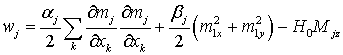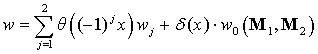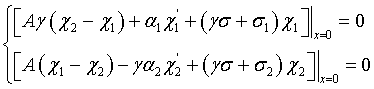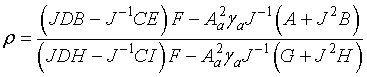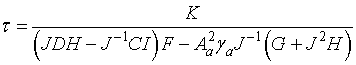Ôèçèêà/ 1. Òåîðåòè÷åñêàÿ
ôèçèêà
Doctor of Phys. and Math. Sci. Reshetnyak S.O.
National Technical University of Ukraine «Kyiv
Polytechnic Institute»
Reflecting
properties of ferromagnetic spin lens with non-ideal boundaries
In the present paper a spin-wave lens is proposed to be constructed on the
base of three-layer ferromagnetic material
with layers located perpendicularly to x axis. The
first and third (along the x axis)
parts are semi-infinite homogeneous uniaxial ferromagnets with corresponding
parameters of exchange interaction ![]() ,
, ![]() , uniaxial magnetic anisotropy
, uniaxial magnetic anisotropy ![]() ,
, ![]() , saturation magnetization
, saturation magnetization ![]() ,
,![]() , and between them a uniform layer is
located having thickness a and
magnetic parameters
, and between them a uniform layer is
located having thickness a and
magnetic parameters ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() . Easy axis
is parallel to the
direction of external permanent uniform magnetic field and z
axis.
. Easy axis
is parallel to the
direction of external permanent uniform magnetic field and z
axis.
The energy density of such
magnetic structure in exchange mode and taking into account the condition ![]() looks like
looks like
|
|
(1) |
where Mj = M0jez+mj,
mj are unit vectors
describing deviations of magnetization vector from equilibrium state.
Equilibrium state of magnetic moment is along z axes.
Boundary conditions. Boundary conditions are proposed for the case of
non-ideal interfaces. Suppose, two uniform unbounded ferromagnets contact
along yz plane and the system’s
energy density can be written as
|
|
|
where ![]() is Heaviside function,
is Heaviside function, ![]() is delta function,
is delta function,
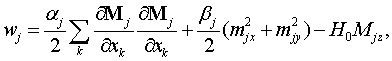
and
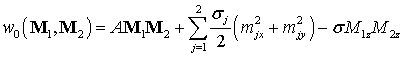 .
.
A
boundary is characterized with a coupling parameter A of interaction between two parts of system, parameters of
inhomogeneous magnetic anisotropy of the parts in an interface![]() ,
, ![]() , and a
parameters of inhomogeneous magnetic anisotropy
, and a
parameters of inhomogeneous magnetic anisotropy ![]() caused by interaction of lattices of two
subsystems in an interface.
caused by interaction of lattices of two
subsystems in an interface.
Integration
of a corresponding equation of magnetization dynamics on a small area in a
vicinity of a boundary with subsequent convergence to zero of area’s square
results in the following boundary conditions:
|
|
(1) |
where ![]() .
.
Spin wave reflection. Taking into account that we use a model of thin lens,
we approximate the distribution of magnetic parameters by the way shown in
fig.1 to calculate reflection characteristics of our inhomogeneity that we
named “lens”. Obviously, this object carries out the function of lens if only
gives a good transmission of spin waves, and we obtain a mirror if not.
Therefore, we need estimate a reflecting ability of an inhomogeneity.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Figure
1. The model of the structure to estimate its reflecting ability.
Using boundary
conditions (1) for both boundaries, we obtain:
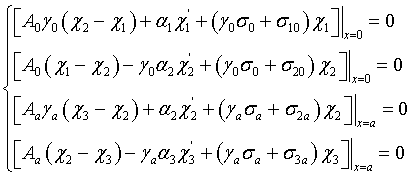 (2)
(2)
Let’s associate in (2) the following expressions to incident, reflected
and transmitted waves:
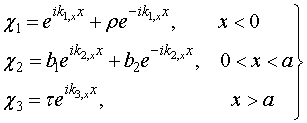 (3)
(3)
Here ρ
is a complex reflection amplitude
of a spin wave, τ
is a transmission amplitude. Then, taking into account (2), (3),
we obtain (parameters in the next expression characterize functional
dependencies):
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 2 shows
field and frequency dependencies of reflection coefficient.
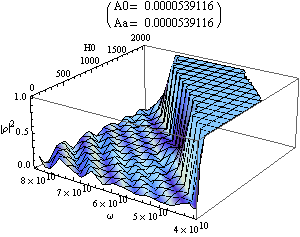
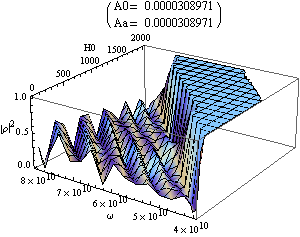 Figure 2. Dependence of reflection
coefficient on frequency and magnetic field at different values of coupling
parameters A0=Aa.
Figure 2. Dependence of reflection
coefficient on frequency and magnetic field at different values of coupling
parameters A0=Aa.