Agriculture 4. Technologies of
storage and processing of agricultural products
Assoc.
Prof. V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, graduate
student Ya.I. Kondratyeva,
graduate student A.A.
Korchinskiy, student A.S. Moskalenko
Voronezh State University of
Engineering Technologies, Russia
Kinetics of the partial crystallization of moisture in
the apparatus for periodic action with the concentration of
the liquid media
At present there is
a sufficiency of works, dedicated to the mathematical simulation of the
processes of crystallizing ice in the apparatuses for periodic and continuous
action with the refrigerators concentration of liquid media; however, the
united stochastic kinetic theory of formation and increase in ice is absent.
The attempt to solve this problem in this work is made [1].
It is accepted
during the construction of mathematical description that an increase in the
crystals of ice is accomplished in the initial liquid medium, where the
diffusion processes of the transfer of substance to the crystal boundary of ice
proceed with the maintenance of the required conditions for cooling [2-3].
Let us introduce
the following designations, let ![]() – the density of the function of
the distribution of a quantity of crystals of ice with the mass m per unit of
volume of apparatus at the moment of the time
– the density of the function of
the distribution of a quantity of crystals of ice with the mass m per unit of
volume of apparatus at the moment of the time ![]() ;
; ![]() - the concentration of the dry
solutes in the liquid phase at the moment of the time
- the concentration of the dry
solutes in the liquid phase at the moment of the time ![]() ;
; ![]() – the rate of growth in the
crystals of ice;
– the rate of growth in the
crystals of ice; ![]() – the rate of formation of
the new crystallization centers with a mass of
– the rate of formation of
the new crystallization centers with a mass of ![]() , formed as a result of the melting of particles by a mass of
, formed as a result of the melting of particles by a mass of ![]() ;
; ![]() – the initial mass of the
crystal of ice. Then, taking into account stochastic of the process of
formation and increase in the crystals of ice, from the balance in a quantity
of micro particles taking into account the law of mass conservation we write
down the following system of equations:
– the initial mass of the
crystal of ice. Then, taking into account stochastic of the process of
formation and increase in the crystals of ice, from the balance in a quantity
of micro particles taking into account the law of mass conservation we write
down the following system of equations:
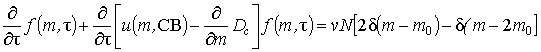 , (1)
, (1)
![]() , (2)
, (2)
where ![]() - the stochastic parameter
(diffusion coefficient);
- the stochastic parameter
(diffusion coefficient); ![]() - the number of crystals of ice
per unit of volume of apparatus at the moment of the time
- the number of crystals of ice
per unit of volume of apparatus at the moment of the time ![]() ;
; ![]() - delta is Dirac's function;
- delta is Dirac's function; ![]() - the economic coefficient. For
solving the represented system of equations let us introduce the initial and
boundary conditions
- the economic coefficient. For
solving the represented system of equations let us introduce the initial and
boundary conditions
![]()
![]()
![]() , (3)
, (3)
![]() for
for ![]() è
è ![]() , (4)
, (4)
thus the function ![]() there exists only in the
region
there exists only in the
region ![]() , and beyond the limits of this region
, and beyond the limits of this region ![]() it is identically equal to
zero.
it is identically equal to
zero.
After multiplying
expression (1) to the left and to the right on ![]() and integrating by from
zero ad infinitum; taking into account conditions (3)–(4) we will obtain
equation for the presence
and integrating by from
zero ad infinitum; taking into account conditions (3)–(4) we will obtain
equation for the presence ![]() the moment
the moment
![]() (5)
(5)
From the equation (5), with ![]() it follows
it follows
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() ,
, ![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
Equations (2), (6)
– (8) they make it possible to define such values as ![]() è the
dispersion of the distribution
è the
dispersion of the distribution![]() .
.
The theoretical
description of the process of freezing – crystallization from the solution be
based on two basic approaches. The first of them examines crystallization
front by one-dimensional and continuous, crystallization inside the volume of
liquid phase is not considered, but the temperature On the border of the
division of phases starts to the equal equilibrium temperature of the
crystallization of the solution of the assigned concentration. With the second
approach the kinetics of crystallization are limited to examination,
disregarding thermal processes inside the solid phase. The complexity of the
task because of the insufficiently complete development of theory in question
allows in some special cases to only bring it to the solution [3-5].
Let us examine the
special cases, which are of scientific and practical interest.
Let the process of
crystallization be limited by thermal processes inside the crystal itself. In
this case the equations will be valid
![]()
![]()
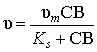 (9)
(9)
where ![]() - the maximum specific rate of
growth in the crystal of ice;
- the maximum specific rate of
growth in the crystal of ice; ![]() - the constant. Taking into
account equations (9) from the dependences (2) – (7) they follow the equation
- the constant. Taking into
account equations (9) from the dependences (2) – (7) they follow the equation
![]()
![]() , (10)
, (10)
solution of which can be
presented in the form
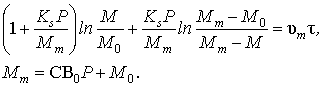 (11)
(11)
![]() . (12)
. (12)
Let the process of
crystallization be limited by diffusion, then
![]()
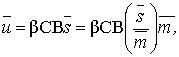 (13)
(13)
where ![]() - mass exchange coefficient,
depending on the temperature (through the diffusion coefficient) and mixing
conditions in the apparatus;
- mass exchange coefficient,
depending on the temperature (through the diffusion coefficient) and mixing
conditions in the apparatus; ![]() - the surface area of crystal.
- the surface area of crystal.
Taking into account
dependences (13), the equations (2) – (7) are converted to the form
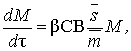
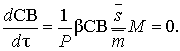 (14)
(14)
Equations (14)
contain the unknown relationship ![]() . However, as show calculations, the value
. However, as show calculations, the value
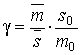 (15)
(15)
in effect constant and close
to one. Taking into account that presented, equation (14) is solved in the form:
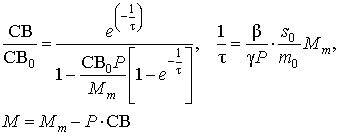 (16)
(16)
Thus, stochastic
the model of formation and increase in the crystals of ice with the
refrigerators concentration of liquid media proposed makes it possible to solve
the wide spectrum of the tasks of applied nature [3-5].
Literature
1. L.
Pap Freeze concentration. Translation. with Hungarian, edited by O.G.
Komyakova. - M.: Light and Food Industry, 1982. - 97 p.
2.
Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Study of the process of freezing moisture from the extracts
of the endocrine and special raw material. Diss. cand. tech. the sciences.
Voronezh. State. tech. Acad., 2003. 184 p.
3.
Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyev Ya.I. Kinetics of the process of
concentration by freezing the cherry juice. Herald of the Voronezh state university
of the engineering technologies. 2014, ¹ 4 pp. 44-48.
4. Ovsyannikov V.Yu.
Optimum regimes of the concentration of the plasma of the blood by freezing.
Meat industry. 2012. ¹ 1. S. 65-68.
5. Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyeva Ya.I., Bostynets
N.I. Concentration of apple juice in the drum freezing out installation. Storage
and processing agricultural 2014. ¹ 4. pp. 41-44.