PhD, associate professor Mahanbetalieva
Kamshat Torgaybaevna1, master
of technical sciences Tashmukhamedov Farkhad2
Tasks of the modern process of winding yarn
M.Kh Dulaty Taraz State University, Kazakhstan
The process of winding the textile yarn on a package at the body in the
form of rotation involves in two interrelated processes: the process of winding
yarn with a spinning (torsion) and packing process of filament coiled winding
on a package at (coils, coil bobbin tubular space, spool, etc ).
In order to increase the quality of the winding becomes very
essential question, related to the creation of new specialized equipment, to
form a winding packing with predetermined properties.
Work in this area started at the
beginning last century, was continued a number of domestic and foreign authors.
Initially, the greatest contribution to the development of the theory of
winding yarn on the package made by the scientists spinners as N.A. Vasiliev, I.I. Babarykov, S.S Kovner,
V.A. Voroshilov, E.I Krzhyzhanovski, U.I Vinogradov and others. This was due to
the fact that the roving, spinning and twisting machines required to ensure
that the speed of winding yarn or twine is strictly equal to the rate of
release of the product from the drafting
system. In addition it was necessary to get a package at a certain shape and
structure ( for example, roving coil ends, must be chamfered and closeness
parallel winding, winding from the spinning machine must be carried out on a
cone, moving upward as winding cop).
In all the above works was identified
traverse motions (dots layout- carriage
ring rail) and winding point ( points
of crowding or entry point into a package). At the end of circumstances led to
errors in the design of winding mechanism and unsatisfactory of quality winding roving, spinning and torsion
package irregular shape coiling and ears, lack of equilibrium winding etc.
First remark was mismatch
movements of crowding yarn points on the package did I.S. Myasnikov. In this work,
devoted to the study of winding yarn on a spinning machine batch, it is noted
that the thread during winding is tangential to the helix, and not normal to
the axis of the spindle. We conclude, that the scale of the movements must be
greater that the height of the cone winding, from the point moves along the
winding bobbins not like the layout point. Then I.S Myasnikov with certainly
notes that as a result of mismatched point motion and winding yarn guide eyelet
can not get end portions of packing a given structure.
In more details on this issue was
investigated by G.K Moiseev [1], who used the technique of V.A. Bluer, that researched the form transitional spiral thread
and bobbin winding density. Part of the equation transition coil was not found,
but the dependence between the height H winding
thread guide and scope HH:
![]() (1)
(1)
where λ- the free length of the thread between the
point and the point of the winding
layout;
ϑí- the speed
movement of the filament in the axial direction of the packing;
ϑî - speed winding.
The theory of spinning bobbin winding mostly
developed by A.F.Proshkov. Exactly, he developed the theory of the work
of designing mechanisms for winding
roving, spinning and twisting machines based on the constancy of the speed of
winding, free winding interval filaments and, the most important, the
conditions of equilibrium winding obtained by prof. A.P. Minakov [2].
A.F.
Proshkov derived a general equation in differential form if winding [3].
![]()
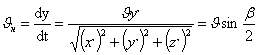 (2)
(2)
where
ϑí - the velocity of the wire in
clash of the body winding;
x;y;z- coordinate of the point on the yarn package at crowding (where the y
axis is directed along the rotation packing);
β - crossing wind
turns.
Using the above formula, A.F. Proshkov determined that regularity can
move the winding, pitch wind and pitch of axis
package of various shapes.
Professor A.P. Minakov gave
conditions for obtaining equilibrium winding in which the coils do not fall
from the surface of the packing it is wound. The first (and main) condition for
the equilibrium is winding forms on the surface coil winding, it has the form:
tgӨ≤ μ (3)
where Ө- geodesic deviation winding turn;
μ- the coefficient of fiction the surface coil winding.
Geodesic
deviation winding depends mainly in crossing turns and taper winding of
packing.
![]() (4)
(4)
where
R- radius of the winding current
packing;
β-
current crossing wind turn;
At
the constant rates of the yarn guide and the corner velocity of rotation of the
packing:
![]() (5)
(5)
where -the taper angle of
packing.
