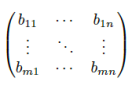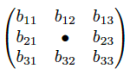2 simple methods to find broken in the set of ibeacons Akylbek Mnazhatdinov Kazakh British Technical University, Almaty, Kazakhstan amnazhatdinov@gmail.com Ibeacon.
Working principle. What
is iBeacon? Ibeacon
utilizes Bluetooth technology which allows Mobile Apps (running on both iOS and
Android devices) to listen for signals from beacons in the physical world and
react accordingly. In essence, iBeacon technology allows Mobile Apps to
understand their position on a micro-local scale, and deliver hyper-contextual
content to users based on location. The underlying communication technology is
Bluetooth Low Energy. [3] What
is Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)? Bluetooth
Low Energy is a wireless personal area network technology used for transmitting
data over short distances. As the name implies, it's designed for low energy
consumption and cost, while maintaining a communication range similar to that
of its predecessor, Classic Bluetooth. [2] How
is BLE different from Regular Bluetooth? -
Power Consumption: Bluetooth LE, as the name hints, has low energy
requirements. It can last up to 3 years on a single coin cell battery. - Lower Cost: BLE is 60-80% cheaper than traditional
Bluetooth. -
Application: BLE is
ideal for simple applications requiring small periodic transfers of data.
Classic Bluetooth is preferred for more complex applications requiring
consistent communication and more data throughput. How
does iBeacon use BLE communication? With iBeacon,
Apple has standardized the format for BLE Advertising. Under this format, an
advertising packet consists of four main pieces of information[1].UUID:
This is a 16 byte string used to differentiate a large group of related
beacons. For example, if Adidas company maintained a network of beacons in a
chain of clothes stores, all Adidas beacons would share the same UUID. This
allows Adidas' dedicated smartphone app to know which beacon advertisements
come from Adidas-owned beacons. Major: This is a 2 byte string
used to distinguish a smaller subset of beacons within the larger group. For
example, if Adidas had four beacons in a particular clothes store, all four
would have the same Major. This allows Adidas to know exactly which store its
customer is in. Minor:
This is a 2 byte string meant to identify individual beacons. Keeping with the Adidas example, a beacon at the front of the store
would have its own unique Minor. This allows Adidas' dedicated app to know
exactly where the customer is in the store. Tx Power: This is used to determine
proximity (distance) from the beacon. How does this work? TX power is defined
as the strength of the signal exactly 1 meter from the device. This has to be
calibrated and hardcoded in advance. Devices can then use this as a baseline to
give a rough distance estimate. Example: A beacon broadcasts the following packet
UUID: 1122334455667 Major:
2 Minor: 1 A device receiving this packet
would understand it's from the Adidas Beacon (UUID) in the Target on 2-nd
Street (Major) at the front of the store (Minor). 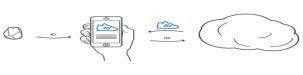 Figure
1: Working principle of Ibeacon Ibeacon problem.
Determination of broken beacon Main
problems of beacon The
advertising interval is the second important parameter for the radio module.
This defines how frequently radio signals are broadcast. Beacons can be thought
of as tiny lighthouses, intermittently flashing information into the
surrounding area. The more frequent the ashes, the greater the chance a
receiver will see them. Of course, beacons can be set to broadcast all the
time, but that requires a lot of energy and dramatically reduces the battery
life. This table (Figure 3) indicates typical beacon life expectations for new
CR2450 battery depending on power and advertising interval settings. As you see
on Figure 3, battery life durations of beacons are different and depend on some
parameters. This information on the table is only expected and is not static.
As we mentioned above, beacon's range is affected by many obstacles such as
walls, furniture or people. This may be cause of lowing battery very fast. And
we can see that the main problem of beacon is its battery. The
corpus of beacon is plastic and it is fragile. That is another problem. If
people accidentally touch it, it may be broken. Also temperature and pressurecondition can affect to beacon.There
are many crashing causes, and defining process of broken beacon is problematic.
For example, medium type stores need 2000-5000 beacons to cover all products.
They will crash at different time, so we cannot predict specific date of
crashing or lowing the battery of beacon.
Figure
1: Working principle of Ibeacon Ibeacon problem.
Determination of broken beacon Main
problems of beacon The
advertising interval is the second important parameter for the radio module.
