitors in the samples. In
order to get purified DNA, not containing inhibiting admixtures, you must use
the most appropriate methods for selection. There are several methods to solve
this problem, also developed commercial kits. Therefore there was a necessity
of a choice of an optimum method of DNA extraction experiment.
In our research on selection of optimum
schemes of DNA extraction of cultures of mushrooms were used the following methods:
- detergent-enzyme method of using
dodecylsulfate with the subsequent extraction of phenol/chloroform;
- with application of detergent Òween - 20 and the
subsequent extraction of phenol;
- using
lyse buffer containing detergent Nonidet P-40. and with the further extraction
phenol/chloroform;
- the modified method of using the detergent
cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB).
The
first method is based on the use of enzyme proteinase K for lysis of protein
structures with further phenolic deproteinization. The second method of
extracting DNA from bacteria provides for the use as detergent Òween - 20. Òween well analyzes
the cell membrane, but weaker effect on nuclear envelope , if to consider, that in bacterial cells,
the kernel has no shell is the best option.
When
using the third and fourth methods as detergents used Nonidet P-40. and the
detergent cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB).
The
method is based on use as detergent CTAB (retitration - money bromide), well
soluble cell membrane. In addition, its use can be divided DNA and
polysaccharides, since they are different solubility in the presence of CTAB.
At high concentrations of salts (0,7M NaCl) nucleic acids form stable, but
soluble complexes with CTAB. Lowering the concentration of salt below 0,4M NaCl
is the precipitation of complexes CTAB/nucleic acid, whereas the majority of
polysaccharides remains in solution.
The main criteria when developing optimal
methods were concentration and purity of the drug.
After DNA isolation of the fungus Septoria of
the above methods was conducted qualitative and quantitative analysis of the
sample. Spectrophotometric measured the relationship between the optical
density at 260 and 280 nm. The maximum absorption for nucleic acids logged in
at a wavelength of 260 nm. DNA preparation is free from impurities with the
value of the relations E/280 1.8 and above. If the rate is lower than
specified, then the sample is contaminated protein or phenol.
DNA
samples of cultures of mushrooms, obtained with the use of detergents Nonidet
P-40 and Òween - 80, were of poor quality. The relationship
between the optical density at wavelengths 260 and 280 nm averaged 1.65-1.7,
which talked about the contamination of DNA protein and other impurities. The
obtained results showed the ineffectiveness of these methods.
The
best results were obtained in the processing of filamentous suspension
detergent - cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). Extracted DNA was observed
in the form of sludge in the bottom microtubes. DNA concentration was
determined on the spectrophotometer. Prior to the introduction into the
reaction mixture DNA extracted from fungal cultures, diluted up to 10 ng/ml.
The optical density (E/E280) obtained
DNA preparations had average 1.93±0.04 (n=4).
Thus,
research has shown that for our purposes, what is optimal is a modified method
of extraction of genomic DNA from culture mushrooms with as detergent
cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB).
Assessment of the efficiency of allocation
of DNA PCR. For confirmation of the results of the microscopy conducted
identification of isolates based on polymerase chain reaction in accordance
with the Protocol of PROIZVODITELYA.
Evaluation
of effectiveness to extract DNA from samples of biological material was
performed by means of comparison of PCR results involving DNA extracted different
ways. Parameters used for the appraisal was the level of sensitivity and
reproducibility PCR using a method of extracting DNA (figure 2).

Figure 2 - the Process of amplification in the
Real-time mode
The sensitivity of PCR is the number of
initial vegetative component in the analyzed sample. The reproducibility of the
results of PCR - positive samples from 100 studies.
The sensitivity of PCR using DNA extracted
with the help of ionic detergents, followed phenolic deproteinization somewhat
lower, which testifies to the incomplete removal of inhibitors. The sensitivity
of the methods based on the use of CTAB as detergent much higher and the same
for all methods of allocation plant DNA (figure 3.4).
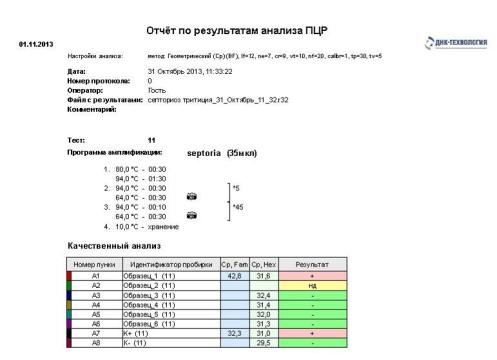
Figure 3 - the Report on the results of the
analysis of PCR
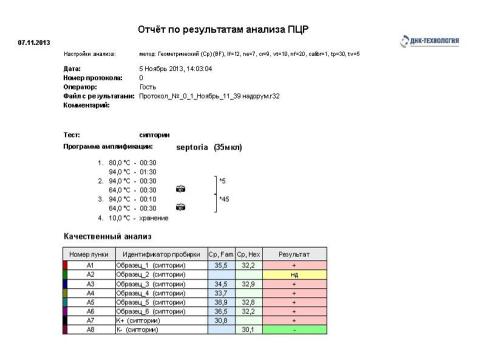
Figure 4 - report on the results of the
analysis of PCR
Thus the introduction of
Septoria rapid diagnostic methods based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in
Real-Time modification will allow to quickly and accurately diagnose the
disease.
References:
1.
I. M. Polyakov, E. M. Shumakov, article
"Protection of plants" Big Soviet encyclopedia. - M: Soviet
encyclopedia. 1969-1978
2.
Stephen B. Goodwin, Theo A.J. van der Lee,
Jessica R. Cavaletto, Bas te Lintel Hekkert, Charles F. Crane, Gert H.J. Kema,
Identification and genetic mapping of highly polymorphic microsatellite loci
from an EST database of the septoria tritici blotch pathogen Mycosphaerella
graminicola /Fungal Genetics and Biology, Volume 44, Issue 5, May 2007, Pages,
398-414.
3.
Nicolas Feau, Jerry E. Weiland, Glen R.
Stanosz, Louis Bernier, Specific and sensitive PCR-based detection of Septoria
musiva, S. populicola and S. populi the causes of leaf spot and stem canker on
poplars/Mycological Research, Volume 109, Issue 9, September 2005, Pages
1015-1028.
4.
Zhonghua Ma, Themis J. Michailides,
Approaches for eliminating PCR inhibitors and designing PCR primers for the
detection of phytopathogenic fungi/ Crop Protection, Volume 26, Issue 2,
February 2007, Pages 145-161
5.
Fraaije B. A. - Hollomon, D. W. 1997. Novel
DNA diagnostic technology in plant disease control using Septoria tritici as a
model. In: Project report no. 245, IACR-Long Ashton Research Station, Bristol,
1997, 27 p.