Экономические науки/13. Региональная экономика
Postgraduate student Malakshinova Margarita I.
East Siberian State University of
Technology and Management, Ulan-Ude.
THE PROBLEM OF UNEVEN REGIONAL ECONOMIC
DEVELOPMENT UNDER MODERN CONDITIONS
Abstract: This article deal with basic concepts in the
process of uneven development of economic space in the regional economy of
Russia. The basic characteristics of the economic space, connected with the
unevenness of its development and factors contributing to spatial smoothing of
uneven regional development are discussed in the paper.
Keywords: economic space, socio-economic unevenness,
the region's economy and development, uneven development.
In modern
conditions integration of Russian into world economic community is growing
steadily. Uneven economic development predetermined characteristics for its
periods of ups and downs.
Heterogeneity of the Russian
economic space in the process of transition from a planned to a market economy
has significantly increased. In the territorial aspect uneven economic
development of Russia is due to the following factors:
- Availability of
natural resources in the region,
- Infrastructure,
- Climatic conditions,
- The mentality
of the population,
- The degree of
economic isolation.
Differentiation processes of
socio-economic development of certain territorial entities are proved by
dynamics of basic socio-economic indicators.
One of the reasons for the uneven
development of Russian regions is excessive centralization of power and lack of
local financial authority.
Fig.1. Dynamics of gross regional product in the federal districts of
Russian Federation , 2002-2012
(gross value added at basic prices)
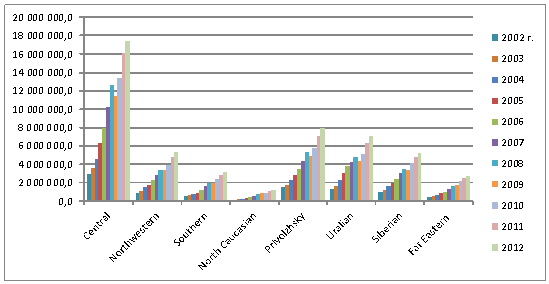
For example the Central Federal
District, which is home to more than a quarter of the population, is the most
economically developed region in Russia. Its average per capita income and
expenditure exceed the national figures by almost 30%; the region accounts for
36% of GRP. The per capita expenditure figures for the Siberian Federal District
were 79% of the Russian Federation, which is less than half the performance of Central
Federal District in 2012.
So, GRP (gross
regional product) can be considered the main indicator of economic development
of the region.
Dynamics of gross regional product
in the last decade shows that the most rapidly developing are the Volga and the
Urals Federal Districts in which, then have highly developed production and
large reserves of minerals. Slow developing are the Far Eastern and the
Southern Federal Districts (The North Caucasian District included). Despite
significant income and expenditure differentiation of regions, the rate of
investment in fixed assets was the lowest in the Far Eastern Federal District (7%),
as compared to the average 12% across the Russian Federation.
According to expert estimates the
regional coefficient of variation of GRP increased for the period 1998 to 2012 by
1.45 times. This suggests that changes in per capita GRP for the period
increased noticeably. A GRP growth rate is markedly higher in the Central, the
Volga Region, the North- Western Federal District and the Urals; this index is
much lower in the Siberian and the Far Eastern and the Southern Districts.
The Republic of Buryatia GRP is 3.2
% of that of the Siberian Federal District. The Republic of Buryatia is behind
the center of the Siberian Federal District Novosibirsk region by 20%, the
Krasnoyarsk region by almost 30%.
Thus, in modern conditions to solve
the problem of uneven economic development of the regions is to turn the areas
into economically self-governing territories. This would entail the growth of
responsibility of regional authorities for economic and social consequences of
their work.
So, the priorities for the
administrative operations should be as follows:
- Aligning the parameters of quality
of life in urban and rural areas;
- Focusing on symmetrical social and
economic development in specialized regions characterized by extreme
environmental conditions;
- Improving the efficiency of the
management of regional economic regulators in socio-economic systems;
- Strengthening cooperation between
business and government due to the diffusion of innovations in management.
Setting these priorities would
promote the model of balanced socio-economic development of the regions.
Literature:
1. Alexander Granberg Fundamentals of the regional economy. - M. Publ HSE,
2007; Nesterov MP, Nesterov AP Regional economy. - Moscow: Unity - Dana, 2009;
2. Golchenko, V. Ozerov , PV Managing the development of the region : transformational
economic aspect / / Electronic scientific journal Wax . 2011. - № 9
3. Bagautdinova NG, Gafurov IR Changing the configuration of economic
space in the region, based on the potential of industrial areas / / Russian
Entrepreneurship. 2012. - № 2 (200). - P.166 -171.
4. Zinoviev, AA Problems smoothing spatial polarization in the regional
economy / / Problems of the modern economy. 2011. - № 4. - P.40.