Kharitonov S.F., Evseeva A.V., Koltsova E.A.
Ivanovo State Power Engineering University
Ivanovo,
Russia
MODELLING OF AIR DIFFUSION USING CUDA PARALLEL
PROGRAMMING TECHNOLOGY
One of the most important steps in design and construction of buildings
is calculation of air flow force impact on them. Despite all the advantages of
mathematical modeling usage it requires huge computational and time resources
for calculations and information processing. Usage of parallel programming
technologies increases productivity and reduces computing time.
The article aims at describing the development of computer software
system that will simulate airflow within a complex of buildings using CFD
methods and CUDA technology.
The objectives of this project are as follows:
·
Investigate the trends of modeling
techniques of liquids and gases.
·
Compose a mathematical model of
airflow.
·
Implement parallel algorithm using
CUDA technology.
·
Implement graphical user interface
for visualization of simulation processes.
·
Conduct simulation experiments.
·
Analyze results of the experiments.
The Institute of Numerical Mathematics of the Russian
Academy of Sciences has developed a solution in the considered area. They have designed
an application that uses parallel algorithm to calculate turbulent airflow in
the ground layer of the atmosphere using MPI technology.
In this paper airflow is modeled in two-dimensional
system using “Pressure-Speed” equation system. The equation system contains Navier-Stokes
equations and continuity equation. The system also contains boundary. This
system assumes calculation of fields by the following algorithm:
1. At the initial time point initial values
of velocity and pressure are defined for each field.
2. Pressure values are calculated for a new time
point using velocity values.
3. New pressure values are used in the
Navier-Stokes equations to calculate new velocity values for the new time point.
These actions are repeated iteratively.
A graphical user interface was implemented to
visualize sequential and CUDA algorithms. The graphical interface was
implemented as a Windows Forms application using C# programming language.
The user interface supports
the following functionalities:
·
airflow
visualization;
·
ability to configure
the complex of buildings;
·
preservation
of modeled areas as templates.
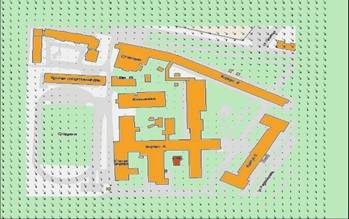
Several experiments have been conducted to check
that the modeling system shows correct results. Airflow in Ivanovo State Power
Engineering University premises was modeled during one of the experiments. The
results of the experiment are present in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Performance testing was also conducted as part of this
work. Figure 2 shows the calculation time dependence on the size of calculation
area for sequential and CUDA algorithms. The graph shows 1000 iterations
execution time. The sequential program was launched on a dual-core AMD 2.2-GHz
processor. CUDA program was launched on the GeForce GT 610 graphics card.
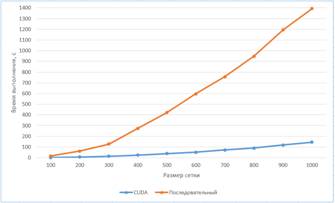
Figure 2
Thus, usage of CUDA technology
significantly reduces the calculation time (on average 10 times). It allows
calculating for large areas reducing the time costs by several times.
The results of the simulated airflow
process are similar to expected in given conditions. The program developed
using CUDA parallel programming technology in combination with graphical
interface can be used for simulation of airflow effect in a single building or
a group of buildings.
References
1.
Loitsiansky, L.G. Fluid Mechanics. - Moscow: Drofa, 2013
2.
Filatov E.Y., Jasinski F.N. Mathematical modeling of flows of liquids and gases:
Proc. allowance. - Ivanovo: State Educational Institution of Higher
Professional Education "Ivanovo State Power University", 2007. - 84
p.
3.
Boreskov, A.V. Parallel computing on the GPU. The architecture and the CUDA
programming model. - Moscow: Publishing House of Moscow University in 2012.