This defines how frequently radio signals are broadcast. Beacons can be thought
of as tiny lighthouses, intermittently flashing information into the
surrounding area. The more frequent the ashes, the greater the chance a
receiver will see them. Of course, beacons can be set to broadcast all the
time, but that requires a lot of energy and dramatically reduces the battery
life. This table (Figure 3) indicates typical beacon life expectations for new
CR2450 battery depending on power and advertising interval settings. As you see
on Figure 3, battery life durations of beacons are different and depend on some
parameters. This information on the table is only expected and is not static.
As we mentioned above, beacon's range is affected by many obstacles such as
walls, furniture or people. This may be cause of lowing battery very fast. And
we can see that the main problem of beacon is its battery. The
corpus of beacon is plastic and it is fragile. That is another problem. If
people accidentally touch it, it may be broken. Also temperature and pressurecondition can affect to beacon.There
are many crashing causes, and defining process of broken beacon is problematic.
For example, medium type stores need 2000-5000 beacons to cover all products.
They will crash at different time, so we cannot predict specific date of
crashing or lowing the battery of beacon.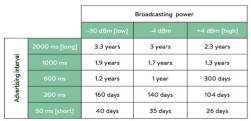 Figure
2: Broadcasting power
Figure
2: Broadcasting power
Determination
of broken beacon. Linear trajectory method. As we mentioned above, normal distance
for getting signal well is 3-5 meters. And most of stores try to keep this
distance between two neighboring beacons. It allows to know the client's
location and show appropriate information. If beacons are located in linear
way, we can de ne broken beacon by "linear trajectory method". The linear trajectory method's
working principle depends on client's path. First of all, we create service
that will show map of the beacons (Figure 4). When client enter to range of the
beacon, application installed on smartphone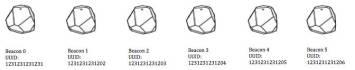 Figure
4: Linear map of beacons will send request with UUID of beacon to the
server, and server de ne which beacon got signal and where client is now. After
getting the signal server service tracks it and draws trajectory of client
(Figure 5)
Figure
4: Linear map of beacons will send request with UUID of beacon to the
server, and server de ne which beacon got signal and where client is now. After
getting the signal server service tracks it and draws trajectory of client
(Figure 5)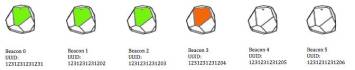 Figure
5: The path of the client. The last signal was received from beacon 3 If the trajectory of client
splits, system will track UUID of beacons which are located between the last
and the previous beacon (Figure 6). As we see on Figure 6, trajectory of the
device jumped from beacon 1 to beacon 4, it means that beacons 2 and 3 are
broken.
Figure
5: The path of the client. The last signal was received from beacon 3 If the trajectory of client
splits, system will track UUID of beacons which are located between the last
and the previous beacon (Figure 6). As we see on Figure 6, trajectory of the
device jumped from beacon 1 to beacon 4, it means that beacons 2 and 3 are
broken.  System tracks only broken beacon's UUID. And there device causes may affect.
For example, client may switched o the phone near the beacon 1 and turn it on
near the beacon 4. In this situation system will insert to table 2-nd and 3-rd
beacons. However, this is not problem. After each iteration, when system
receives signal from device, it will retrieve data from the table of broken
beacons, and compare with received UUID, if the table contains same UUID it
will be removed Figure 6: The path of the client when some of the
beacons crashed
System tracks only broken beacon's UUID. And there device causes may affect.
For example, client may switched o the phone near the beacon 1 and turn it on
near the beacon 4. In this situation system will insert to table 2-nd and 3-rd
beacons. However, this is not problem. After each iteration, when system
receives signal from device, it will retrieve data from the table of broken
beacons, and compare with received UUID, if the table contains same UUID it
will be removed Figure 6: The path of the client when some of the
beacons crashed
"Three neighbors"
method. We told about the "linear trajectory" method. And this
is only for small markets which have only single gate. However, as we know,
most of stores have more complex structure and the method mentioned above
doesn't work there. Complex structure stores use
more than 10000 beacons and locate them in matrix form. The matrix form of
beacons can interact system with client continuously, and get user's current
location. The matrix form contains big amount of beacons, accordingly finding
broken beacon in this situation is not easy process. And "Three
neighbors" method is very useful here. 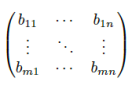 In the matrix formed map distances
between beacons bij to bi+1j and bij to bij +1 are
same. This option will help us to find broken beacon. First of all, we must
create monitoring map for beacons in the store like in linear trajectory
method. In this type of map, system receives 3 or more signals simultaneously.
