Ýêîíîìè÷åñêèå íàóêè / 10. Ýêîíîìèêà ïðåäïðèÿòèÿ
À. Gerassimenko, L. Sorokina
D. Serikbayev East Kazakhstan State Technical University
Assessment
of organizational financial and economic state as a basis for its innovative
development
Limited partnership enterprise «Epidbiomed» was registered in the
institution of justice on May 20, 1999 as a subject of small business. It is
located in the Republic of Kazakhstan, East Kazakhstan region, Ust-Kamenogorsk,
on Kanysh Satpayev street, district ¹ 25.
The main line of business
of the limited partnership «Epidbiomed» is import of medical equipment,
medicine and other medical products from Ukraine and Russia and their
distributing across Kazakhstan. The major consumers of the enterprise are state medical institutions,
private clinics, business people and individuals.
The enterprise
stuff is 8 people: a director, a senior accountant, a customs specialist, 2
sales managers, a pharmacist, a pharmaceutist and a technical specialist.
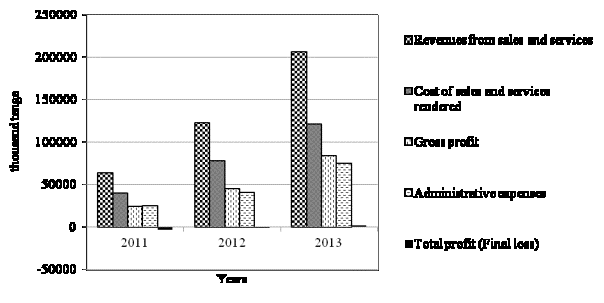
The enterprise profit-and-loss report analysis makes us notice that the
expenditures on sales and service tend to increase. In 2013 product sales and
service expenditures increased by 142118 tenge or 69%. The similar tendency is
observed in the dynamics of gross margin and administrative expenses. There
were no significant changes in financial and other expenses. In 2011 they
experienced the decline before taxation; both 2011 and 2012 faced the declines
after paying a corporate income tax. The very negative effect is connected with
the increase of administrative expenditures, the feature article of which was
writing off inventories. It was caused
by the Ukrainian partner’s postponed licensing of medicine. In 2013 they gained a positive total work
effect – income of 2167 thousand tenge.
The graphic presentation of profit-and-loss report data of limited
partnership «Epidbiomed» and its dynamics for a 3-year period is shown on
picture 1.
Picture 1. Dynamics of
profit-and-loss report data
of limited partnership «Epidbiomed» for
2011-2013 years
The
horizontal analysis of «Epidbiomed» balance sheets proved that the changes in currency
of assets and liabilities occurred without any certain tendency. In 2012 they
experienced a drop of means and sources of their financing equal to 3076
thousand tenge or 5,8%, but in 2013 there was an increase by 10879 thousand
tenge or 16,9%.
The
most relevant changes in the structure of short-term commitments happened as a
result of decreasing other short-term commitments. The short-term account
payable was cut down by 19791 thousand tenge. It proves the growth of company’s
private assets and strengthening of economic independence. In the structure of
long-term commitments did a significant change occur, such as the increase of
long-term financial commitments by 69,8%.
The
absolute capital value of 2012 declined by 748 thousand tenge because of the
retained income, in 2013 there was a growth by 2167 thousand tenge or 20,3%.
The vertical analysis of balance sheets showed that
the assets are characterized by the prevailing unit weight of short-term assets, the share of which in 2011 was 98,9%
out of all enterprise assets. Such correlation is typical for trade
companies because they neither produce anything nor need a good amount of major
assets [1]. By the end of 2013 the correlation of short- and long-term assets
became almost the same. The main share of assets refers to resources. During
the period under study their unit weight is decreasing in the whole number of
assets that is caused by company’s successful sales rate. The main assets are
about 1% out of all company’s assets in 2011; within the time span from 2012 to
2013 their share in total quantity has increased.
Own
capital equals approximately 16% of all balance liabilities, the largest share
of which was16,57% in 2013.
