Lazaruk O.V.
Bukovinian State Medical
University,
Department of
Pathological Anatomy
Chernivtsi (Ukraine)
EXPRESSION VIMENTIN LIPOCYTES AND CELLS OF LEUKOCYTE INFILTRATION IN THE
STROMA OF TUMOUR AND TISSUE AROUND A TUMOUR IN THE DUCTAL BREAST CANCER
Tumour site of the ductal breast
invasive carcinoma is composed of clusters of neoplastic epithelial cells, which
are separated with strands of connective tissue. The latter performs a very
important role in tumour growth, invasion and metastasis; forms a frame that
separates the tumour structure and nourishes the tumour cells in blood vessels
[1, 2]. Tumour connective tissue differs from normal with the the presence of
multiple loops vessels, their blind processes. High expression of vimentin is
observed in various epithelial carcinomas and tissue around the tumour,
including breast cancer. Vimentin in tumours correlates with tumour cell
proliferation, invasion and poor prognosis [1, 3]. In recent years, vimentin
was important as a marker of epithelial tumours [3, 4]. Determination of
vimentin expression may be useful in clarifying the maturity of cells of
mesenchymal origin, including cells that belong to leukocyte infiltration in
the stroma of ductal breast carcinoma tumour and tissue around the tumour.
Object of investigation: to determine the
expression of vimentin features in leukocyte infiltration zone cells of the tumour
site and tissue around the tumour; to investigate epithelial-mesenchymal
transformation.
Materials and methods. The material obtained
owing to surgical removal of breast tumours was immediately sent to the
histological laboratory. At the same time tissue fixation was performed in
buffered formalin and alcohol group. The fixed material was filled in paraffin
blocks. Sections were prepared at microtome (MS-2) size 5-7 micron, were fixed
and subject to special glasses. Next 20 hours after histological confirmation
of the diagnosis by standard protocol DAKO were performed immunohistochemical
studies to vimentin receptors in cells of leukocyte origin.
Results of investigation and their discussion. In evaluating the results of noteworthy special vimentin expression in
the cell wall of lipocytes. The intensity of coloring chromogen the wall cells
of lipocytes divided into 4 types: Type I - lipocytes, in which expression of
vimentin wall is negative. Most of these lipocytes are located singly in the
thick clusters of tumour cells; Type II - lipocytes with little color of the
cell wall; Type III corresponds to the second type as to the cell wall in color,
but there are available area in the form of granules of rich brown colour in
the cell wall; Type IV is characterized by accumulation on the lipocytes
membrane rich brown granules. This cell type is located mostly on the periphery
of the tumour site. The accumulation of these "granules" located on
the outside and inside the cell membrane. In addition to heterogeneous
expression of vimentin we observe thickening
of the lipocytes membrane.
Leukocyte infiltration in tumour and
tissue around the tumour is characterized by an accumulation of cells. The
degree of positive expression of vimentin can be divided into 4 groups. I group
- cells with negative expression of vimentin; ІІ group - with few positive
expression of vimentin; III group - characterized by a moderate expression of
vimentin; IV group - with a pronounced expression of vimentin. The intensity of
color from 0 to III scores. Group I - cells colored with hematoxylin and have no
shades of brown (0 points), second - on a background of blue color visible
brown shade (1 point), III - color brown (2 points), IV reddish-brown (3
points).
Conclusions. There are 4 types of
lipocytes with individual features of vimentin expression in tumour and tissue
around the tumour invasive ductal breast cancer. The expression of vimentin varies
in lipocytes. This may indicate a close relationship between changes in adipose
tissue and tumour cell proliferation, the influence of one tissue to another
with further amendments.
Cells of leukocyte infiltration in
tumour and tissue around the tumour invasive ductal breast cancer for feature
positive expression of vimentin divided into 4 types. This may indicate the age
of the cells, youth leukocytes have a pronounced expression to vimentin.
Literature
1. Swerdlow S.H., Campo E., Harris N.L. (Eds). et al.
(2011) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues.
IARC Press, Lyon. P. 439.
2. Siegel R. Cancer statistics, 2013 / R. Siegel, D.
Naishadham, A. Jemal // CA Cancer J. Clin. - 2012. - Vol. 62. - P. 10-29.
3. M.Y. Davydov, V.P. Letyahyn (2013) Cancer breast
gland, Moscow. P. 456.
4. Paltsev M.A., Anichkov N.M. (2001) Patological
Anatomy. Medicine, Moscow, Vol.2, Part 1. P. 710-731.
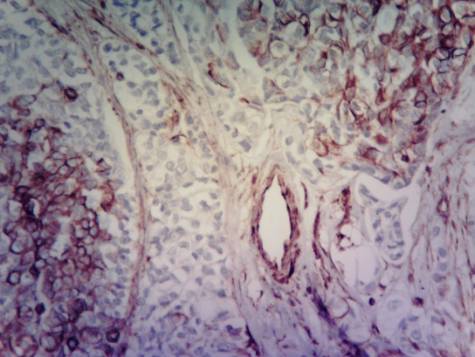
Carcinoma
ductal breast cancer. Tissue around
the tumour. Accumulation of
cells of leukocyte infiltration with different degree of expression.
Immunohistochemical technique for vimentin.
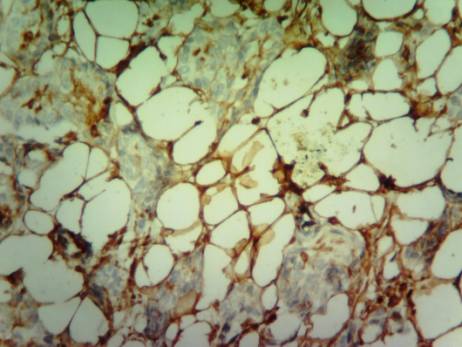
Carcinoma ductal breast cancer. Tissue
around the tumour. There are
vessels with bright brown staining in all layers of
the cell walls in places where vimentin-positive
lipocytes existing. Immunohistochemical technique for vimentin.