Gladky F. F., DPhil, professor, Chumak O.P., candidate of technics,
DPhil, professor, Markov K. V., junior research fellow, Gasuk K. V., senior staff
scientist,. Usichenko O. V, master
National Technical University “
Kharkov polytechnic institute”, (Ukraine)
To question about enzymatical technology of
modification and refining of fats
Transformation
of accompanying to fats substances (phospholipids, fatty acids) using enzymatic
preparations was studied and the results of such transformations were analysed.
During the research there were determined new ways for developing of refining
methods, main regularities in fats (acylglycerines) enzymatic transformation
like ethanolysis and hydrolysis. Modifying of acylglycerines was carried out by
their interesterification with the appropriative esters using specific
lipolythic enzymatic preparations, that allowed producing of special
confectionary fats of high quality.
Рассмотрены результаты исследований преобразования
сопутствующих жирам веществ (фосфолипидов, жирных кислот) с помощью ферментных
препаратов. Определены новые пути развития методов очистки жиров, основные
закономерности преобразования жиров (ацилглицеринов) под влиянием ферментов, в
частности етанолиза и гидролиза. Осуществлено модифицирование ацилглицеринов
путем переэтерификации с этиловыми эфирами
соответствующих жирных кислот при участии специфических липолитических
ферментных препаратов, что дало возможность получения специальных кондитерских
жиров высокого качества.
Presently in Ukraine as wells in
other countries, fats are refined from accompanying substances with traditional
methods which are based on usage of alkalis, acids, etc.
A part of accompanying substances
are extracted from fats in vacuum/ This process is highly energy consuming and
produces waste substances. Thus, studing and research of substances
accompanying to fats is an important problem.
The substances which accompany to
acilglycerines in fats are: fatty acids, waxes, phospholipids, coloration,
taste- and odour related substances: sterols, non-specific accompanying
substances.
The object to research is a group of
activated and water soluble enzymes, both specific and non-specific, and substances
accompanying to fats like phospholipids and fatty acids.
All the exiting methods and
technologies of enzymatic hydrotation are based on the reaction of oil
phospholipid hydrolysis usingphospholipases hydrolase subclass enzymes
(according to the international
classification К. Ф
3.1).
They catalyze the the process of
transforming of phosphorous-containing compounds (contained in fats, so-called
phosholypids), i. e. stimulate the reactionof hydrolysis of ester-link in a
phosholypid molecul. Among them are, phospholipases A1, A2,
C and D which differ from each other in their ways of influencing the
substrate.
The fundamental mechanism of enzymes
influencing phospholypids looks like:
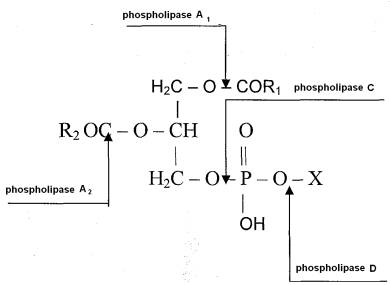
where R1, R2 – saturated
or unsaturated oil carbonic remainder of fatty acids;
X – hydrogen, nitrogen base or polyol
remainder.
Phospholipases
A1 (К.Ф. 3.1.1.32, phosphatid-1-acilgidrolases), catalyze
hydrolysis of phospholypid molecule’s ester-link in α-position. They are
contained in pancreatic gland juice of animals and people [1].
Phospholipases A2 (К.Ф. 3.1.1.4,
phosphatid-2-acilgidrolases), which catalyze hydrolysis of phospholypid
molecule’s ester-link in β-position are divided into 3 classes: venom
enzymes (insects, snakes, scorpions, bees, etc); grass enzymes; intracellular
which are contained in plants and microorganisms tissues [2]. They differ
substantially in structure, substrat specificity, biological effects, and
physicochemical properties [3]. An active and the most studied enzyme of this
type is contained in venoms [1-4].
Phospholipases A2 (К.Ф. 3.1.1.4.3, catalyze
hydrolysis of molecule’s ester-link between diacylglycerin and substitute
phosphoric acid; well-known phosphatidilholine-holinephosphohydrolasa and
phosphatidilinizitol-inozitolhosphohydrolasa) are contained in bacterial
toxins. It was found in tissues of animals, including brain tissues in little
quantities in bound state [1,5,6].
Phospholipases A2 (К.Ф. 3.1.4.4, catalyze
hydrolysis of molecule’s ester-link between
phosphatic group and alcohol in a phospholipid molecule) is contained in
plants’ tissues (cabbage, roots of radish, cotton plant seed, etc), as well as
in tissues of some animals like rats.
After having analyzed an assortment
of phoshpolipase and having studied a proposition of enzymatic specimens on
the market , it was decided to choose the industrial phospholipase A specimens (produced by Denich “Novozymes” company) and available in Ukraine titled
phospholipase.
