Ìàòåìàòèêà/4.Ïðèêëàäíàÿ ìàòåìàòèêà
O.F. Ryaboshtan,
Ph.D. A.M. Milenin, Ph.D. S.M.
Skofenko
Kharkov National Technical
University of Agriculture after P. Vasilenko
Differential equations manifold surface of gas turbine blades
Consider the set of surfaces
![]() ,
, ![]() (1)
(1)
where the ![]() - factors that affect both the shape and the position
of the turbine blades.
- factors that affect both the shape and the position
of the turbine blades.
Try to determine the differential
equation of all varieties envelope surfaces, which can be obtained from a given ![]() - parametric set. Differentiating (1) with respect
- parametric set. Differentiating (1) with respect ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
![]() (2)
(2)
For the two-parameter set (1) is
sufficient (1) and (2) delete parameters ![]() and
and ![]() . We obtain the differential equation in partial
derivatives of order I, for which (1) is a complete integral. To obtain
. We obtain the differential equation in partial
derivatives of order I, for which (1) is a complete integral. To obtain ![]() equation containing only variables
equation containing only variables ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and the partial derivatives
and the partial derivatives ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() need to equations (2) to apply well-known algorithm
and equate
need to equations (2) to apply well-known algorithm
and equate
![]() (3)
(3)
And see equations (1) - (3) together.
In more detail, equation (3) has
the form:
![]() . (4)
. (4)
At ![]()
![]() equation (3) to differentiate to the desired number of
times until the number of equations (together with (1) - (3)) will be
equation (3) to differentiate to the desired number of
times until the number of equations (together with (1) - (3)) will be ![]() . From the resulting system of equations exclude
. From the resulting system of equations exclude ![]() coefficients
coefficients ![]() To give the desired differential equation.
To give the desired differential equation.
However, in many cases, the design
of engineering surfaces do not need to search for an equation that does not
contain parameters ![]() . On the contrary, the parameters must be secured in
order to meet given geometric conditions, and differential equations need to
make such an order, given what extent differential conditions.
. On the contrary, the parameters must be secured in
order to meet given geometric conditions, and differential equations need to
make such an order, given what extent differential conditions.
At that time, when the differential
equation which does not contain ![]() for this (1), is the only equations with parameters,
you can obtain an infinite set.
for this (1), is the only equations with parameters,
you can obtain an infinite set.
For example, for a plurality of
areas of constant radius ![]()
![]() (5)
(5)
have
![]() ,
, ![]() (6)
(6)
from where
![]() (7)
(7)
or
![]() (8)
(8)
The differential equation for (5),
does not contain the coefficients ![]() has the form:
has the form:
![]() (9)
(9)
and expresses the differential
conditions for all of canal surfaces radius ![]() .
.
For a set of conical surfaces
![]() .
(10)
.
(10)
The only differential equation that
does not contain the coefficients ![]() has the form:
has the form:
![]() . (11)
. (11)
For a set of conical surfaces of
revolution
![]() (12)
(12)
Partial differential equation that
does not contain the coefficients ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() is
is
![]() (13)
(13)
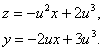 (14)
(14)
To determine the edge of
regression, it is necessary from the equations (14) to differentiate ![]() and the resulting equation for
and the resulting equation for ![]() considered in conjunction with (14).
considered in conjunction with (14).
![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() . (15)
. (15)
Above the surface of the blades
allows the construction of raised their special lines (curvature, transition,
etc.). In this case, as previously indicated, it is necessary
to take appropriate equipment curve and apply equation (13).
We consider the problem of constructing
the blade surface, which passes into the surface of the hub
![]() ,
, ![]() .
(16)
.
(16)
It is assumed that there are a lot
of planes, moving from ![]() to
to ![]() .
.
Is the condition of tangency of the
plane (1) to the surface (16)
![]() ,
, ![]() , (17)
, (17)
![]() ,
, ![]() . (18)
. (18)
Ruling out ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (coordinates of the point of contact with the surface
(coordinates of the point of contact with the surface ![]() ) (1)
) (1) ![]() and (17) we obtain the dependence
and (17) we obtain the dependence
![]() (19).
(19).
Similarly, from (1) ![]() and (18)
and (18)
![]() (20)
(20)
Considering together (19) and (20),
determines the dependence of the two factors in the third example
![]() ,
, ![]() . (21)
. (21)
Substitute in (1) and determines
the desired surface envelope of the set of planes (1) with (21).
Note that the above algorithms can
refuse in some cases more simple compared to previously developed. A common drawback is the complexity of analytic
transformations, difficulties with the exclusion of parameters. The way out of this difficulty can be:
- go to the interpolation and approximating
methods;
- develop a method elementating
design, widespread problems in the surface profiling of gas turbine blades .