Assoc. Prof. V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, Assoc. Prof. S.L. Panchenko, graduate student
Yu.S. Kraminova, student A.S. Moskalenko, student T.S. Kirichenko
Voronezh State University of Engineering Technologies, Russia
Features concentrating cheese whey freeze
In this paper, a study of the process of refrigeration concentration cheese whey freeze moisture using a screw mold design. Separation of ice and concentrated cheese whey was produced using a laboratory centrifuge.
During the research process, freeze concentration of moisture
cheese whey starting temperature was controlled serum values ranged boiling
temperature of the refrigerant in the heat exchange crystallizer jacket, screw
speed and the initial solids content of the original product to be concentrated
[1].
Process refrigeration freeze concentration moisture cheese whey was carried out at boiling temperature change of refrigerant in the evaporator jacket t from minus 20.0 to minus 10,0 ° C, the screw rate of rotation n of the mold from 0.06 to 0.18 sec-1, initial dry content EHV substances in cheese whey was varied in the range of 6.3 to 16.3 % .
According to research results according to the multiplicity of graphic concentration cheese whey were constructed (Fig. 1.) and the specific energy costs of refrigeration concentration (Fig. 2.).
Analysis of the graphs showed that with the increase in the value of the boiling point of the refrigerant concentration multiplicity decreases monotonically. Increasing the solids content in the original serum and increasing the screw speed also causes a decrease in the value of the concentration ratio.From the analysis depending on the multiplicity of the concentration of the solids content of the starting material can be seen that the increase in dry matter content in the original serum reduces the degree of condensation, characterized by the value of the concentration ratio. This is due to the fact that with increasing solids content in the original serum values causes an increase in heat and mass transfer resistance , thereby slowing the passage of moisture in the solid state, which requires more time and energy consumption for freezing it [2].
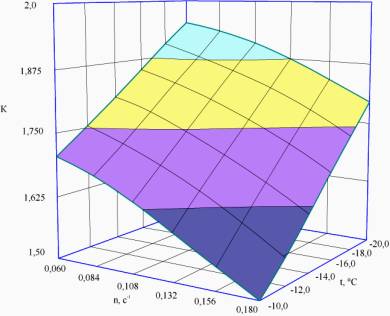
Fig. 1. Dependence multiplicity by
concentrating the cheese whey at an initial solids content
EHV = 7.3 % of the boiling crystallizer
speed n, s-1 and temperature of the refrigerant screw
t, °C in the jacket of the
crystallizer
Increasing the refrigerant boiling temperature in the heat exchange jacket mold causes displacement curves in the charts in the direction of decreasing concentration ratio. At constant solids content in the initial product and the boiling point of the refrigerant quantity multiplicity concentration decreases with increasing screw speed crystallizer.
The dependence of the specific energy consumption by concentrating the freeze is not linear, and rises when the temperature of the refrigerant in the boiling heat exchange jacket that naturally associated with increased thermal load on the chiller and proportional energy consumption.Depending on the specific analysis of the frequency of the input energy of rotation of the screw can be concluded that an increase in frequency of rotation of the screw mold monotone nonlinear energy costs are reduced by reducing the load on the screw drive, the transporting fewer frozen ice and reduce the discharge refrigeration unit heats water of crystallization.
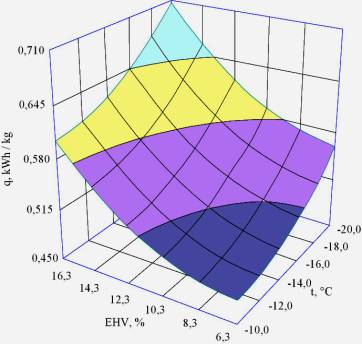
Fig. 2. Dependence of the specific energy consumption for refrigeration concentrationcheese whey at a frequency of rotation of the mold n = 0,152 with screw - on-1initial solids content in cheese whey EHV % and temperaturemold wall t, °C
Increased costs for energy
concentration observed in the case of increasing the initial solids content in
the original serum, due to the need to create additional serum hypothermia due
to decreasing heat capacity and decreasing cryoscopy temperature more
concentrated serum.
Literature
1. Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu.,
Kondratyeva Ya.I. Kinetics of the process of concentration by freezing the
cherry juice. Vestnik Voronezhskogo gosudarstvennogo
universiteta inzhenernyh tehnologij [Herald of the Voronezh state
university of the engineering technologies]. 2014, ¹ 4 pp. 44-48. (In Russian).
2. Antipov S.T., Dobromirov V.E.,
Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Teplo- i massoobmen pri koncentrirovanii zhidkix sred
vymorazhivaniem [Heat- and mass exchange with the concentration of liquid media
by freezing]. Voronezh. State. tech. Acad. Voronezh, 2004. 208 p. (In Russ.).