The target was to: 1) define the
conditions for using hydrolyze-type enzymes for producing phosphoypidic lysoforms and etherification of fatty acids, contained in fat; 2)
identifying main regularities of fat
accompanying substances bioconversion.
The main scientific results of the
performed research consist in identify regulation of substances accompanying to
fats – phospholipids and fatty acids using lipolitic enzymes. Also there were
calculated content and composition of phospholypids and fatty acids in new
breeds of sunflowers, provided by Ukrainian Academy for agricultural sciences.
It was investigated kinetics of
phospholipids hydrolysis and the maximal speed of this reaction was calculated
as well as effective temperature and Michaelis constant.
It was proved scientifically that
mainly lysophosphoydilamins and lysophosphoydilcholin content is increased
after enzymatic hydrotation.
Also it was proved a possibility of fatty acids(which
are contained in sunflower oil) by ithanol. This fact makes possible creation
of a new foodstuff, i. e. oils enriched by easy digested components (ethyl
esters of fatty acids).
Authenticity of scientific results
was confirmed by data obtained in industrial conditions at Pology oil-extracting
plant.
It is known a method of refining
oils from fatty acids by distillation under reduced pressure and high
temperatures. The imperfections of the method are appearing of dark-colored
substances having unpleasant smell, and highly energy-consuming.
There is a method of oils and fats
refining when they are treated with alkaline agents, for example, by sodium hydroxide
water solution under the temperature of 40 - 90°C [7].
Imperfection of the method is that
fatty acids (which are refined, when being
processed by alkaline agent) are transformed into fatty acids salt –
soaps. During this process, water solutions of soaps are formed which emulsify
oil or fat, creating fat – containing yield of production process – a
soapstock. A mass of soapstock increases when oil’s acidic number is increased.
In addition, sodium hydroxide is a dangerous substance that requires specific
measures for safe using of the method.
The goal was to simplify the
technology of oils and fats rectification using enzymes. And the goal was achieved
by using glycerin (instead of alkalines) which was used for treating oils and
fats in presence of specific lipolytic immobilized (or non-immobilized) enzyme, kipping the mass
proportion of oil or fats: glycerin: enzyme equal to 100: 0,5÷5 :
0,1÷10, the temperature is 30 – 80°C, pressure is 20 – 50 mm Hg vacuum
during 0,5 – 15 hours.
After enzymatic refining, acidic
number changes for oils is shown in table 1.
Table 1 – Changes of acidic number for oil
using enzymes
|
№ |
Enzyme |
Initial acidic number, mg KOH/g |
Final acidic number, mg KOH/g |
Time of reaction, hours |
|
1 |
Lypozyme RMIM |
4,5 |
0,3 |
7 |
|
2 |
Novozeme 435 |
5,2 |
0,2 |
3,5 |
|
3 |
Novozeme 435 |
5,8 |
0,25 |
7 |
|
4 |
Lypozyme TLIM |
3,0 |
0,3 |
6 |
Advantages of such a refining method
are; single-stage refining; fatty acids are not extracted from oils or fats buy
are transformed into acylglycerins; lack of wastes; degreased losses of product
oil or fat; glycerin as an agent, is
much more ecological and safe stuff comparing to o-phosphoric acid and caustic
soda.
A patent №30031 “Method of oils and
fats refining” was issued on 11 Feb 2008.
A particle value of performed research is
outlining of new ways of development methods refining fats from accompanying
substances using enzymes.
It has to be said, that now in
Ukrain, as in other CIS countries producing of foot supplement – ethyl esters
of fatty acids, mono- and diacylglicerins, which are classified as substances
for improving food stuff quality, is performed
using chemical agents (alkaline, acids etc).
The technology of such products is
quite complicated and energy consuming. More than that, refining of final
products leads to appearing of essential amount of waste products. For example,
mono- and diacylglicerins synthesis requires using of special equipment (target
monoacylglicerins fraction is extracted by molecular distillation) [8,9].
That is why researching of fats
transformations by using enzymes, and finding conditions for producing target
products using lea energy consuming methods and high yield are actual and necessary.
The researches’ goal was to
determine fundamental laws of fats (acylglicerins) transformation under
influence of enzymes, particularly
ethanolysis and hydrolysis.
The final goal of design was
implemented by the following steps:
· appraisal of properties of enzymatic
preparation produced industrially or having experimental-industrial status;
· determining of external factors
influencing the parameters of the appropriative reactions;
· determining of optimal conditions
for obtaining esters of fatty acids and incomplete acylglycerines.
Stated below are the results of this
scientific research.
It was proved a possibility of using
enzymatic preparation on the carrier Lipozym TLIM, Lipozym RMIM and Novozym 435 to transformation of acylglycerines
(fats), particularly alcoholysis, aided by mono- and polyatanomic alcohols.