The
company’s loan capital draws up the biggest part of the total amount of
liabilities; the greatest unit weight is for short-term account payable. During
the very period the share of account payable tends to decline. If in 2011 it
was 63,84%, so in 2013 – 25,35%. We can explain the fact that the enterprise
has decreased the amount of external debts. Due to 3-dimensional figures of
financial soundness we could make a conclusion that during the whole analyzed
period the enterprise has been financially unsound. The data are shown in table 1.
|
Table 1 Characteristics of financial stability of limited
partnership «Epidbiomed» |
||||||
|
Indexes |
Years |
Variation |
||||
|
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2012/2011 |
2013/2012 |
2013/2011 |
|
|
1 Equity capital, ths. tenge |
9248 |
8500 |
10667 |
-748 |
2167 |
1419 |
|
2 Fixed assets and
investments, ths. tenge |
608 |
33730 |
30616 |
33122 |
-3114 |
30008 |
|
3 Availability of working
capital (Aw), ths. tenge |
8640 |
-25230 |
-19949 |
-33870 |
5281 |
-28589 |
|
4 Long-term borrowings,
ths. tenge |
10604 |
31362 |
35074 |
20758 |
3712 |
24470 |
|
5 Availability of own
long-term and medium-term debt sources of inventory and costs (At) , ths.
tenge |
19244 |
6132 |
15125 |
-13112 |
8993 |
-4119 |
|
6 Short-term loans and
borrowings, ths. tenge |
36714 |
13629 |
18628 |
-23085 |
4999 |
-18086 |
Table
1 (continued)
|
7 Total value of the
major sources of inventory and costs (AΣ), ths. tenge |
55958 |
19760 |
33753 |
-36198 |
13993 |
-22205 |
|
8 Total value of stocks
and costs, ths. tenge |
50700 |
18957 |
24131 |
-31743 |
5174 |
-26569 |
|
9 Excess (+) or lack (-)
of working capital (+-Aw), ths. tenge |
-42060 |
-44187 |
-44080 |
-2127 |
107 |
-2020 |
|
10 Excess (+) or lack (-)
of own long-term and medium-term debt sources of inventory and costs (+-At),
ths. tenge |
-31456 |
-12825 |
-9006 |
18631 |
3819 |
22450 |
|
11 Excess (+) or lack (-)
of Excess (+) or lack (-) (+-AΣ), ths. tenge |
5258 |
803 |
9622 |
-4455 |
8819 |
4364 |
|
12 Ternary type indicator
of the financial situation (S) |
(0, 0, 1) |
(0, 0, 1) |
(0, 0, 1) |
- |
- |
- |
The analysis of balance liquidity showed that the
company’s balance is not absolutely liquid. That
means that the company is not able to fulfill all its commitments within the
shortest period of time, because liquidity correlation is not followed through
the period under study: À1 ≥ L1, À2 ≥ L2, À3 ≥ L3, À4 ≤ L4 [2]. The
analysis of balance liquidity is shown in table 2.
|
Table 2 Characteristics of balance sheet liquidity of limited partnership «Epidbiomed» |
|||
|
Indexes |
2011 year |
2012 year |
2013 year |
|
Assets |
|||
|
The most liquid assets |
3060 |
777 |
998 |
|
Quickly realizable assets |
737 |
436 |
1108 |
|
Slowly realizable assets |
52161 |
18546 |
31647 |
|
Sticky assets |
608 |
33730 |
30616 |
|
Balance |
56566 |
53490 |
64369 |
|
Liabilities |
|||
|
The most urgent liabilities |
36111 |
12996 |
16320 |
|
Current liabilities |
603 |
633 |
2308 |
|
Long-term and medium-term
liabilities |
10604 |
31362 |
35074 |
|
Table
2 (continued) |
|
|
|
|
Permanent liabilities |
9248 |
8500 |
10667 |
|
Balance |
56566 |
53490 |
64369 |
|
Surplus or lack |
|||
|
À1 – L1 |
-33051 |
-12219 |
-15322 |
|
À2 – L2 |
134 |
-197 |
-1200 |
|
À3 – L3 |
41557 |
-12816 |
-3427 |
|
À4 – L4 |
-8640 |
25230 |
19949 |
During the analyzed period calculated results
of funding ratio proved that company’s own capital does not exceed the loan one,
therefore company’s financial soundness was on a dangerous level:
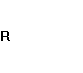 =
= ![]() =
0,195;
=
0,195; 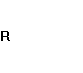 =
= ![]() =
0,189;
=
0,189; 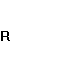 =
= ![]() =
0,198.
