Zaytseva O., Zhukov V., Telegin V., Knigavko V.,
Miroshnichenko N.,
Grankina S.
Kharkiv National Medical University, Kharkiv, Ukraine
Determination of sewage allowable load
value on biological purification plants in polyols production by mathematical
model
It is known that the bad purification of industrial sewage leads to
the reservoirs pollution, harms to fishing industry and
worsens sanitary conditions of water-supply and water-use. The basic amount of sewage in the production of polyols formed at the stage of catalyst
preparation, adsorption drying
and cleaning products, washing filter presses
returnable packaging and equipment,
as well as their rinsing [1]. Many
of these chemicals are well studied in regard to hygiene. In certain
concentrations, they change the organoleptic properties of water, violate
processes of natural self-purification of reservoirs, have a toxic effect on
the organism of warm-blooded animals. Most of them violate the function of the
central nervous system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems, as with
prolonged admission to the organism have a polytropic action [2, 3]. To render harmless sewage in polyols production the most widely combined method is used. Its essence is following: the boiler residuums are burned, and
part of the sewage has purification in
the biological structures.
With eco-hygiene products,
this method has a drawback – the thermal deactivation pollutes
the air space by thermal decomposition
products, which represents a danger to
public health. In some industries the method of vapor-phase thermocatalytic oxidation is used, which increases the degree of sewage purification up to 98%
and by hygienic and technological
indicators is the most effective. But despite the high efficiency of this
method and reagentless it did not find a proper application in the production of polyols due to the
economic unprofitability. Thus,
the leading method is thermal incineration of the boiler residuums
and next sewage biological purification.
In assessing the effect of toxic
contamination of reservoirs methods of bioindication are widely used.
By it the species diversity in biocoenosis of reservoir is
considered as a measure of its
structure and stability. The objective
function of such biological
system is the maintenance of
the highest possible level of
destruction and utilization of
organic matter. The active silt state is mainly
determined by the character of the load coming into the aerial tank, i.e. qualitative and quantitative composition of
the sewage. At steady-state load on the sewage purification plant the steady state,
is formed defined as standard which characterizing by the
highest level of metabolism and
energy. Changing the load goes beyond the functional
standards, leads to disruption of
the structural and functional organization
of the biocoenosis of active silt
and a qualitative change in the state of biological system.
In this connection the aim of this research
was to determine the value of allowable
load of the sewage
on biological purification plants
and the study of
optimal conditions for their functioning.
Materials and research methods. The effect of polyols
brands Laprol 4003
(L-4003) and Laproxid 703 (L-703) on the condition of active silt with subsequent determination
of concentrations that do not have
toxic effects on him was investigated.
It is important to determine the effectiveness of the structures and in the event of the sewage entrance on a
biological purification in a volley.
To assess the quality (I) of the
biosystem can use the criterion
of quality, which takes into
account the additive and
multiplicative properties:
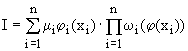
where ji(xi) – is a factor that
reflects the functional state of biological
systems; mi – is coefficient
installed as a result of the estimates of experts, and for ensuring
normalization – ![]() ;
; ![]() – is the penalty function of the corresponding state
factor that reflects the identity of the described object to the model,
which is, for example, in the odd set of the corresponding algorithm.
– is the penalty function of the corresponding state
factor that reflects the identity of the described object to the model,
which is, for example, in the odd set of the corresponding algorithm.
The multiplicative part of the quality
criterion contains information about the functional properties of biological system.
It is known for the given level of the
biocoenosis the highest quality of biosystem is ensured at the maximum possible value of the coefficient of species diversity, and the number of
species in biocenosis is a finite quantity, which depends on the type of nutrient substrate and conditions of existence. Given the properties of the penalty function to strive depending on the value of factor to the two limit values, namely ![]() at a value
at a value ![]() , and
, and ![]() when the value
when the value ![]() in the optimal mode of biological system, in the simplest case,
the multiplicative part can be represented as follows:
in the optimal mode of biological system, in the simplest case,
the multiplicative part can be represented as follows:
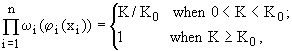
where K – is number
of species in given conditions;
K0 – is the number of species in the optimal conditions
for the existence of a biosystem.
Additive part of the biosystem quality
functional can be represented by a function of the
entropy measure in the form of,
for example, the entropy index of species diversity according to Shannon,
calculated by the formula:
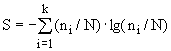 ,
,
where
k – is number of species, units.; N – is total number of organisms, thousands of specimens / g; ni – is the number of
individuals of i-th species.
Characteristics of species diversity is taken into account in the reliability index R.
In addition, in the additive part it is necessary to take into account parameters,
reflecting the protective function of biological
system. Functional properties of biological
system to provide structural and
functional integrity and regulation of
protective mechanisms for the given active silt is proposed to evaluate by the formula
I = (0.86R + 0.14a) × K/K0,
where R – is an indicator
of reliability of the biocoenosis
of active silt, cu; a – is an indicator of the enzyme activity
response amplitude in given conditions of
active silt operating, cu; K, K0 – is the number of species of aquatic organisms
of active silt at the time of measurement, and for optimal work, respectively, rel. units.
The coefficients 0.86 and 0.14 are installed
as a result of computer simulation
to optimize the model parameters based on the actual characteristics
of the active silt of aerial
tank. A factor a
that reflects the protective function of
biological system, defined as the amplitude of the silt response to the effect of sewage by catalase activity according to the formula
![]()
where I – is the
criterion of quality; and KAwash off and KAunwash off
– catalase activity of silt after 20 minutes of contact with the sewage under aeration
for the washed off and unwashed off from
sewage silt, respectively, mg H2O2/mg silt.
