Assoc.
Prof. V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, graduate
student A.A. Korchinskiy,
student A.S. Moskalenko,
student T.S. Kirichenco
Estimation of the influence of impurities on the
conditions of
Concentration of liquids by freezing
Concentration by
the freezing out method of moisture is used for obtaining the high-quality
liquid concentrates due to the application of temperatures lower than
With the
concentration the frozen out water is moved away from the solution until are
formed the high-purity crystals of ice, which then are separated from the
concentrated liquid phase.
The analysis of the
basic types of the substances of the dissoluble and undissolved
nature is the most important stage before the designation of the corresponding
technological regimes of working the food or biological liquid before its
sub-zero treatment for the purpose of obtaining concentrate. Furthermore, the
nature of admixtures has the most important effect on the final state of liquid
after its concentration.
Three basic stages
of crystallization are present in all types of the freezing out installations,
namely: the over-saturation of solution, formation of nucleus and an increase
in the ice crystals. After these three stages ice crystals can undergo other
processes, such as exhaustion, the agglomeration and ripening. These last three
processes compulsorily do not occur with freezing of ice, but they can be used
in order to obtain the necessary properties of the crystals of ice, for
example, their size and form for the subsequent best separation of ice and
concentrated solution.
Crystallization
occurs with the presence of a sufficient motive power; therefore the
over-saturation of stock solution is required. This state, when solution is not
located in the equilibrium and is a difference in the chemical potential
between the phase of solution and the solid crystalline phase.
With freezing of
ice, is created the solution, oversaturated by water. After the primary nuclei
of the crystals of ice were formed, the supersaturating of solution decreases.
Ice crystals are formed, until the difference in the chemical potential
decreases to saturation state.
With a crystalline
increase in the nucleus they are converted into the crystals by the addition of
molecules from the oversaturated solution. This process consists of three
stages: mass transfer by the diffusion of molecules from the volume of the
solution through the boundary layer around the nucleus, the association of molecules
into the surface and simultaneous heat transfer from the crystal to the volume
of solution, heat, necessary for the phase transition. Depending on the type of
the freezing out installation and utilized solution, any of three stages can
limit the rate of increase in the crystals of ice.
If crystal is
subjected to action, the part of the crystal can be broken, which is called
exhaustion. Stresses can be caused by collisions with other solid particles,
the type of other crystals, walls, by the elements of mixer and by circulating
pumps. Crystalline fragments form product nuclei.
Exhaustion occurs
under the effect of several factors. With the destruction of crystals with the
rough surface will appear more fragments, than with the destruction of crystals
with the smooth surface. In some types of the freezing out installations the
exhaustion serves for the decrease of size of ice crystals.
Agglomeration – the
process, in which the crystals encounter and stick to each other, and, in the
final analysis, form larger crystal and total accumulation.
Agglomeration is –
the side effect, which can occur in the freezing out installations in the
process of concentration and is not used not in order to govern the sizes of
ice crystals.
The distribution of
the size of the crystals, scattered in the saturated solution, can change
because of the ripening. Ripening is - the effect of difference in the
solubility between the small and large crystals. Smaller crystals have a
tendency to be decomposed, and then the obtained solution is based on the large
crystals.
Admixtures are
divided into those dissolved and not dissolved. Solutes, such as salts, sugar
and glycols are their kind depressors, since they reduce the temperature of the
crystallization of solution. Solid admixtures – these are the undisclosed
particles, they call them additives. Additives and depressors exert different
influence on the process of obtaining ice with the freezing. In this case the
concentration and the form of depressor in the mixture influences the thermo
physical characteristics of the process of freezing.
The phase state of substance i characterize the beginning of the appearance of crystals
of ice in the mixture, respectively substance concentration can be calculated
according to the formula
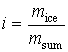 , (1)
, (1)
where mice – the mass of frozen out
ice, kg; msum
– the overall mass of frozen out ice and concentrated product, kg.
In the initial state with the point of the beginning of freezing i, the
concentration xi can be found from the formula:
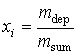 , (2)
, (2)
where mdep – the mass of the
solution in the state of concentration, kg.
In
the final state solution xf
concentration f is expressed:
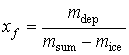 . (3)
. (3)
Of
the equations given above, the relation (1) and concentrations can be expressed
by the following equation:
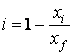 (4)
(4)
The dissoluble
admixtures depending on chemical composition are subdivided into the inorganic
- mineral salts, the bases, and also the acids and organic, number of which
includes water-soluble clean connections, amino acids, highest alcohols,
polysaccharides. In this case cryoscopic
characteristics directly depend on the complex of the connections in the
solution indicated. It is also noted, that on a decrease in the krioskopiseskoy temperature of the solution in the larger
degree have an effect the inorganic connections in the solution and lowest
alcohols, and smallest polysaccharides and dissoluble proteins.
To an increase in
the effectiveness in the regulation of an increase in the crystals of ice in
the solutions and the obstructions “of the adhesion” of it on the heat exchange
surface contribute different additives – this, in essence, the fine dispersed
solid particles of the cellular structure of fruits and vegetables, which can
serve as the crystallization centers in the process of ice formation. Their
application also makes it possible to regulate the mass concentration of ice in
the mixture. However, the presence of solid admixtures in the solution,
subjected concentration by freezing moisture contributes to an increase in the
soluble-matter losses substances of concentrate, which are seized during the
agglomeration by the crystals of ice due to from the adsorption in the laminar sublayer, which surrounds the particle of additive.
Literature
1.
Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Study of
the process of freezing moisture from the extracts of the endocrine and special
raw material. Diss. cand.
tech. the sciences.
2.
Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyev Ya.I. Kinetics of the process of concentration by freezing
the cherry juice. Herald of the
3. Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Optimum regimes
of the concentration of the plasma of the blood by freezing. Meat industry.
2012. ¹ 1. S. 65-68.
4. Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyeva Ya.I., Bostynets N.I. Concentration of apple juice in the drum
freezing out installation. Storage and processing agricultural 2014. ¹ 4. pp.
41-44.
5.
Antipov S.T., Dobromirov V.E., Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Heat- and mass
exchange with the concentration of liquid media by freezing.
6. Methods of
comparison and evaluation of refrigeration plants concentration by freezing
moisture. Ovsyannicov V.Yu.,
Kraminova Yu.S., Kirichenko T.S., Moskalenko A.S. Perspektywiczne opacowania sa nauka I technikami
-2015. Materialy XI Miedzynarodwei
naukowi-praktycznej conferencij.