Экономические науки/ 14.Экономическая теория
Mukhashev A.K., master of group “E-12P”
Karaganda Economic University of Kazpotrebsoyuz, the Republic of
Kazakhstan
FACTORS, CRITERIA, INDICATORS OF
COMPETITIVENESS OF THE INDUSTRY
Under the
competitiveness of the industry should understand the performance of individual
sectors of the national economy, estimated, in addition to the traditional
criteria, in terms of characteristic and describes the degree of vitality and
dynamism of the sector in different types of economic development of the
country and the world at large. Competitiveness of the industry assumes that
competitive advantages over similar industries abroad, which are expressed in
the presence of a rational branch structure: a group of highly competitive
enterprises-leaders; effective development - design and production -
technological base, the development of industrial infrastructure; flexible system
of scientific - technical, industrial and logistical cooperation both within
the industry and with other industries in the country and abroad, an effective
system of distribution of products.
M. Porter in the
evaluation of the competitiveness of the industry offers based on figures for
the industry in world exports, the share of a particular industry or cluster of
total exports; share a cluster of world exports.
According to this
method competitive food industry we define as exports. The most competitive industries
in Kazakhstan - feed processing and meat food industry.
Competitiveness
of the industry is determined by the presence of her technical, economic and
organizational conditions for the creation of production and sales (with costs
not exceeding international) high quality products to satisfy the requirements
of specific groups of consumers. Competitiveness of the industry assumes that
competitive advantages over similar industries abroad, which can be expressed
in the presence of a rational branch structure. A group of highly competitive
business leaders, firms other companies within the industry to all levels,
streamlined development - design and advanced production technology base, the
development of industrial infrastructure: flexible system of scientific,
technical, industrial, logistical, technical and commercial cooperation, both
within the industry and with other industries in the country and abroad, an
effective system of distribution of products.
Competitiveness
at the industry level can also be assessed using the following parameters (or
combinations thereof): productivity, specific wages, capital-intensive and
knowledge-intensive, technical level of production, the body of knowledge and
scientific capacity needed for self-development and production of its
reproduction, the volume of technical groundwork for realization of scientific
project design development, the degree of export orientation or import
dependency industry, the degree of compliance with the level of development of
the industry's overall development of the national economy, the degree of use
of the product in various sectors of the economy. This set of indicators may be
amended or supplemented taking into account the specifics of the industry.
The
competitiveness of a particular industry depends on the ability of industry to
innovate and modernize. As a result of the test pressure and demands of the
market, companies are increasing their lead in the fight with the strongest
presence in the global market competition. In the current economic situation,
when competition on a global scale has been steadily increasing, competitive
advantage is created and maintained through a highly localized process. There
are very strong differences in the structure of the competitiveness of each country,
because no state can be competitive in all, or at least in most industries.
Ultimately, countries achieve success in certain sectors due to the fact that
their internal conditions are appropriate in the most dynamic and promising.
Competitiveness of the industry develops under the influence of many factors,
changing their significance in changing in the environment. In addition, each
region has its own branch of the "set" factors. In accordance with
the principle of systematic research, competitive analysis is conducted our
industry from the perspective of a systematic approach. Factors of
competitiveness food industry are analyzed, taking into account:
- Integrity,
understood as fundamental to the competitiveness of the whole can’t be reduced
to the sum of its constituent factors;
- Structural as
possible analysis of competitiveness through the establishment of the structure
factors, their priorities and the conditionality of competitiveness in a global
structural and interaction of its constituent elements;
- The
interdependence of system and environment, which means that the competitiveness
of the industry is formed in the process of interaction with the competitive
environment of a competitive region, being a leading active component
interaction;
- The hierarchy,
wherein each factor in the competitiveness of the industry turn can be
considered as a system.
Therefore, to
analyze factors competitiveness of the industry just is not enough quantitative
assessments are needed and qualitative characteristics, as well as integrated
assessment. We believe that no industry can’t be considered in isolation,
without taking into account the overall economic - political situation in the
country and abroad. These are undertaken by the State administrative and economic
measures: financial credit, tax, depreciation, customs policy, state insurance
system, the development and implementation of legislation to stimulate economic
development, political parties, movements, forming socio - political situation
in the country.
Table 1 - Factors
affecting the competitiveness of the industry
|
Levels
of influence |
factors that shape the
competitiveness of the industry |
|
1.
Macro
level |
-
state economic policy - The national legal
framework, emerging economies - legal conditions of functioning and
protection of domestic producers - External political
independence and security - The internal
political and social stability |
|
2.
Meso
level |
- resource potential
of the industry -
Economic potential and economic policy -
Demographic potential -
Sectoral consumer market |
|
3.
Micro
level |
-
productive assets and technology development -
Financial resources -
Management - organizational resources - Marketing policy and
demand factors |
Improving the
competitiveness of any industry may in the stably developing economy with a
stable socio - political environment. External and internal stability of the
country increases its investment attractiveness, stability and economic
relations at all levels, provides optimal conditions for production.
Set of industry
factors (meso) can be represented in the form of four sub-groups: natural,
economic, demographic and market. These factors are closely related, although
different in nature. The value of individual factors depends on the specifics
of the industry, and sometimes on the specific sub-sectors, that is, factors
that in some industries are key, others are secondary. Moreover, one and the
same factor at different stages of the process operates in the industry with
varying intensity. Relationship between the factors, their relative importance
varies with the development of science and technology.
