Performed by:
student of KhNUE
I.S. Sedlovskyi
Scientific director: prof. I.V. Zhuravlyova
One of the priorities of any business in a modern market economy is to improve working capital management. High
cost and complexity of traditional methods of raising funds necessitates
optimization of enterprise
financial policy by means of searchig for new sources of
working capital, the growth rate of their turnover .
The analysis of the dynamics of current assets and their
elements led to do the conclusion, that national enterprises characterized by the tendency of increasing of receivables
(see Fig. 1.1). Thus, in the period from 2005 to 2012, trade receivables
of domestic enterprises increased more than in 2.5 times (from 316.956 billion. to 705.200 billion.). The share of receivables in the
total current assets reached 62.3%. This situation is due to the two following reasons. Firstly, the market
economy is characterized in the desire of companies to expand markets, increase sales and attract new
customers.
Supplier has a conflict of interests in case of
postponement: on the one hand the commercial loan promotes the growth in sales
and increases profits, but on the other hand - there are a number of new
problems. Rising receivables leads to "freezing" of working capital,
which increases the duration of their turnover. In addition, the supplier has a
"cash gaps" reduce liquidity and financial stability; he assumes the
risk of default of payment, which is due to insolvency of the buyer etc. Thus,
the company needs to replenish working capital, which can be achieved using the
following financial instruments (see Fig.1.1)
Own funds Commercial loan Bank loan Overdraft Factoring
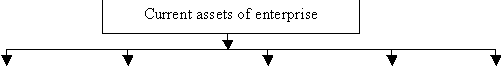
Fig. 1.1. Formation instruments of current
assets [27, p.55]
All of the
financial instruments have specifics and reasonable conditions of use. Analyzing
the peculiarities of each instrument, choosing any of them should be guided by
the general financial policy of the enterprise.
It should be
noted that the interpretation of factoring presented in the relevant legal
acts, is somewhat narrowed.
According to the
"Convention on International Factoring", to which Ukraine acceded in
11.01.06, factoring involves performing at least two of the following features:
credit in the form of prepays debt claims, and cash collection of debts (credit
management), insurance against the credit risk.
The
most common view is factoring as commission and brokering. Factoring is often
determined as operations related to intermediary refusal for unpaid payment
claims for goods (works, services) and, accordingly, the right to receive
payment for them that is collecting receivables.
The other view
interprets factoring as financial services. According to this view, factoring
take a special place among the operations with financial assets, along with
leasing, insurance and trust services. Also the Law of Ukraine "About
Financial Services and State Regulation of Financial Services" interprets
factoring as the category of financial services.
The another one
view consider factoring as an activity or a complex of services, which provides
specialized financial institution in exchange for the assignment of
receivables.
Taking into
account the provisions of the UNIDROIT Convention and the results of the
analysis, factoring is defined as a financing method in which a business owner
sells accounts receivable at a discount to a third-party funding source to
raise capital.
In each case
organization of factoring services has its own features, which depend on a
number of factors that determine the type of factoring. However, the typical
mechanism of factoring can be generally reduced to next. Three participants are
involved in the implementation of factoring agreement:
the factor –
intermediary (a bank, specialized financial institutions or an individual
(entrepreneur));
the supplier (in the process of
factoring agreement becomes a factors client);
the buyer (serves as the debtor in
factoring contract).
Factoring is presented schematically
in Fig. 1.2.
Factor Buyer Supplier
![]()

Su 1

2 3 5 4
Where: 1.
Selling goods on deferred payment; 2.
Debt rights assignment; 3. Down
payment (app. 90%); 4.
Delivered goods payment; 5. Fund
balance payment (app. 10%).
Fig. 1.2. Schematically presented
factoring
1.
Внукова Н. М. Можливості та ризики
факторингу в ракурсі SWOT- аналізу
/ Н. М. Внукова, К. Шапошникова // Фінансовий ринок України. – 2007. - №2 (40).
– С. 6 – 11.
2.
Внукова Н.
М. Основи факторингу: навч. посіб. [для екон. та фін. вищ. навч. закл.]
/ Н. М. Внукова. – К.: Т-во “Знання”,
КОО, 1998. – 174 с.
4.
Все о кредитоспособности заемщика
[Електронний ресурс]. – Режим доступу:
http://www.
solvency. boom. ru/ 4mepthod. html.