Cand.Sci.Tech.
Bazhenova B., post-graduate student Balzhinimaeva S.,
post-graduate student Budaeva A.
The East-Siberian state university of technology and management
Research of functional-technological
properties of
meat product
The
modern human food ration testifies of the insufficient consumption of vitamins
and minerals, including selenium. The spectrum of selenium action in a human
body is wide enough. According to the data of the epidemiological research more
than 80 % of the of Russian population are provided with selenium below an
optimum level (1). The paper deals with developing and processing a functional
meat product enriched with selenium.
Meat
products, including paste, are highly nourishing foodstuff. Minced paste meat
is the ground homogeneous substance of the paste like consistence with aroma of
spices. Paste belongs to emulsified products and its quality is mostly defined
by the functional and technological properties of minced meat.
One
of the ways of the improvement of the minced paste meat technological
properties is the combination of the
vegetative and animal origin proteins.The proteins of a vegetative
origin are added into the structure of meat products in a dry or a
hydrated way or as part of the
protein-fatty emulsions which allow to
rationally use meat raw materials and to regulate consumer properties of a
ready product.
The
objects of the research were the minced
paste meat combined with the protein-fatty emulsion and wheat flour (control)
and minced paste meat combined with the protein-fatty emulsion enriched
with selenium flour and the protein
stabilizer (experience). In developing the recipe of the minced paste meat we used the pork skin as a
protein stabilizer which had been boiled and ground with water. Then it was
nessesary to define its water retaining ability (2), as the basic functional and technological indicator of the
minced paste meat.
As
a result, the water-retaining ability of the minced paste meat sample without the protein-fatty emulsion was 92.8
% (fig. 1). But its water retaining ability increased by 2.1 % after the
addition of 5 % protein-fatty emulsion with wheat flour into the recipe. The
protein-fatty emulsion increased the product´s binding properties due to
dairy protein additive called
"Anisomin".
The
increase of the dose of the added protein-fatty emulsion by 10 % resulted in
higher water-retaining ability of minced paste meat by 1.5 %. But on the
contrary, more than 10 % of the
protein-fatty emulsion added to the substance did not bring about higher water
retaining ability.
We
found out that the addition of the selenium flour into the composition of the
protein-fatty emulsion resulted in the increase of the water-retaining ability
of the product, for the proñess of starch gelation started at
620 Ñ and higher which enabled the product to retain water.
The
differences in the indicator studied are also caused by the changes of β-gluñan which is released from the walls of endosperm cells while the process of wheat germination. High-molecular β-gluñan seems to act as the
additional gelation formation factor while the thermal processing. all this
brings about higher gelation formation
ability of the minced paste meat.
The
introduction of the protein stabilizer with high gelation forming properties
into the structure of the trial samples enhanced the water-retaining process.
As a result the more the dose protein-fatty emulsion samples, the higher the
water-retaining ability of the minced paste meat because of the increase of the
constituents of "Anisomin", biologically active additive, phosphates
and the protein stabilizer in the dose.
Thus,
the introduction of the protein-fatty emulsion with the selenium flour and the
protein stabilizer into the minced
paste meat raised the functional and technological indicators of the minced paste meat. In such a way the product
is enriched with selenium.
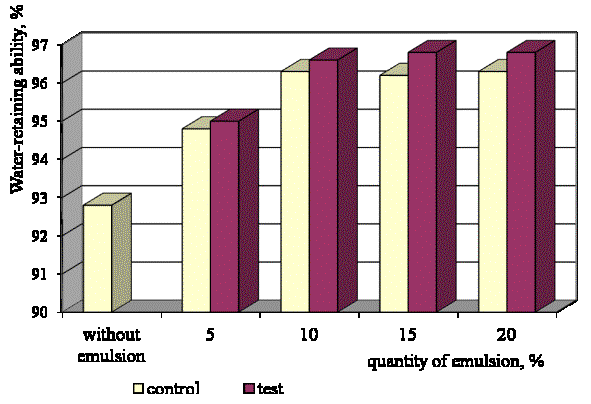
Fig.1. Water-retaining
ability of the minced paste meat
List
of Readings:
1. Tuteljan V. A. Selenium in a Human
Body: Metabolism, Antioxidant
Properties, Cancerogenesis Role/ V. A Tuteljan, etc. – Ì: Publishing House of the Russian Academy of Medical Science, 2002.
– 224 p.
2. Antipova L.V., Glotova I.A., Rogov I.A.
Research Methods of Meat and Meat Products/ L.V.Antipova, etc. – Ì: Kolos, 2001. – 376 p.