A.L. Lohvinenko, I.Y.Shubin
Kharkov national university of radioelectronics
Acceleration of multi-core multimedia converters
Video converters are computer programs that can change the
storage format of digital video. They may recompress the video to another
format in a process called transcoding, or may simply change the container
format without changing the video format. One of the disadvantages to
transcoding is that the process is highly CPU intensive. As a result
conversion may take hours.
Parallelization has become the
solution of the too long conversion.
We all used to think that CPU is the
only component of a computer that can execute any code. However, it appears
that producing and constructing multi-core processors too difficult and
expensive. Therefore, the increasing number of cores significantly slowed down. GPUs, devoid of their CPU deficiencies, have become
the excellent and very fast counting machines.
Unlike the CPU is able to solve any
problem including graphics, but with the averaged performance graphics
processor is adapted to high-speed solution of one problem: converting the
input polygons piles into a pile on the output pixels. Moreover, this problem
can be solved in parallel on hundreds of relatively simple cores in the GPU. A
schedule of productivity CPU and GPU is shown in Figure 1.
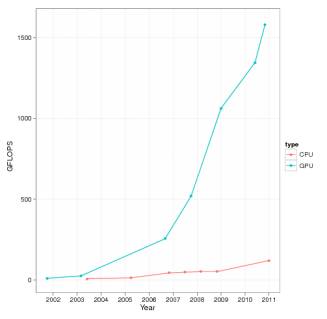
Figure
1 Ц CPU vs GPU
Theoretical performance video chip
far superior CPU.
CUDA (Compute Unified Device
Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and programming model created by
NVIDIA and implemented by the graphics processing units (GPUs) that they
produce. CUDA gives developers access to the virtual instruction set and memory
of the parallel computational elements in CUDA GPUs. Using CUDA, the latest
Nvidia GPUs become accessible for computation like CPUs.
CUDA work is this: the program is
executed on the CPU as long as it appears the piece of code that can be
executed in parallel. Then, instead of being carried out slowly in two (yes
even if eight) nuclei the steepest CPU, it is transmitted to the hundreds of
cores GPU. At execution time of this portion is reduced in times, and hence
reduced time and the entire program.
Video - a set of frames that show
consistently at a certain speed. The process of encoding video is divided into:
-
reducing the redundancy of video in
the time dimension, based on the fact that neighboring frames tend to be not
much different;
-
compression of individual images.
Compression algorithm:
-
preparation of macroblocks. For each
macroblocks determines how it will be compressed;
-
translation macroblocks in the color
space YUV. Getting the right amount of 8x8 matrices;
-
for P-blocks and B-blocks produced
by calculating the difference between the corresponding macroblocks in the
reference frame;
-
discrete cosine transform (DCT);
-
quantization;
-
zigzag scan;
-
batch encoding;
-
Huffman coding.
View this generalized algorithm can
notice that it is subject to parallelization.
Image contains macroblocks, which
can encode and decode whatever. Each macroblocks contains six blocks of data to
DCT. Parallelize DCT is very important because, in addition to finding
displacement vectors is very slow operation. The result is a parallel-pipelined
processing circuit video stream.
Discrete cosine transform is the
kind of Fourier transform. Code fast Fourier transform (FFT) for CPU is shown in
Figure 2.

Figure
2 Ц FFT core code for CPU
Code fast Fourier transform (FFT)
for GPU is shown in Figure 3.
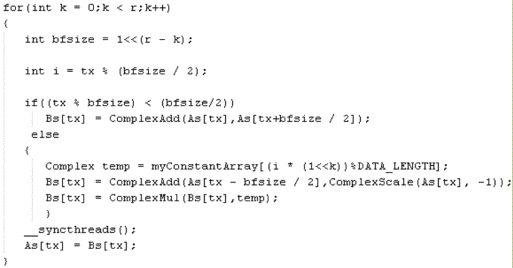
Figure
3 Ц FFT core code for GPU
With the implementation for the GPU
we have:
-
GPU code makes two parallel inner
loop of the CPU code. This results in increased performance for large data
sequences.
-
simplified algorithm, internal loops
replaced by the condition IF-ELSE.
Using DCT algorithm on GPU get
better performance for large matrices (> 256 * 256).
Productivity of handle different amounts of data on
the CPU and the GPU is shown in Figure 4.
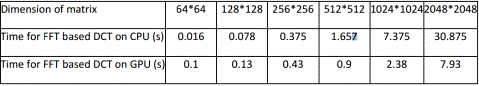
Figure
4 - Productivity of handle different amounts of data on the CPU and the GPU
Dependence of the code on the CPU and GPU on the size
of the matrix is shown in Figure 5.
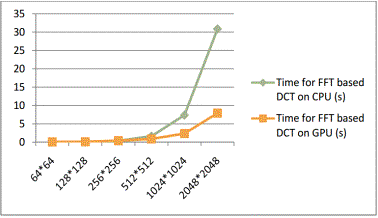
Figure
5 - Dependence of the code on the CPU and GPU on the size of the matrix
Speed up is shown in Figure 6.
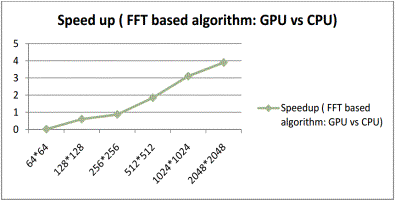
Figure
6 Ц Speed up (FFT based algorithm: GPU vs CPU)
GPU has reached a point of
development where many real world applications are easily implemented on them
and faster than on multi-core systems.