PhD doctor Amirasheva B.Ê1., Rahimbaeva À2., Kaldybekova R.E.2,
Amirasheva L.Ê1
Institute of microbiology and virology CS ÌES RK
Kazakh national pedagogical university named after Abay
Emulsifying activity halotolerant strains of bacteria isolated from oil
reservoirs deposit "KAZRUSOIL" Kyzylorda region
Abstract. From an oil reservoir
oil wells "KazRosOil" allocated 17 bacterial strains are selected 3
strain (12RZH, 13RZH, 14RZH) able to grow at 10% NaCI, and 3 of culture (12RZH,
13RZH, 14RZH) has a high emulsifying activity.
Keywords: oil reservoirs, strain, halotolerant bacterium, emulsifying activity
Currently,
high-viscosity oil is regarded as the main reserve of world oil production. Its
reserves of about 5 times higher than the recoverable oil reserves of low and
medium viscosity. Existing technologies allow extracting only half of the oil
contained in the oil fields. Currently still in the depths of more than 70% of
oil reserves. In this regard, markedly increased interest in finding ways and
means of enhancing secondary oil recovery and in particular to the
microbiological methods. At the present stage the task EOR clean technologies
can solve the method of microbial stimulation. Unlike chemical
reactants lose activity as a result of dilution with formation water, the
microorganisms are capable of self-development, i.e. reproduction and
reinforcement biochemical activity, depending on the physical and chemical
conditions of the environment.
As a result of
microbiological synthesis directly in the reservoir formed metabolites such as
gases, acids, surfactants, thereby reducing the viscosity of the oil and
enhanced oil recovery by 40%. Practical application of biotechnology allows
5-7% increase in stocks involved in the design, 1.5-2 times increase the
productivity of wells, and current oil production - by 15-25%. With ever rising
energy prices biotechnological methods pay off within 1.5-2 years [1].
The
possibility of using a microbiological effects in order to increase oil
recovery and oil production intensification first patented C.E Zobell (1946)
[2], is now confirmed by many researchers and successful fishing experiments
[3-5].
One of the most effective oil
displacement agents are biosurfactants. Due to its physical and chemical
properties, the ability to exercise them in the presence of high concentrations
of salts and is not adsorbed on the limestone and sandstones, bioemulsifiers,
mixed with other, for example, nonionic surfactants, can be an effective means
of increasing oil production [6-10]. Introduction of the surfactant-producing
microorganisms in an oil field, followed by breeding them and form a seam
directly bioSAS significantly affect oil displacement.
Biogenic surfactants synthesized by
bacteria, yeasts, microalgae and some mitsellialnymi mushrooms. The most
studied biosurfactants bacteria Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, Rhodococcus erythropolis, Bacillus licheniformis, B. subtilis, B. brevis, B. polimixa, Acinetobacter
calcoaceticus, and yeast Torulopsis
[11-14].
When using
microorganisms for enhanced oil recovery, it is important to input strains
exhibited high tolerance to salinity. In this connection, the allocated
halotolerant bacteria investigated.
The purpose of research - definition of
emulsifying activity halotolerant microorganisms isolated from oil reservoirs
deposits "KazRusOil" of Kyzylorda region.
Materials
and methods
Object
of recearch is the samples of oil reservoirs deposits "KazRosOil"
Kyzylorda region.
Isolation
of microorganisms from halotolerant oil reservoirs Kyzylorda region was
performed by enrichment cultures on medium-Voroshilova Dianova (VD) of the
following composition (g/l) NH4NO3 - 1,0, K2HPO4 - 1,0, KH2PO4 - 1,0, MgSO4 -
0, 2, CaCl2 · 6H2O - 0,02, FeCl3 - traces, pH = 7,0-7,2. As carbon and energy
source oil used in an amount of 1%.
Impact factor salinity on the growth of strains studied on agar medium
supplemented with different salt concentrations: 3%, 5%, 7%, 10% NaCI.
Emulsifying activity of the culture medium was determined by Iguchi
[15]. As used hexadecane, hydrophobic substrate.
Results and discussion
A search for
halophilic microorganism cultures isolated from hot oil reservoirs deposits
"KazRusOil" of Zhusaly area, well ¹5, at a depth of 610-640 m. Total
allocated 17 strains: 1RZH, 2RZH, 3RZH, 4RZH, 5RZH, 6RZH, 7RZH, 8RZH , 9RZH 10
AJ 11RZH, 12RZH, 13RZH, 14RZH, 15RZH, 16 RZH, 17RZH.
The
test results showed that all of the culture grown at 3-5% salt content in the
medium. Increasing the salt concentration up to 7% of the strains was kept:
1RZH, 3RZH, 4RZH, 6RZH, 7RZH, 11RZH, 12RZH, 13RZH, 14RZH, 15RZH (Table 1).
