Ñîâðåìåííûå èíôîðìàöèîííûå òåõíîëîãèè/
3.Ïðîãðàììíîå îáåñïå÷åíèå
Zharmagambetova G.Î.
Kostanay State
University of A. Baitursynov, Kostanay
AUTOMATION CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT
The main task of the higher education system is
meeting the needs of professionals in the desired.
Models allow us to find the optimal structure of the
learning process based on the goal. Means of optimizing training are: the
selection of training content and sequencing in the study of academic
disciplines, strong links and relationships between objects and types of
learning.
Thus, simulation learning process is not only
desirable but necessary. Without studying the structure and content of
education in modern conditions is impossible quality training.
The aim appears as the main criterion for selection of
tools and methods-ing organization of the educational process. It is a landmark
and a criterion for determining the extent to which the outcomes of the
learning process.
The main purpose of the system of higher education is
and Professional training of highly qualified specialists in accordance with
the social order. Therefore, it sets the professional activity and determines
the learning objectives of all disciplines, and hence both the content and the
structure and forms of relevant learning activities of students preparing for
this professional work. To improve the educational process necessary to
accurately constructed model, if not formal, at least in the form of a fairly
complete list of the basic properties, qualities and abilities of a specialist.
In this case, the content of the specialist training
should be built as a complex target program, focused on outcomes, rather than
as a simple sum of independent disciplines.
![]() (1.1)
(1.1)
m - number of s in the specialty;
![]() - content i-discipline;
- content i-discipline;
SO - content
of learn.
By the
quality of graduates universities, we mean a system of property professionals,
which determines the suitability to meet the social needs.
![]() (1.2)
(1.2)
![]() - property of specialist.
- property of specialist.
The
process of memorizing meaningful influenced by factors such as the structure of
the material, the formation of an association between the concept-sfi usage
concepts. But not only the consistency of presentation affects the storage
material. It is known that the process of learning and forgetting information
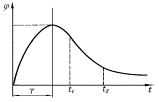
can be represented in the simplest case of the curve shown in Fig. 1.1.
Ascending
branch of the curve corresponds to the process of perception, Descending, ducting
- forgetting. The time corresponding to the greatest amount of information held
in memory (T) - this time the end of the presentation. Immediately after that
begins the process of forgetting. The whole process is described by the equation: ![]() (1.3)
(1.3)
l1 and l2 - parameters
depending on the quantity and quality of associative connections and
statistical characteristics of forgetting.
Function t ®∞ j(l1,l2,t)®0, corresponding to
a total forgetting information after a sufficiently long period of time.
An important role in remembering plays
periodic repetition of information. The latter occurs in the course of
self-study, laboratory and workshops, as well as repeated references lecturers
on familiar material.
Fig. 1.1
Empirically found that the material has been successfully recall, the
EU-whether the volume remains in the memory information is not less than 0.7
times the original: j³0.7j0. Time in which the
memory is less information, depending on the parameters of information, but one
thing is clear: the less time between repetitions of the information, the
stronger the material covered and absorbed by the new material based on the
creation of associative connections in the understanding of the student.
Analyzing Fig. 1.1 can be seen that, if the presentation of the concept
requires the concept of j i, then at some time t2 after time t1 after the
presentation of the concept of i, it becomes available for perception, because
in the memory of the student have less than 0.7 times the original volume of
information.
If there is a single repetition of the material, the curve will have the
form shown in Fig. 1.2.
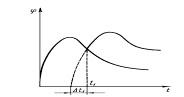
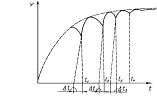
Fig. 1.2 Fig. 1.3
Under
repeated, resulting in the formation of stable associative links, the curve can
be approximated by the dotted around the curve in Fig. 1.3.
Based
on the above, we can conclude: the smaller the time interval will be divided
interconnected concepts, the better it is for mastering the material.
References
1. Kagan V.I. Fundamentals of optimizing the learning process in higher
education, 1987.
2. Tinbergen Jan, Bos
H.S. Blum James, Emmerij Lonis, William Gareth
Econometric Model of Education. Some Applications. Paris, OESD,
1965.
3. Agranovich B.L. The
model estimates the quality of training in higher educational institutions,
1987.