Ïåäàãîãè÷åñêèå
íàóêè/2.Ïðîáëåìû
ïîäãîòîâêè
ñïåöèàëèñòîâ
.
R. Ismagul
Kostanai State University named after A. Baitursynov, Kazakhstan
MAKING DECISIONS BASED ON FUZZY SETS
1.
Fuzzy Sets
Let A - a lot. A subset B of A is characterized by its characteristic
function.
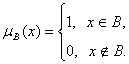
What is
a fuzzy set? It is usually said that the fuzzy subset C of A is characterized
by its membership function ![]() The value of the membership function at x
shows the degree of membership of the fuzzy set point. A fuzzy set describes
the uncertainty corresponding to a point x - and at the same time it is and is
not included in the fuzzy set C. For entry -
The value of the membership function at x
shows the degree of membership of the fuzzy set point. A fuzzy set describes
the uncertainty corresponding to a point x - and at the same time it is and is
not included in the fuzzy set C. For entry -
![]() chances for a second -
chances for a second - ![]() a chance. If the membership function of the
form
a chance. If the membership function of the
form ![]() for some
B, then C is the usual (strict) subset of A. Thus, the theory of fuzzy set is
not less than the general mathematical discipline than the usual set theory, as
usual set - a special case of fuzzy. Accordingly, it can be expected that the
theory of vagueness as a whole generalizes the classical mathematics. However,
later we will see that the theory of vagueness in some sense be reduced to the
theory of random sets, and thus is a part of classical mathematics. In other
words, the degree of commonality ordinary mathematics and fuzzy mathematics
equivalent [1]. However, for the
practical application of the theory of decision-making in the description and
analysis of the uncertainties with the help of the theory of fuzzy sets is very
fruitful. Standard subset could be identified with its characteristic function.
That math does not do as for defining a function (in the current approach
taken), you must first define a set. Fuzzy same subset from a formal point of
view, can be identified with its membership function. To date, this theory
published thousands of books and articles published by several international
journals, made a lot of both theoretical and applied work. La zadeh
considered the theory of fuzzy sets as a tool for analyzing and modeling the
humanistic systems, ie systems in which the person involved. His approach is
based on the premise that the elements of human thinking are not numbers, and
some elements of fuzzy sets or classes of objects for which the transition from
the "accessories" to "not belonging" is not abrupt, but
continuous. Currently used methods of the theory of vagueness in almost all
application areas, including the management of the company, the quality of
products and production processes. Là
zadeh
used the term "fuzzy set" (fuzzy set). In the Russian language the
term "fuzzy" translated as fuzzy sets, fuzzy, and even as fluffy and
foggy. Cumbersome apparatus of the theory of vagueness. As an example, we give
definitions of set-theoretic operations on fuzzy sets. Let C and D-two fuzzy
subsets of A with the membership functions, respectively -
for some
B, then C is the usual (strict) subset of A. Thus, the theory of fuzzy set is
not less than the general mathematical discipline than the usual set theory, as
usual set - a special case of fuzzy. Accordingly, it can be expected that the
theory of vagueness as a whole generalizes the classical mathematics. However,
later we will see that the theory of vagueness in some sense be reduced to the
theory of random sets, and thus is a part of classical mathematics. In other
words, the degree of commonality ordinary mathematics and fuzzy mathematics
equivalent [1]. However, for the
practical application of the theory of decision-making in the description and
analysis of the uncertainties with the help of the theory of fuzzy sets is very
fruitful. Standard subset could be identified with its characteristic function.
That math does not do as for defining a function (in the current approach
taken), you must first define a set. Fuzzy same subset from a formal point of
view, can be identified with its membership function. To date, this theory
published thousands of books and articles published by several international
journals, made a lot of both theoretical and applied work. La zadeh
considered the theory of fuzzy sets as a tool for analyzing and modeling the
humanistic systems, ie systems in which the person involved. His approach is
based on the premise that the elements of human thinking are not numbers, and
some elements of fuzzy sets or classes of objects for which the transition from
the "accessories" to "not belonging" is not abrupt, but
continuous. Currently used methods of the theory of vagueness in almost all
application areas, including the management of the company, the quality of
products and production processes. Là
zadeh
used the term "fuzzy set" (fuzzy set). In the Russian language the
term "fuzzy" translated as fuzzy sets, fuzzy, and even as fluffy and
foggy. Cumbersome apparatus of the theory of vagueness. As an example, we give
definitions of set-theoretic operations on fuzzy sets. Let C and D-two fuzzy
subsets of A with the membership functions, respectively - ![]() end
end ![]() . Intersection, the
product CD, union, negation, the sum of C + D called fuzzy subsets of A with
the membership functions
. Intersection, the
product CD, union, negation, the sum of C + D called fuzzy subsets of A with
the membership functions
![]()
![]() .
.
The
theory of fuzzy sets in a sense, is reduced to the theory of probability,
namely, the theory of random sets. The corresponding cycle theorems below.
However, in solving applications of probabilistic and statistical methods, and
methods of the theory of vagueness is usually considered to be distinct. In
what follows we assume that all the above fuzzy sets are subsets of the same
set Y.
2. Example of
uncertainty description using fuzzy set.
The notion of
"rich" is often used when discussing the social and economic
problems, including in connection with the preparation and decision-making.
However, it is clear that different individuals are investing in this concept
different content. Employees of the Institute of High-tech statistics and
econometrics held in 1996 case study represent different segments of the
population about the concept of "rich man."
3. Fuzzy conclusions
In the expert and control systems for machinery
fuzzy conclusions basically has the knowledge base formed by domain specialists
in the form of a set of fuzzy predicate rules of the form:P1:
if x is A1 then y is B1,P2:
if x is A2, then y is B2,...Pn:
An are there if x, then y is Bn,
where x - input variable, y - the variable O, A
and B - the membership functions defined by x and y, respectively.
Expert knowledge A → B reflects the fuzzy
causal relationship premise and conclusion, so it is called a fuzzy relation:R
= A → Bwhere «→» - fuzzy implication.
REFERENCES: