Ìàòåìàòèêà / 5. Ìàòåìàòè÷åñêîå ìîäåëèðîâàíèå
Kakzhanov
M.U
Using mathematical methods
in reliability theory
Reliability theory [1] - the science of how to ensure
the conservation and reliability in the design, manufacture and operation of
systems. A necessary condition for the simulation of the Elements of
reliability theory is the use of mathematical methods.
Quantitative indicators of reliability of elements and
systems include:
- reliability coefficient Rã
;
- the probability of failure-free operation for a specified time P(t); ;
- mean time to first failure Òm for non-repairable systems;
- MTBF for tñð
recoverable systems:
- the failure rate λ(t);
- mean time to repair τm;
- recovery rate μ(t);
- reliability function Rã
(t).
Definitions of these values:
Rã - the probability of detecting the product in an efficient condition.
P(t) - the probability that in a given
period of time (t) the system does
not fail.
Òm - mean time to the first
system failure.
t m - mean operating time
between successive failures of the system.
λ(t) - the expected number of failures
per unit time; for easy flow of failures:
λ(t)= 1/ tm.
τm- the expectation of
recovery time.
μ(t) - the expected number of rebounds
per unit time:
μ(t) = 1/ τm
Rã
(t) - the change in the system reliability over time.
Systems for the purposes of calculating reliability
are grouped into several following criteria using the mathematical apparatus of
queuing systems (QS)
- with periodic maintenance - system in which measures
to ensure reliability are realized only during scheduled maintenance work at
preset intervals that Òî
;
- with a random period of service - systems in which
the measures to ensure the reliability implemented at random intervals;
Depending on the mode of "a compound" of
elements in the flowchart distinguished: a. serial (basic compound); b.
parallel (redundant connection); in a. combined (in the flowchart holds primary
and redundant connection elements); see. Fig. 1.
|
à. |
1 |
|
2 |
|
….. |
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
á. |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
….. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
… |
|
n |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
…. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
… |
|
n |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
1. The structures of systems for
the purpose of calculating reliability.
Redundant system structures referred to are those in
which the failure occurs when the failure of all or a certain number of
elements that make up the system.
Redundant
structures may be shared with redundant elements of redundant groups and
element-wise redundant (see. Fig. 2, a., B., C.).
|
à. |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
á. |
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
â. |
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Figure 2. Options for backup systems.
As shown by the experimental data carried out in
various fields of technology, the flow of failures and recoveries is the
simplest [2], has ordinary, stationary
and lack of aftereffect.
Reliability of complex systems is subject, as a rule,
exponential, which is characterized by dependency:
- the probability of failure-free operation: ![]()
- distribution function uptime: ![]()
- density distribution uptime: ![]()
These dependencies
correspond to simple flow failures and are characterized by constants:
- The failure rate λ(t) = const; Recovery rate μ (t) = const; MTBF tm = 1 / λ (t) = const; Time to repair τsr = 1 / μ (t) = const.
The parameters λ (t), tm; μ (t) and τsr - prepared by treatment of a number of variations on the work
chronometer observation elements and systems.
Reliability coefficient element is determined according to the
statistical treatment of variation series by the formulas:
 or
or  (1)
(1)
as well as in terms of intensity and failure recovery λ (t) and μ (t):
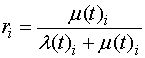 (2)
(2)
Reliability
characteristics of elements in the technical and technological relations are
the coefficients of technical ròi and technological rci reliability elements. Reliability element is
determined by the following relationship:
rãi = ròi ·rci . (3)
Reliability
of the main systems (series-connected cells) is determined by the presence of
only technical failures dependence:
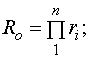 (4)
(4)
when
reliability elements:
![]() (5)
(5)
where n -
the number of series-connected elements in the system;
In the calculations of quantitative indicators and
composite structures redundant systems is necessary to know not only their
reliability, but also unreliable elements; because the reliability ri and unreliability qi element
determines the sum of probabilities, forming a complete group, equal to one,
then:
qi = (1 - ri). (6)
The unreliability of the redundant system (for
parallel connection of elements) is defined as the probability that all
elements of the system failed :
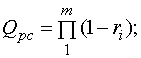 (7)
(7)
Accordingly, reliability, determine the dependence:
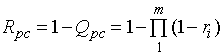 (8)
(8)
Or, if
reliability elements
![]() (9)
(9)
where m - number of redundant
elements.
The degree (m +
1) for calculating the reliability of the system because the system is one
element is required, and the number of backup can vary from 1 to m.
Reliability of redundant systems combined with the
overall redundancy (system redundancy) defined by the relationship:
 (10)
(10)
at reliability elements (hence, subsystems):
![]() (11)
(11)
Reliability combined
systems with redundant groups of elements determined sequentially; first
determined the reliability of redundant subsystems, then - the reliability of
series-connected subsystems.
Reliability combined
systems with element-wise (separate) redundancy is determined sequentially;
first determined the reliability block elements (element redundant one, two,
and so on up to m elements), then -
the reliability of series-connected block elements.
Reliability block element is:
![]() (12)
(12)
Reliability combined with Rêj system is element-wise reservation:
 (13)
(13)
Or, if
reliability elements
![]() (14)
(14)
The Literature:
1. Methods of technical decisions: Trans. with nem.- Mushik E., P.
Muller, M .: Mir, 1990. - 208 S.
2. The reliability and effectiveness of the technique:
A Guide In 10 v. V. 5 Design analysis reporting / Ed. VI Patrushev and AI Rembeza.
M. Machinery, 1988.- 224 pp