Pedagogy / 2. The
training of specialists
A.H. Tleuov,
I.A. Pyastolova, A.A. Tleuova
S.Seifullin Kazakh Agro Technical University, Kazakhstan
The educational program "Energy Management"
in Kazakhstan
Summary
In this
work, based on the analysis of experience in developing competence-oriented
education programs in different countries, including the proposed work plan for
the development of educational specialization "Energy Management" in
the specialty "Power" in Kazakh universities.
Keywords: energy management, energy
audit, competence, work curriculum disciplines blocks, modules disciplines.
I. Introduction
In the
development of the educational program "Energy Management", we were
guided by the Decree of the "State Program for Development of Education of
the Republic of Kazakhstan for the period from 2011 to 2020" (07.12.2010 ¹
1118) and the "Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan On energy saving and
energy efficiency " (13.01.2012 ¹541-IV
ZRK) approved by the President N. Nazarbayev.
In the
development of the educational program "Energy Management", we were
guided by the Decree of the "State Program for Development of Education of
the Republic of Kazakhstan for the period from 2011 to 2020" (07.12.2010 ¹
1118) and the "Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan On energy saving and
energy efficiency " (13.01.2012 ¹541-IV
ZRK) approved by the President N. Nazarbayev.
Ensuring
integration into the European Higher Education Area can be achieved by bringing
the content and structure of higher education in line with the parameters of
the Bologna process and the implementation of mandatory and recommendatory parameters
in the process.
World
experience shows that the implementation of economically viable energy-saving
policy of the enterprises in the use of fuel and energy resources is one of the
most important tasks of enterprises in market conditions. This has caused a
spread in countries with developed market economy practices of energy auditing
companies to economically sound use of energy-saving measures and improve
energy efficiency. Energy programs of all developed countries in the first
place include the introduction of energy-saving measures and technologies and
renewable energy sources. In some countries, energy audits are the basis for
the decision whether to banks providing loans to enterprises.
Energy
management can be described as part of the overall business management system
(organization), which has a clear organizational structure and aims to profit
by efficient power management. Then the energy manager - a specialist, which
aims at ensuring that the energy policy of the company, organization of events
aimed at continuity, providing communication functions between all objects,
planning and control of activities designed to maximize the efficiency of
energy management.
The
introduction of energy management is a more detailed picture of the energy
consumption, to give an accurate assessment of energy savings projects planned
for implementation in the enterprise (workplace). This is a management system
based on standard measurements and conducting audits, providing a performance
of the enterprise for which consumed only absolutely necessary for the
production of energy.
Given
the environmental crisis, shortage of energy resources, especially gas, oil and
nuclear fuel, one of the strategic directions of the creation of an independent,
secure and reliable fuel and energy sector of any country is to accelerate the
development of clean energy. This includes the widespread use of alternative
and renewable energy sources.
It
should be noted that the June 17, 2011 Technical Committee ISO / TC 242
"Energy Management" approved the new international standard ISO
50001: 2011 "Energy management systems - Requirements with guidance for
use."
II. Problem Statement. One of the major educational documents for the organization of the
educational process is a model and work curriculum. As a model curriculum
framework adopted for model curriculum in "Power." Our task was to develop
a work plan for the school to meet the requirements of the Bologna process and
the national SES Republic of Kazakhstan.
One of the major educational documents for the
organization of the educational process is a model plan and work curriculum. As
a model plan for the basis of the adopted curriculum in the specialty “Electrical
energy industry”. Our task was to develop a work plan considering the requirements
of the Bologna process and the State educational standards of the Republic of
Kazakhstan.
Methods of research used the following:
analysis of primary data, expert interviews, media monitoring, specialized
databases, monitoring of official statistics, and industry-specific publications,
conference proceedings.
III. Results. In 2010, the Department of operation of electric
energy department has been invited for the project Tempus Project 511347 -
TEMPUS-1-2010-1-DE-TEMPUS-JPSR-Development and implementation of
curriculum-based Energy Management distance learning in higher education in
Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan.
In this
project from the European Union are involved: the Higher School of Economics,
the Bielefeld (Germany), Technical University of Graz (Austria), University of
Technology, Kaunas (Lithuania). As the partner countries are the S.Seifullin
Kazakh Agro Technical University; Engineering and Economics of Kostanai,
Polytechnic University of Ashgabat and Power University, Mary (Turkmenistan).
Global
objectives of the project are: a scientific long-term support of the regions of
Kazakhstan to sustainable energy and energy efficiency; promotion of development
and the strengthening of economic and ecological approach to the energy producing,
distributing and consuming enterprises and organizations.
The
specific objectives of the project: development and implementation of educational
degree Bachelor "Power Management" in the curricula of partner universities
in the Republic of Kazakhstan, the development and promotion of distance
learning technology through the introduction of electronic technologies.
For successful development of the project
created 6 working groups, the tasks of which are shown on Figure 1.