For ex-ample, if client in the center of the store, there are may be 9 beacons
that can get signal from device. In the matrix below client is on the beacon b22 now.
In this situation all other neighbors may receive signal. However, b11, b31, b13 and b33 are
not in normal distance range, and we cannot confidently say that they always
can get signal. Therefore, these neighbors are not important for us.
In the matrix formed map distances
between beacons bij to bi+1j and bij to bij +1 are
same. This option will help us to find broken beacon. First of all, we must
create monitoring map for beacons in the store like in linear trajectory
method. In this type of map, system receives 3 or more signals simultaneously.
For ex-ample, if client in the center of the store, there are may be 9 beacons
that can get signal from device. In the matrix below client is on the beacon b22 now.
In this situation all other neighbors may receive signal. However, b11, b31, b13 and b33 are
not in normal distance range, and we cannot confidently say that they always
can get signal. Therefore, these neighbors are not important for us. 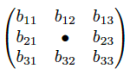 The
"Three neighbors" method uses only 3 nearest beacons. If 3 beacons
simultaneously get signal from the device, the 4-th nearest beacon that has
same distance from all of them must get signal too. If the 4-th beacon doesn't
get signal, we confidently can say that it is not working. For example, on Figure 7 if beacons b12, b21 and b23 get
signal, it means that the nearest beacon for device is beacon b22. If b22
doesn't get signal, we can say that it is not working and insert it to the
table. There is a problem if 2 or more
The
"Three neighbors" method uses only 3 nearest beacons. If 3 beacons
simultaneously get signal from the device, the 4-th nearest beacon that has
same distance from all of them must get signal too. If the 4-th beacon doesn't
get signal, we confidently can say that it is not working. For example, on Figure 7 if beacons b12, b21 and b23 get
signal, it means that the nearest beacon for device is beacon b22. If b22
doesn't get signal, we can say that it is not working and insert it to the
table. There is a problem if 2 or more Figure
7: Matrix formed map
Figure
7: Matrix formed map
neighbors are crashed.
However, system will check it by client which come from another side. And
according to statistics, probability of crashing simultaneously 4 neighbor
beacons is very small, we can say impossible in general.
Conclusion With an iBeacon network, any
brand, retailer, app, or platform will be able to understand exactly where a
customer is in the brick and mortar environment. This provides an opportunity
to send customers highly contextual, hyper-local, meaningful messages and
advertisements on their smartphones.[4] And there some problems occur. Beacons
are fragile and we cannot predict battery life duration. Beacons may be crashed
at different time, and main problem is to determine broken beacon in the large
set of beacons. And we offer 2 methods to deal with this problem. First method called
"linear trajectory" useful when beacons are located in linear way. It
is generally small markets, small museums and etc. The second method is
"Three neighbors" method. This method is useful for matrix formed map
of beacons. It will help to determine broken beacon by using three neighbor
working beacons. Of course, there are so many
complex structure used in buildings. And in the most of them both of offered
methods may not work. However, these two methods only start of our research.
And I believe that deeply research will help us to develop more complex
solution and these two methods will serve as a basis of it. References [1]
http://blogs.aerohive.com/blog/the-wi-
-security-blog/ibeacon-part-23a-how-does-it work. iBeacon: What is it? Aerohive
Networks, 2014. [2]
https://passkit.com/how-ibeacon
works. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Communication. PassKit, Inc, 2014. [3]
https://www.passbeemedia.com/ibeacon/.
iBeacon. Passbeemedia, 2014. [4]
http://www.ibeacon.com/what-is-ibeacon-a-guide-to
beacons/. iBeacon. 2014.






 System tracks only broken beacon's UUID. And there device causes may affect.
For example, client may switched o the phone near the beacon 1 and turn it on
near the beacon 4. In this situation system will insert to table 2-nd and 3-rd
beacons. However, this is not problem. After each iteration, when system
receives signal from device, it will retrieve data from the table of broken
beacons, and compare with received UUID, if the table contains same UUID it
will be removed
System tracks only broken beacon's UUID. And there device causes may affect.
For example, client may switched o the phone near the beacon 1 and turn it on
near the beacon 4. In this situation system will insert to table 2-nd and 3-rd
beacons. However, this is not problem. After each iteration, when system
receives signal from device, it will retrieve data from the table of broken
beacons, and compare with received UUID, if the table contains same UUID it
will be removed