It was revealed that during
ethanolysis reaction, the highest level of triacylglicerins transformation
using Lipozym TLIM is 82% (weight), using Lipozym RMIM is absolute 80% (weight)
and the highest level of transformation
is 94% (weight) when using Novozym 435.
It was found that during glycerolysis reaction
the transformation level os triacylglycerins using Lipozym TLIM is 34,4%
(weight), using Lipozym RMIM – is 17,4% (weight), and the highest level of
transformation is 85,5% (weight) when using Novozym435.
The optimal conditions for
alcoholysis are determined as: period length for the most high speed reaction –
2 hours; tge temperature for Lypozym
TLIM and Lypozym RMIM is 30 – 35°C, and for Novozym – is 60 - 70°C;components
proportion is stoichiometric.
Posibility of the pbtained results
is proved by their correlation on conditions using different measuring ways.
For example, the data related to the reaction product composition, calculated using thin-film chromatography, are
proved by dividing those product on adsorbing columns, by measuring viscosity,
refraction factor, and using chemical methods.
Also important is the problem of
detection of main regularities of enzymatic interesterification implemented to
ethers of mono- and polyatomic alcohols as a method of fats modification.
Promising and timeliness of research
work is proved by the possibility of creating new fats – related technologist
based on the obtained results. Such technologies are also important for
confectionary industry.
For the moment , such fats are imported
from abroad.
Scientific actuality of research is
proved by absence of important related to interesterification of esters of
mono- and polyatomic alcohols in special literature.
Producing of high quality confectionery fats possible by
multifunctional fractionating of palm
oil and other oils. This method is labor-intensive and requires sufficient
power inputs. Using partky-hydrogenizated oils (for example, sunflower oil,
rape oil, etc) as special confectionary
fats does not allow to produce high- quality confectionary. In addition, there
is a considerable quality of trans-isomers in such fats. Such substances, in
the judgment of some specialists, shoud
be of limited quantities in foodstuff.
One of the feasible ways of
resolving the problem is acylglycerins (fats) modification using specific
lypolotic enzymes.
We carried out acylglycerins (fats)
modification by their
interesterification with ethyl ethers of the appropriate fatty acids
using specific fat-splitting enzymatic preparations. This method allows to
obtain symmetric acylglycerine, and also asymmetrical acylglicerines when using
mixtures of esters.
A patent №79728 «Method of obtaining modified fats” was registered for this technology.
The research was awarded whit a gold medal at the III International show of
inventions and new technologies “New time” in Sevastopol city.
Analysis if the research proved the advantage of enzymatic technologies:
production cost price redaction, ecological compatibility of manufacturing,
possibility of obtaining products for
various purposes, creating of waste-free technologies, and etc.
The particular value of the research
consists in rational design and deoploing into industrial production new
energy- - and recourse-saving technologies for producing: esters as food
additives, and as a fuel component for internal-combustion engines;
monoglycerines which are used as food surface-active agent fats; fats enriched with diacylglycerines as a component of foodstuff
– salad oils, margarines, spreds, confactionary fats for special purposes, etc.
Reference:
1. Арутюнян Н.С., Корнена Е.П. Фосфолипиды растительных масел. – М.: Агропромиздат, 1986. – 256с.
2. Краткая химическая энциклопедия / Под ред. Кнунянц И.Л. – М.: изд-во «Советская энциклопедия». Т.5, 1967. – 1184с.
3. Литвиненко Н.М., Кисель М.А. Эндогенные фосфолипазы А2: Структура и функция. – Минск: Навука і техніка, 1991. – 270с.
4. Муратова Р.И., Борников В.Т., Саатов Т.С. Фосфолипаза А2 и реацилирование фосфолипидов // Биохимия. – 1987. – Т.52, вып. 7. – С.1068-1071.
5. Воронин М.В., Селищева А.А., Василенко И.А., Щвец В.И. Особенности кинетики гидролиза фосфолипидов фосфолипазой С из Bacillus cereus. Гидролиз фосфатидилхолина в присутствии дезоксихолата//Биохимия. – 1990. – Т.55, вып.1. – С.75-77.
6. Евстратова Н.Г., Кленова Ю.Б., Серебренников Г.А. Получение биоспецифических сорбентов для выделения фосфолипазы С Clostridium perfringens методом аффинной хроматографии // Биотехнология. – 1992. - №6. – С.69.
7. Тютюнников Б.Н., Бухштаб З.І., Гладкий Ф.Ф. и др. Хімія жирів. – Харків: НТУ “ХПІ». – 2002. – 452 с.
8.
Krog N. Food
emulsifiers in Lipid Technologies and Applications end by Gunstone FD, Marcel
Dekker, New York/ 1997, pp.421-534.
9.
Hassenheuttl
G.L. Synthesis and
commercial preparation of surfactants in the food industry, in Lipid Synthesis
and Manufacture, end by Gunstone FD, Sheffield Academic Press, Sheffield, UK,
1999, pp. 371-400.