Based on the fact that the active silt
microfauna is the most sensitive to the action of toxic substances,
it is proposed to evaluate the
reliability of its operation on
the basis of aquatic organisms quantitative in the form of the probability of failure-free operation of the biosystem,
which is calculated by the formula
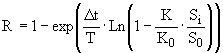
where Dt – is the time
duration from the contact of the
active silt with sewage up to the moment of hydrobiological
analysis, h; T – is the characteristic time of operation of
silt, i.e. turnover time of the active silt in the purification technologies, h; K/K0
– is the coefficient of species
diversity, relative. units.; Si – is
the entropy index of species diversity (by Shannon-Wiener) analyzed
biocoensis, rel. units.;
S0 – is the entropy index
of biocoenosis, operating under optimal
conditions.
Function of the probability of failure-free
operation of active silt R
varies from 0 to 1. In addition, R tends to 1 in the normal course of the purification process and to zero – in the complete
degradation of biocoenosis.
For a comparative assessment of the damaging effects on the active silt it is used the relative change of the reliability (R), calculated by the
formula
![]()
where Ri
– is the index of reliability of
active silt operating in an experiment,
rel. units; Rc – is the indicator of reliability of active slit in the control, rel. units.
For a comparative evaluation of the
effectiveness of the active silt used
the relative content of organic matter
in treated water by index of CCO (chemical consumption
of oxygen), which was calculated as
follows:
![]()
where CCOi
– is CCO by the water in the experiment,
mg / l; CCOc – is CCO in the control, mg / l.
Experiments to assess the effect of chemicals in the cleaning process were conducted in model mixers, of 1 liter
volume, in which the active silt from the regenerator
of industrial aerial tanks was placed. In the control aerial tank one-off
household effluent water in a ratio 1:1 to active silt was placed, and in the experienced
– the investigated substances in a given concentration. The mixture is aerated for
4 h. after then hydrobiological
analysis of active silt by method of calibrating drop
carried out. Then, after 12
h in all aerial
tanks we determined CCO by the treated water in filtered samples by dichromate
method. The concentration of active silt was determined by dry substance.
Results of research and their discussion. To assess the optimal
conditions for the sewage purification plants functioning polyols L-4003 and L-703
are used. The half-life of these substances at the initial their concentration
of 4 g/l for a year of exposure could not be established that bears witness to
the high stability. Normal functioning of the active silt was observed in the
presences of L-703 in concentrations up to 30 mg/l. Increasing concentrations
of L-703 from 30 to 243 mg/l resulted to activation of biocoenosis of active silt.
At concentrations from 729 mg/l and above loss of biocoenosis was noted. The
results suggest that L-703 in concentrations up to 729 mg/l hasn’t toxic effect
on active silt. A similar effect we observed when evaluating the effect of
L-4003: it is poorly exposed to oxidation and degradation; biological purification
using active silt is ineffective; at concentrations up to 30 mg/l hadn’t effect
on the biocoenosis of active silt. The toxic properties of L-4003 appeared in
concentrations higher than 81 mg/l. The effecacy of biological purification from
the L-703 and L-4003 was 50, and 40% respectively.
Thus, in the
course of studying the L-703 and L-4003 polyols influence on the active silt
state in sewage biological purification plants we determined threshold and
toxic concentrations. L-4003 at concentrations up to 30 mg/l had no effect on
the work of the sewage biological purification plants. L-703 at concentrations
up to 243 mg/l and L-4003 at concentrations up to 81 mg/l increased the silt
activity. Consequently, the concentrations of 243 and 81 mg/l for L-703 and L-4003,
respectively, should be considered as threshold. At more higher concentrations
polyols have a toxic effect on the biocoenosis of active silt and operation of sewage
biological purification plants. The efficacy of biological purification from
L-4003 is slightly higher than L-703, and is respectively 50% and 40%, which
makes this purification ineffective. In this connection there is need for
improved methods of sewage purification. Based on the mechanisms of degradation
of polyols, it follows that their decay is carried out by way of free radical
oxidation. The initiator of these processes is reactive oxygen species [1],
which accelerate the mechanism of free radical oxidation of polyols. These
results give reason to take into account this mechanism in the biological purification
of sewage containing polyols, using activators of organic substrates biotransformation
processes – ozone, chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, which will increase the
efficiency of neutralization of sewage. Optimum conditions for the functioning
of the sewage biological purification plants in the production of polyols
should be considered as the concentrations of L-4003 and L-703 up to 81.0 and
243.0 mg/l, respectively. At higher concentrations these plants are not capable
of effectively neutralize the sewage containing polyols.
List of reference
1. Жуков В.И., Попова
Л.Д., Зайцева О.В. Простые и макроциклические эфиры: научные основы охраны
водных объектов. Х.: Торнадо, 2000. – 438 с.
2. Зайцева О.В., Жуков
В.И., Резуненко Ю.К. Влияние лапроксидов на генеративную функцию и генетический
аппарат белых крыс. Проблемы экологии и медицины. Полтава, 1999; 2: 55-60.
3. Жуков В.И.,
Золотаревская Л.А., Григоров В.И., Зайцева О.В. Структурно-функциональная
теория биологического действия радиотоксинов. Х.: Основа, 1998. – 225 с.