=
0,198.
The calculation of financial leverage ratio
showed a significant excess of loan capital over the own one, that in turn
explains a good opportunity to use a financial leverage – to increase the
profitability of own capital with using borrowed means. At the same time, the necessary condition of
company’s capital efficiency increase is a positive difference between assets
profitability and bank credit interest rate in favor of the former item [4]:
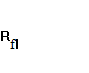 =
= ![]() =
5,117;
=
5,117; 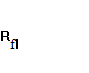 =
= ![]() =
5,293;
=
5,293; 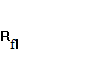 =
= ![]() =
5,034.
=
5,034.
The value of
current liquidity ratio depicted a positive tendency that is viewed as a
beneficial factor. The company is able to fulfill its current commitments by means of
short-term assets. Due to the specifics of «Epidbiomed» business the calculated
figures are normal, because in the assets structure of trade company are inventories:
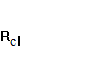 =
= ![]() =
1,524;
=
1,524; 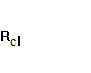 =
= ![]() =
1,45;
=
1,45; 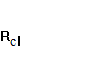 =
= ![]() =
1,812.
=
1,812.
However, the quick
assets ratio of the period is lower the optimal bound, hence, the company is
unable to fulfill all the commitments by means of cash and short-term debit
debts:
![]() =
= ![]() =
0,103;
=
0,103; ![]() =
= ![]() =
0,089;
=
0,089; ![]() =
= ![]() =
0,113.
=
0,113.
The calculated value of circulating assets
turnover ratio states the growth of company’s business activity through the
analyzed period. The enterprise gains the profit that exceeds its circulating
assets in 6 times in 2012 and 2013:
![]() =
= ![]() =
1,15;
=
1,15; ![]() =
= ![]() =
6,25;
=
6,25; ![]() =
= ![]() =
6,12.
=
6,12.
During 2011-2013 the turnover period
dramatically dropped, so it influences positively the company’s business
activity, because it takes less time to get the profit of circulating assets:
![]() =
= ![]() =
313;
=
313; ![]() =
= ![]() =
57;
=
57; ![]() =
= ![]() =
59.
=
59.
The group of profitability ratios has got the
same positive tendency, because they use the same profit indicator in
calculations. The figures are given in table 3.
Table 3
Profitability ratios of limited partnership «Epidbiomed»
|
Indexes |
Years |
Variation |
||||
|
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2012/2011 |
2013/2012 |
2013/2011 |
|
|
1 Return on sales, % |
-2,81 |
0,81 |
2,06 |
3,62 |
1,25 |
4,87 |
|
2 Return on costs, % |
-7,15 |
-0,96 |
1,78 |
6,19 |
2,74 |
8,93 |
|
3 Return on
current assets, % |
-5,21 |
-3,79 |
6,42 |
1,42 |
10,21 |
11,63 |
|
4 Return on equity, % |
-31 |
-8,8 |
20,32 |
22,2 |
29,12 |
51,32 |
The calculated Altman’s five-factor model of business bankruptcy
likelihood shows that the company is unlikely to go bankrupt, as the lowest
ratio exceeds the bottom limit of bankruptcy likelihood (1,23) [3]:



To summarize the company’s business analysis, we can
state that during the analyzed period there was an increase of assets and
liabilities currency by 7803 thousand tenge or
12,1%, also the profit from
product sales and services grew by 142118 or 69%. The company has a got a good
opportunity to use the effect of financial leverage by increasing the
profitability on the whole. The calculated data of company’s profitability and
business activity tend to develop positively, so it proves the growth.
Still, in spite of it, during the analyzed period
«Epidbiomed» does not own enough assets, and, as a result, it influences
company’s financial soundness. The calculated Altman’s models show that with
such an unsound financial situation the company is unlikely to go bankrupt.
References
1 V. Kovalev. Financial
analysis. – Ì.: Finance and Statistics, 2008.
2 N. Plaskova. Economic analysis. – Ì., EKSMO, 2010.
3 K. Raitsky. Economics of
enterprise. – Ì.: Marketing, 2009.
4 G. Savitskaya. Analysis of the economic performance of an enterprise.
– Ì.: INFRA-M, 2005.