The methylotrophic yeast, immobilized in sol-gel
matrix, as a basis for stable heterogeneous biocatalysts
Kamanina O.A. Burmistrova T.V., Rogova T.V.
Tula State University
At present we have acute problem of development of
rapid methods of ethanol determination in fermentation mass for quality control
at biotech industries. There are several methods of determining of alcohol
concentration: bottle method, aerometric method and gas chromatography. Thus,
the development of analytical method, which would simplify and reduce cost of
analysis is very important. The biosensor method me propose do not require
highly qualified personnel and helps to increase the economic returns of
facilities.
Immobilization
of microbial cells is very efficient in intensification and increasing of
economic attractiveness of advanced biotechnological processes, because it
allows us to use the same cells for a long time. It greatly simplifies the
process and reduces the cost of analysis comparing to processes that require using
of free cells. In these latter days method of biomaterial immobilization by
including it into bimodal silicon sol-gel matrix attracted particular interest.
Because of its properties the matrix can be applied for the immobilization of
whole cells in creating heterogeneous biocatalysts.
The purpose was to create a stable heterogeneous biocatalysts by
encapsulating the methylotrophic yeast Pichia
angusta in sol-gel matrix based alkoksiproizvodnyh silica and polyethylene
glycol. The influence of hydrophobic additives alkilalkoksisilana on the
properties of heterogeneous biocatalysts that depend on the structure and
properties of crosslinked polymer, physiological and biochemical behavior of
immobilized microorganisms. As an analytical signal representative of the biocatalyst
used the methylotrophic yeast respiratory activity in the presence of ethanol.
A convenient tool for studying the properties of the immobilized biomaterial
are biosensors that biocomponent is in direct contact with the physical and
chemical transmitter (oxygen electrode). In this work we received five receptor
elements, which are immobilized in bimodal silicon sol-gel matrix
methylotrophic yeast Pichia angusta.
We have determined the main characteristics of the developed receptor elements:
sensitivity, detection range, operational and long-term stability. Comparative
analysis of parameters of heterogeneous biocatalysts showed that the increase
in the share of alkiltrialkoksisilana matrix up to 83% increase in the
hydrophobicity of the matrix, which results in an increase in the coefficient
of sensitivity and decrease the detection limit (Fig. 1).
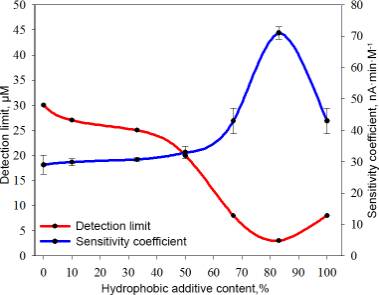
Fig. 1 Detection limit and sensitivity coefficient for different
heterogeneous biocatalysts
However, a further increase in the content of hydrophobic additives not
recommended, as it results in a decrease of analytical characteristics obtained
heterogeneous biocatalysts.
As a result of the work, received receptor elements were tested on
commercial samples of vodka and model samples of fermentation mass (table 1).
Table 1
|
Vodka sample |
Concentration C2H5OH , % |
||
|
Gas chromatography |
The biosensor method |
||
|
Zhuravli |
40,1±0,5 |
40,1±0,4 |
|
|
Slavyanskaya |
40,0±0,3 |
39,9±0,2 |
|
|
Zelenaya marka |
40,3±0,8 |
40,1±0,3 |
|
|
Belenkaya |
39,9±0,2 |
39,7±0,3 |
|
|
|
|||
|
The fermentation,
h |
Concentration C2H5OH, mM |
||
|
0 |
20±3 |
20±4 |
|
|
24 |
43±1 |
46±5 |
|
|
48 |
168±1 |
173±2 |
|
|
72 |
205±3 |
209±5 |
|
We carried out a statistical analysis of the data (Fisher criterion and
the modified t-test). These two methods (gas chromatography and biosensor
determination of ethanol content in the samples) are homogeneous in
reproducibility and differ insignificantly.
The work was supported by the Federal Program
"Scientific and scientific-pedagogical personnel of innovative
Russia" (GK № 14.B37.21.1231 and № 16.740.11.0766)