Agriculture 4. Technologies of storage and processing
of agricultural products
Assoc. Prof. V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, student A.N. Denezhnaja,
student T.S. Kirichenko, student Yu.S. Kraminova
Voronezh State University of Engineering Technologies,
Russia
The design of the tubular section of
the mold for
the concentration of liquids freeze
The use
of modern methods of concentrating liquid food environments based on advanced
science and technology creates favorable prospects for high quality
concentrates in the processing of large volumes of fruit enough raw materials
with minimum labor costs. Expansion of production of natural and concentrated
juices, extracts of tea, coffee, production of elite wines thickening enzyme
solutions, blood plasma, preparations of extracts from the organs of
slaughtered animals and other liquid media food and biological applications on
large highly mechanized enterprises is only feasible through the introduction
of new high-performance, energy-efficient appliances and advanced technology,
one of which is the concentration of liquid food media freeze.
Concentration
of food and biological media by freezing moisture provides the most complete
preservation of the chemical composition and properties of substances in the
concentrated product. At the same time, this process involves the allocation of
water in the form of ice at temperatures below the crystallization of pure
water, which is especially important in the case of production of concentrated
fruit and vegetable juices of high quality products for children and dietary
food, with energy costs of the process are comparable to traditional methods of
concentrating the membrane and a vacuum evaporation method [1].
Processes
concentrating food liquids by concentrating refrigeration especially
appropriate in cases where the mixture contains components shared extremely
unstable even in a slight increase in temperature, which include primarily
amino acids such as lysine, tryptophan and cysteine, which undergo significant
structural changes in the molecular chain, even at temperatures of the vacuum
evaporation, the components of the order of 333 ... 343 K, sugar, coloring and flavoring.
By increasing productivity and reducing heat and mass
transfer equipment energy consumption for processing of liquid food and
biological materials is the creation and implementation of effective
technological equipment with low specific energy and materials having a high
impact on the environment to be treated. This requires new engineering
teplomassoobmennyh equipment using intensive methods effect on work environment
created on the basis of advanced engineering - technical research [2].
In
plants the concentration of liquid foods freeze moisture exploit different
types of molds, different features work, structural design and surface area of
cooling. [3 – 5].
Multi-system
concentration of liquid products involve the use of several steps, the first of
which is an intensive nucleation, then provide the conditions for their growth
and consolidation, followed by separation of ice and concentrated solution.
Typically, nucleating requires intensive cooling and mechanical action, so are
used for this purpose scraper with the tubular molds mixing devices of various
designs.
In such crystallizers "pipe in pipe" by moving the inner pipe
is cooled by liquid product from which crystallizes in the form of ice water,
and the annulus moves counter currently low temperature refrigerant or
refrigerant boils.
Section crystallizer "pipe in pipe" (Fig. 1) consists of an
outer tube 1 and inner tube 2 of smaller diameter inserted into each other.
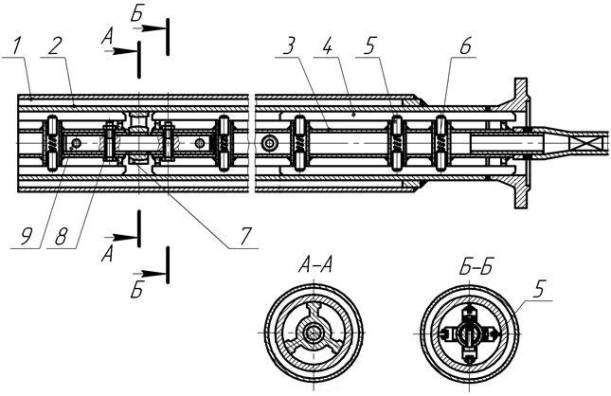
Fig. 1. An element of the mold section:
1 - the outer tube; 2 - the case of the inner tube; 3
- shaft; 4 - scraper;
5 - finger; 6 - spring; 7 - the slide bearing; 8 - a
bolt; 9 - pin
The internal tube to remove the ice deposited on the wall of the hollow
shaft 3 is mounted with scrapers 4. Crystallizer’s high performance due to the
considerable length of the pipe shaft may be made of separate parts. Separate
link shaft is a tube 3 with welded into it cylindrical sleeves to install
scrubbers 4. The links connect the shaft insertion rod bolts 8 and 9.
Scraper fingers inserted into the grooves 5 and can be
welded thereto. Fingers free entry to the cylindrical shaft sleeve and bursting
springs 6. This creates the possibility of moving the scraper in the radial
direction. The scrapers are arranged in pairs on the shaft at a 90º angle
relative to one another. Each scraper has three spring-loaded supports, and
each scraping device several pairs of scrapers.
Shaft mounted inside the tube in bearings 7. The front
ends of the shaft coming out of the doubles sealed Gland. The difference
between the thermal expansion of inner and outer tubes perceived wavy (lens)
compensators. Drive shafts made engine - gearbox through the drive sprocket.
A driven sprocket mounted on the drive shaft of the
scraping device. For torque transmission is used duplex chain drive. The outer
tube is also connected through a common adapter stamped coil.
Outside the housing unit in any link of the drive
(gear, clutch) provide for the safety pin, which is cut off when excessive
force arising from the binding or other malfunctions in the scraping device. As
a result, the scraper device is disconnected one pipe while the other continues
to operate.
It should be noted a number of positive features
inherent in the developed design section of the mold for freezing liquids.
Production and execution of individual sections of
parts and does not require sophisticated equipment and technical accessories.
The construction of the section of the mold is simple in design and reliable in
operation. Maintenance is easy enough and is not intended to attract highly
qualified staff.
Control and regulation of the amount of ice in the
frozen section may be implemented as a change in the heat load on the liquid
medium to be treated and mode of mixing and purging the internal cylindrical
surface of the frozen layer of ice consumption of starting material fed to the
concentration and duration of exposure under continuous stirring mixture of ice
and concentrate section.
The use of such structures will significantly simplify
the design scraping mold used for the separation of liquid products by
freezing.
Ëèòåðàòóðà
1. L.
Pap Freeze concentration. Translation. with Hungarian, edited by O.G.
Komyakova. - M.: Light and Food Industry, 1982. - 97 p.
2. Ovsyannikov
V.Yu. Study of the process of freezing moisture from the extracts of the
endocrine and special raw material. Diss. cand. tech. the sciences. Voronezh.
State. tech. Acad., 2003. 184 p.
3. Patent 2221202 (Russian Federation), MKI 7 F 25 C 1/14 Crystallizer
for continuous freezing and teachings of flake ice. / S.T. Antipov, V.Yu.
Ovsyannikov, A.N. Ryazanov. – Zayavl. – 01.11.2001, ¹ 2001129629/13, opubl. v
B.I., 2003, ¹ 17.
4.
Patent 2206839 (Russian Federation), MKI 7 F 25 C 1/14 Apparatus for freezing
and getting flake ice. / S.T. Antipov, V.Yu. Ovsyannikov,
A.N. Ryazanov. – Zayavl. –
01.11.2001, ¹ 2001129629/13, opubl. v B.I., 2003, ¹ 17.
5.
Patent 2220385 (Russian Federation), MKI 7 F 25 C 1/14 Apparatus for producing
flake ice. / S.T. Antipov, V.Yu. Ovsyannikov,
A.N. Ryazanov. – Zayavl. –
05.04.2002, ¹ 200210877/3, opubl. v B.I., 2003, ¹ 36.