Table 1 - Results
of the salt content in the medium of cultured microorganisms
|
Strain |
NaCl concentration |
|||
|
3% |
5% |
7% |
10% |
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1 RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
---- ---- |
|
2 RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
---- ---- |
|
3 RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
---- ---- |
|
4 RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
---- ---- |
|
5 RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
---- ---- |
|
6
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
--- --- |
|
7
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
--- --- |
|
8
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
--- --- |
--- --- |
|
9
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
--- --- |
--- --- |
|
10
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
--- --- |
--- --- |
|
11
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
--- --- |
|
12
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
+++ +++ |
|
13 RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
+++ +++ |
|
14
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
+++ +++ |
|
15
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
+++ +++ |
--- --- |
|
16
RZH |
++++ ++++ |
++++ ++++ |
++ ++ |
--- --- |
|
17 RZH |
+++ +++ |
++ ++ |
++ ++ |
--- --- |
|
Note
- (-) - lack of growth, (++) - moderate growth (+++) - good growth, (++++) -
abundant growth |
||||
It was found that
at a concentration of 10% NaCl, the ability to grow was observed in strains
12RZH, 13RZH, 14RZH (Figure 1).
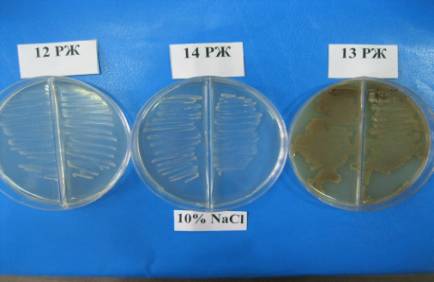
Figure
1 - The growth of the strains in the presence of 10% NaCl
The relatively
high rate control emulsifying activity among isolated from oil reservoirs
bacterial cultures showed strains: 1RZH, 12RZH, 13RZH, 14RZH, 16RZH after 2
days emulsifying activity was 0,449-0,638 units. OD620, and then on the seventh
day has risen to 0,615-1,212 units. OD620. The remaining strains EA was
significantly lower, and the strain 4RZH activity practically does not show.
Thus, it was found that strains (1RZH, 12RZH, 13RZH,
14RZH, 16RZH) had a high degree of isolation thanks to EA bioSAS in medium.
These strains are promising for further research on their use in enhanced oil
recovery.
REFERENCES
1
Ibatullin R.R. Nedra, 2004, - 292 p. (in Russ.).
2
Pat. ¹ 2413278. US. Bacteriological Process for Treatment
of Fluid - Bearing Earth Formanion: / C.E. Zobell. Ðub.1946.
3
Pat. ¹2073712 RF, Krasnopevtseva N.V., Chepnyagin V.À., Yarotskiy S.V. 20.02.97.(in Russ.).
4
Blavin V.D., Krasnopevtseva N.V. Novosti nauki i tehniki, 2006, ¹ 4, 116-117
(in Russ.).
5
Balakin V.V. Vserossijskogo soveshhanija po razrabotke neftjanyh
mestorozhdenij, Al'met'evsk, 2000, ¹ 2, 50-54 (in Russ.).
6
Zhdanova N.V., Sadykov U.N., Bajazitova V.R. Interval, 2000, ¹15-16.- 4ð. (in Russ.).
7 Simaev
Ju.M. i dr. Interval, 2000, ¹ 15-16, - 4ð. (in Russ.).
8
Berdichevskaja M.V. Mikrobiologija, 1989, ¹ 1, 60-65.
9 Nazina
T.N. i dr. Mikrobiologija, 2003, ¹ 2, 206-211.
10 Ron E.Z.,
Rozenberg E. Natural role of biosurfactants // Environ. Microbiol. - 2001.
-Vol. 3. - P. 229-236.
11
Parra J.L. et al. Chemical characterization and physicochemical behaviour of
biosurfactants // J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. - 1989. - Vol. 66. - P. 141-145.
12
McInerney M.J., Javaheri M., Nagle D.P. Properties of the biosurfactant
produced by Bacillus licheniformis strain JF-2 // J. Ind. Microbiol. - 1990.
-Vol. 5. - P. 95-102.
13
Christofi N., Ivshina I.B., Christofi N Microbial surfactants and their use in
field studies of soil remediation // Journal of Applied Microbiology. - 2002. -
Vol.93. - P. 915-929.
14
Karanth N.G.K. Deo P.G., N.K. Veenanadig P.G. Microbial production of
biosurfactants and their importance // Current Science. - 1999. - Vol. 77.
- P. 116 - 126.
15 Iguchi T., Takeda, Ohaswa H. Emulsifying factor of
hydrocarbon produced by a hydrocarbon-assimilating
yeast // Agric.
Biol. Chem. -1969. - Vol. 33. – P. 1657-1658.