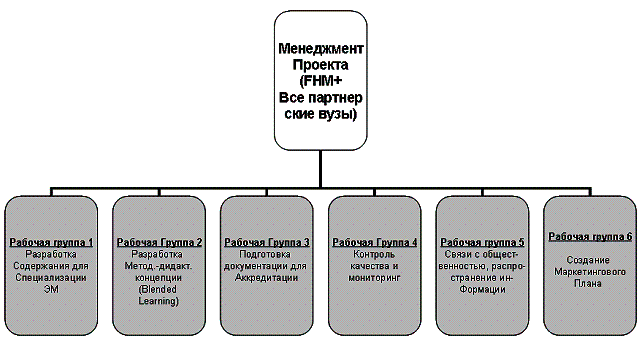
Figure 1 - Results of
partners meeting in Germany (Bielefeld)
An
analysis of the curriculum "Energy management" of higher education
institutions in Austria, Germany, Lithuania, Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and
others, it was determined that this expertise should be based energy
department. Therefore, specialization "Energy Management" opens at
the university within the major "5V071800-Power" according to the
model curriculum approved by order of the Minister of Education and Science of
the Republic of Kazakhstan (¹ 158 of "10" April 2012).
In
difference from domain-specific competence-oriented education programs should
be the ultimate goal of acquiring a particular set of competencies by students
in accordance with the acquired skill. Therefore, the following procedure for the
development of the educational program "Energy Management":
- the
development of a competency model of the graduate;
- development
of documentation skills;
- the
development of the curriculum, the timetable matrix interface competences and
disciplines;
- development
of academic disciplines programs;
- development
funds assessment tools;
- the
development of cross-cutting program of intermediate (incremental) complex
testing of students to meet their educational preparation of the expected results;
- development
of practical training programs;
- to
develop the final state assessment.
Figures
2 and 3 show the approaches to the formation of the educational program
"Energy management".
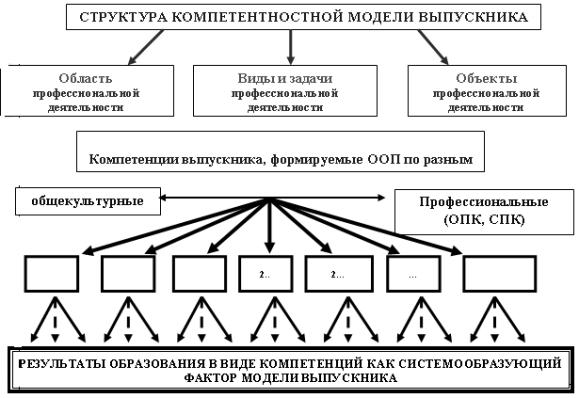 Ðèñó
Ðèñó
Figure 2 -
Competence model of graduate
Assessing the level of training is determined
by the competence of graduates. Along with the general cultural and general
professional competencies defined profile-specialized professional competence
corresponding to the profile of training and the planned result of training.
They are developed in conjunction with leading experts of the enterprises.
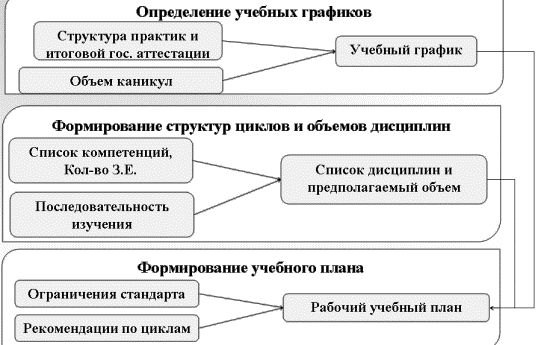
Figure 3 - The
approach to the formation of the curriculum
As a result of the research were identified
and developed units / modules disciplines. It should be noted that to date
there is no exact definition of the module of the educational program. Part of
High Schools under the module includes a block of disciplines, while others
have a view of the discipline as a module. In our case, we offer the following
blocks or modules disciplines.
1.
Humanitarian and socio-economic (compulsory and elective components).
2.
Naturally Science (compulsory and elective components).
3.
Professional (compulsory and elective components).
4. Professionally-oriented.
5. Personality.
It is
also necessary to take into account the practical training, which are
represented by the educational and professional practices. The program ends
with graduation work (the project). Additional mandatory program supports
physical education.
IV. Conclusions. In accordance
with the above stated has been designed competence-oriented working curriculum
specialization "Energy Management", defined modules that focus on the
acquisition of competencies of graduates. These competencies have been
identified as a result of opinion polls of experts and potential employers. The
results presented here have been approved by the partner countries of the
Tempus program at a meeting in Graz (Austria), 29-31 January 2012.
Literature:
1.
Alisultanova Je.D. Kompetentnostnyj podhod v inzhenernom obrazovanii:
monografija.- Izd-vo « Akademija Estestvoznanija», 2010. – 256 s.
ABOUT
THE AUTHORS:
1.
Tleuov A.H. D.Sc., Prof., Head department of Electrical
Equipment Operation S.Seifullin Kazakh Agrotechnical University, tel. 8(7172)
32-74-89, e-mail: tleuov@bk.ru.
2. Pyastolova I.A. Ph.D., associate
professor. Department of Electrical Equipment Operation S.Seifullin Kazakh
Agrotechnical University, tel. 8(7172) 32-74-89.
3. Tleuova A.A.,
Ph.D. Lecturer
of Department of Electrical Equipment Operation S.Seifullin Kazakh
Agrotechnical University, tel. 8(7172) 32-74-89.