Competitive
factors varied food, this commodity and labor, consumer factors (demand for the
products of the industry) and others. On the competitiveness of the food
industry primarily affect consumer factor and human resources. This is due to
the fact that the product provides the satisfaction of basic human needs. Besides
transporting semi compared with the finished product more economically
favorable. Therefore, the most efficient in terms of competitiveness is the
placement of companies in the areas of consumption. All sub-sectors of food
industry labor-intensive, require a significant amount of skilled resources. In
this area, production has historically been primarily targeted to women's work.
Each region has
its own characteristics (competitive advantages and disadvantages of the
territory), which give rise to the development of certain industries.
Competitiveness of the industry in a given region is the result of a unique
combination of socio - economic environment of the region with the competitive
advantages of the industry. The main task is to identify the basis of
competitive advantages of a particular region, its components and to translate
them into reality through the development of industries. At the same mechanisms
to ensure the competitiveness of the industry in one region may fail in
another.
The most
important, in our view, the factors that determine the competitive position of
the food industry are presented in Figure 1
Factors that determine the
competitive position of the industry
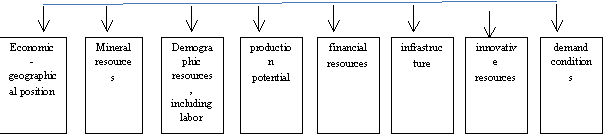
Figure 1 -
factors that determine the competitive position of the industry
1. Economic -
geographical location of any region is characterized by a number of factors:
the availability to other areas of the country, as well as to other countries,
to raw materials, to markets, transport routes.
2. Mineral
resources are characterized mainly by their availability and feasibility.
Isolated mineral - raw, land, forest, water, fauna and others. Resources.
3. Demographic
resources are characterized by the total population, age and sex composition,
changes in population size. Human resources are characterized by the presence,
skills and labor costs.
4. The production
potential is characterized by the presence of productive assets, capacity
utilization and production areas, retirement rate and renewal of fixed assets,
depreciation of fixed assets, the age structure of production equipment,
capital-labor ratio and armament electricity labor.
5. Financial
resources. One of the main reasons for the preservation of the crisis in the
manufacturing and financial sectors is a lack of working capital. Reduction of
investment in production due to a reduction of state financing of investment
programs and the volume of funds of the enterprises themselves.
Production
development and expansion of competitive products is constrained by the slow
pace of modernization. Slow update the active part of fixed assets depreciation
caused by a deficiency of funds, a more rapid increase in prices of the means
of labor. Depreciation absorbed liberalization of prices, inflation and
quantified simply not enough to compensate for incapacitated and obsolete
assets. In addition, the sources of investment in fixed assets of enterprises
are often used to finance current needs and financial incentives for labor
collectives.
6.
Infrastructure. Competitiveness of the industry is largely determined by the
level of development of its infrastructure. Distinguish production, market,
social infrastructure.
In the context of
sustainable development of Kazakhstan's infrastructure is a set of conditions
for effective functioning as the production sector and the industrial market
that enhance living standards. Infrastructure sector covers areas proizvodstva0
circulation and consumption of products, links them in a single chain, makes
efficient use of capacity (industrial, financial, organizational, personnel,
etc.) industry.
The transition
from one form of ownership to the other, the reorganization of production and
management, change all kinds of communication in the field of production,
circulation have a decisive impact on the infrastructure. With the development
of market relations, the formation of new business entities and their
regulatory activities carried out formation of a new infrastructure. And how
effective this is, in many respects depends on the problem and improve the
competitiveness of the industry. Achieving high, "strong" competitive
position requires fundamental changes in the industry.
The system of
indicators characterizing the level of infrastructure development of food
industry Kazakhstan, in our view, should include indicators such as the
development of transport networks; development of communication services, the
increase in wholesale and retail trade; amount of public services, information
- computer services, the number of credit institutions.
7. Innovation
resources food industry in the region determined by the level and the number of
scientific - production capacity, the presence and activities of organizations
involved in training and retraining, as well as characterizing the amount of
product innovation, the costs of research and development.
8. Demand
conditions. Demand of the population is a kind of "pyramidal
hierarchy". The highest demand (main pyramid) on food, cigarettes,
alcohol. The second level - clothes, shoes, followed by the demand for
expensive durable goods - furniture, cars, real estate, etc. Demand for light
industry goods is satisfied when the available funds remain after satisfying
the demand for food. In general, a decrease in effective demand for food
products, caused by a general decline in living standards. Among the indicators
of living standards, including such as: GNP and national income per capita real
income per capita, average wages, the ratio of minimum and average wages, the
cost of the minimum consumer basket, the subsistence minimum, the minimum
pension and other.
You can select a
logical chain competitiveness. At the state level competitiveness is determined
by the successful activities of industries. In turn, the competitiveness of the
industry has a regional dimension, due to the size of the territory of
Kazakhstan, differences in socio - economic development of the region,
especially the industry. Next in the hierarchy are distinguished company, which
is based on the competitiveness of products. In this chain, there is no
secondary level. All units are interconnected, interacting and mutually
conditioning competitiveness of the national economy as a whole. Without
competitive products can’t be effective activity of the enterprise, whose
success is largely determined by the conditions of the region where it is
located. Regional differences contributes to the acquisition of competitive
advantages at the industry level.
Thus,
consideration of problems of competitiveness in whatever level, requires taking
into account the influence of all these levels of competitive relations. In
addition, each level of competitive sphere has inherent factors, or so-called
determinants of competitive advantage, specific criteria, evaluation methods
and competitive strategy to achieve it.
References:
1. Strategy of
industrial - innovative development of Kazakhstan for 2003-2015
2. J. Stigler.
Perfect competition: a historical perspective .. Theory of the Firm //
Milestones economic mysli.-SPb., 1995. = Issue 2, p.301