Masich I.S.
Siberian State Aerospace University, Russia
Random and greedy search algorithms
for conditional pseudo-Boolean optimization
The heuristic algorithms for solving
conditional pseudo-Boolean optimization problems have been developed and
investigated for special problem classes. These algorithms do not demand explicit
assignment of functions. The algorithm of adaptive random search of boundary
points that combines random search and greedy heuristic has been created.
Most of
known at present methods for pseudo-Boolean optimization suppose objective functions
and constraints are given by algebraic expressions. At the same time a part of
functions or all ones in many real-world problems are given by an algorithm. That
circumstance renders impossible to apply usual algorithms of mathematical
programming and requires development of search optimization procedures.
Most
known heuristic search algorithms are adaptive search algorithms like simulated
annealing, genetic and evolutionary algorithms. These algorithms are applied
practically for arbitrary optimization problems, but for all that they don’t
take account of properties of the current problem classes. Moreover, these
algorithms demand tuning of a large number of parameters and don’t have
analytic estimations of efficiency.
Recently
stochastic and local-stochastic algorithms designing for specific problem
classes have became widespread.
In this
work heuristic algorithms are created for monotone pseudo-Boolean function
optimization problems with monotone constraint function. At that the objective
functions and constrains are not required to be defined explicitly.
Consider
a problem of the form
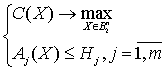 , (1)
, (1)
where ![]() and
and ![]() are pseudo-Boolean functions
given by an algorithm.
are pseudo-Boolean functions
given by an algorithm.
As the
optimal solution of the conditional problem is located among boundary points of
the feasible solution set, the optimization algorithm must be directed just at
search of boundary points.
Consider
the problem of monotonically increasing from ![]() pseudo-Boolean function optimization
with an arbitrary constraint. The optimal solution in that case as shown above
belongs to the subset of limiting points of the feasible solution set.
pseudo-Boolean function optimization
with an arbitrary constraint. The optimal solution in that case as shown above
belongs to the subset of limiting points of the feasible solution set.
The
simplest algorithm for search of the limiting points consists in following [1].
The search starts from ![]() . At each step the algorithm chooses a neighboring point in next level
moving so in a path of increasing of the objective function up to the bound of
the feasible area. If it is necessary, the procedure is repeated for some time,
the best point is chosen from the found limiting points.
. At each step the algorithm chooses a neighboring point in next level
moving so in a path of increasing of the objective function up to the bound of
the feasible area. If it is necessary, the procedure is repeated for some time,
the best point is chosen from the found limiting points.
Random
search
1.
Put ![]() .
.
2.
![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
3. At random choose a
point ![]() ,
, ![]() . If there isn’t such point then to 4 else the cycle is repeated.
. If there isn’t such point then to 4 else the cycle is repeated.
4.
![]() . If
. If ![]() then
then ![]() and to 2.
and to 2.
5.
Determine ![]() from condition
from condition ![]() .
.
Here ![]() is the set of all points k-neighboring to X (level k of point X).
is the set of all points k-neighboring to X (level k of point X).
Run time of the algorithm equals to
![]() .
.
Alternative
for the random search of the limiting points is a regular algorithm using
greedy heuristic.
Consider
the problem (1) when the objective function and the constraint are monotonically
increasing from ![]() pseudo-Boolean functions.
pseudo-Boolean functions.
Two
greedy strategies are possible for monotone objective function optimization
with a monotone constraint: search from the feasible area and search from the
area of unfeasible solutions. Accordingly two greedy algorithms have been
built: the direct and the dual.
The
algorithm of first strategy starts searching from ![]() and chooses a feasible point
and chooses a feasible point ![]() of a next level with the largest
specific value
of a next level with the largest
specific value ![]() on each step. As soon as a found
point will be limiting one, it will be taken for the problem solution [2].
on each step. As soon as a found
point will be limiting one, it will be taken for the problem solution [2].
Greedy algorithm
1.
![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
2.
Compute ![]() and
and ![]() for
for ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
3. If there is no ![]() for which
for which ![]() then
then ![]() is the problem solution.
is the problem solution.
4. Find 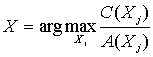 from such
from such ![]() for which
for which ![]() .
.
5.
![]() , to 2.
, to 2.
The
regular and stochastic algorithms described in this work transfer the original
pseudo-Boolean conditional optimization problem being NP-hard to the problem
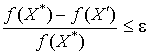
belonging class P (polynomially solvable), where ![]() is the optimal solution,
is the optimal solution, ![]() is an approximate solution.
is an approximate solution.
The
constructed heuristic algorithms allow solving any real-world problem leading
to a monotone pseudo-Boolean function optimization problem with imposed restrictions.
These algorithms have polynomial estimations of run time and so are oriented
mainly for solving the problems of high dimensionality. The follow scheme is
the most effective. At first stage the problem is solved with the greedy
algorithm, and then some solutions are found by means of the adaptive random
search, the best found solution is accepted as the problem solution.
References
1. Antamoshkin A.N., Masich I.S. Heuristic search
algorithms for monotone pseudo-boolean function conditional optimization.
Engineering & automation problems (Ïðîáëåìû ìàøèíîñòðîåíèÿ è àâòîìàòèçàöèè). ¹ 3, 2007, 41-45.
2. Antamoshkin
A.N., Masich I.S. Pseudo-Boolean optimization in case of unconnected feasible
sets. Models and Algorithms for Global Optimization. Series: Springer Optimization
and Its Applications , Vol. 4, edited by A. Törn, J. Žilinskas,
Springer, 2007, XVI, p. 111-122.