Condition
thread tension
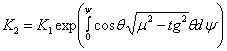 , (6)
, (6)
where
K1 and K2- vanishing tension and turn upwind branches;
ψ –
the angle of coil winding.
Using theoretical developments of
G.K.Moiseev and A.P.Minakov, professor A.F.Proshkov decided a number of issues
in designing winding mechanisms for optimal bobbins shape and structure (packages with the faces of a predetermined shape and having a stable
equilibrium). However, of the
fundamental equation winding he made some inaccuracy, assuming that the point
of winding all the time moves on forming the package. This inaccuracy noticed E.D.
Efremov and to eliminate the mistakes brought the so- called kinematic
equations winding [4], some are as follows:
![]()
![]() (7)
(7)
where γ – the corner between the perpendicular dropped from the
point of winding axle oz, and the
plane xoy;
![]() - length of the perpendicular from the
point of pickup to the axis of rotation of packing oz;
- length of the perpendicular from the
point of pickup to the axis of rotation of packing oz;
X and Y – coordinates of the
current layout – the corner between perpendicular, dropped from a point on the
layout axis OZ, and the XOY plane;
ƒ=
R +(Z- z)R’ – auxiliary function.
R- current winding radius of packing, depends on z;
Z- current applicate point layout;
z- winding current applicate point;
ω- angular speed of the pakage.
Thus, from the A.F. Proshkov, E.D. Efremov the axis of rotation of the
packing took no axis OY , and the
axis OZ of the first equation, and
its practically introduced the concept of the line winding on which entry point
and moves winding filament. Obviously,
if γ-const for the entire course
of the movement of the yarn guide, the line coincides with the generator
winding packing.
Kinematic equation of the
coordinates of points tied winding layout and crowding. Calculations, carried
out by the formulas E.D. Efraim (eg speed winding yarn on the package, the
crossing angle turns, etc.) give more accurate results ( 2-3% different from
the results obtained from the formulas of A.F. Proshkov).
Using the kinematic equation winding
, E.D. Efremov found a more general solution made by G.S. Janitor, V.A. Blyuer
and A.F.Proshkov on the definition of the laws of winding yarn on the package
after the sudden stop of the yarn guide.
All these major theoretical
developments undertaken by N.A. Vasiliev,
I.S.
Myasnikov, V.A. Blyuer, G.K. Moiseev, A.P. Minakov, A.F. Proshkov, E.D.Efremov
and others aimed at finding ways to
stabilize the winding speed, obtaining optimal (not heavily compacted and
beveled)ends packages and creating equilibrium coils. However, the establishing
of high- speed textile production of
crossmotal machines has set theorists
winding yarn, a number of new tasks that require their immediate solutions.
First, the wounding on different spools these machines lack a specific density
of winding, uneven and f importantly in axial and radial direction of the
package.
Secondly, there was sever abrasion of
the wound yarn drum, resulting in loss of its strength properties.
Thirdly, under certain winding
diameter disrupted by dispersion of surface coils, and the packing was observed
the formation of bundles.
Fourth, in some cases, there were
rallies turns on the ends of the wound bobbin.
Fifthly,
there is squeezing turns on the ends of the spool and the corrugations formed.
Literature:
1. Moiseev G.K. Investigation of cross- wound on a cylindrical bobbin on
continuous production process of viscose fiber. Ph.D., Dissertation St. Peterburg.
1958.
2. Minakov A.P. Basis of the theory of winding and unwinding of the thread.
M//Textile industry.- 1994.¹ 10.s11. ¹11-12 p 10.
3. Proshkov A.F. Investigation of the processes associated with the
filament winding and winding design mechanisms. D.t.s. Dissertation. M. 1965.
4. Efremov E.D Basics of the theory of winding yarn on the
package.M.Legpisheprom. 1982.
5. Pannin I.V. Development and research of textile structures packages for
special purposes. Ph.D.,
Dissertation. M. 1996.