Determination of the concentration of the hydrodynamic-active admixture
during the joint operation of the
pump and pipeline
F.A.Amirov, S.A.Agammedova
(Azerbaijan State Oil Academy)
Regulation of the operation regime
of the hydraulic system through the hydrodynamic active admixtures- one of the
famous methods of the reduction of the power losses (1-3). In case of use of
the hydrodynamic active admixtures on the purpose of the reduction of the hydraulic
drop, in term, when the parameters of the pump are determined, there is the
task on the selection of the volume of the admixture through the way that
provides the joint operation of the pump and pipeline.
Lets examine the task, on
conditioned that the liquid is Newtonian. Dependence on the kinematic viscosity
from the concentration of the hydrodynamic active admixtures may be submitted
on the following order:
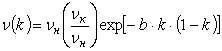 (1)
(1)
there is
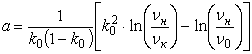 ;
; 
There is k – volume concentration of the hydrodynamic active admixtures; nн, nк –kinematic viscosity of the
Newtonian liquid and the additive on some temperature T; n0 –viscosity of the liquid under the temperature
T0 and concentration of the additive к0.
Lets include the following
designation:
![]() ®
® ![]()
when the dependence (1) acquires the
type:
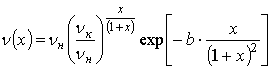 (2)
(2)
there is
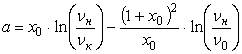 ;
; 
Density of the solution regards with the
density of the Newtonian liquid on the formula:
![]() (3)
(3)
Volumetric flow rate equals:
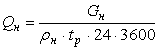 (4)
(4)
there is tp-quantity of the annual
operation days of the pump device.
Index of the regime of the motion of the liquid
will be the index of Reynolds:
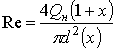 (5)
(5)
Hydraulic gradient shall be determined on the
formulas:
![]() if Re(x) £ 2300 (6)
if Re(x) £ 2300 (6)

if
230aRe(х) £ 105 (7)
there is ![]() -translocation quotient
-translocation quotient
Let’s determine the loss of the complete hydraulic
drop on the formula:
h (x) = i × L (8)
there is i-
hydraulic gradient, selecting on the formula (6) and (7) on dependence from the
regime of the liquid flow; L-length of the pipeline.
For the determination of the
necessary volume of the hydrodynamic active admixture it is necessary to use
the balance equation of the pump hydraulic drop on the pipeline during the
stated characteristic.
It shall be stated on the following
form for the equation of the hydraulic characteristic during the operation of
the solution with hydrodynamic active admixtures:
Hk0 = h (x) + DZ + Hk (9)
there is h
(x) is the loss of the hydraulic drop; DZ-variety of the elevation mark.
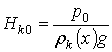 ;
; 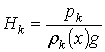 -hydraulic
drop at the beginning and end of the pipeline; p0, pк - hydraulic drop at the beginning and end of the
pipeline.
-hydraulic
drop at the beginning and end of the pipeline; p0, pк - hydraulic drop at the beginning and end of the
pipeline.
Characteristics of the hydraulic
drop of the pumps:
![]() (10)
(10)
there is n-quantity
of the pumps, A (x) and B (x)-taking into consideration the effect
of the hydrodynamic active admixture the empirical coefficient:
The necessary volume of the
admixture may be determined on the basis of the balance of the hydraulic drop
and pipeline:
![]() (11)
(11)
there is Dhx –suction head, that shall satisfy the
condition:
![]() (12)
(12)
there is pk(x)-the
pressure of the enriched steam of the solution, depending on the volume of the
admixture, shall be determined on the formula:
![]() (13)
(13)
there is rн –the pressure of the saturated
steams of the Newtonian components of the solution; rк –the pressure of the saturated
steams of the additives.
Equation
of the hydraulic drop may be solved with use of the mathematical sets (MathCAD
Maple, Mathematica) with use of the program means or graphical methods.
Conclusion
1. Formula for the determination of
the objective concentration of the hydrodynamic active admixture on the basis
of the balance of the hydraulic drop.
2. Equation of the balance of the
hydraulic drop should be solved with use of the modern mathematical sets
(MathCAD Maple, Mathematica), as well as graphical active methods.
References
1. Amirov F.A and others.
Forecasting of the pump characteristics of the centrifugal pumping equipment
under the operation of Newtonian solutions. Scientific records ISU # 1, Baku,
1999
2. Belousov Y.P. Antiturbulent
additive for the hydrocarbon liquid. Novosibirsk, Nauka, 1986, page 145
3. Amirov F.A and others. Toms
effect on vane pumps. AGNA, Baku, 2003, page 75
4. Amirov F.A, Agammadova S.A Toms
effect ion Hydraulic systems, tenth Baku International Congress, Baku, 2009.
ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЕ КОНЦЕНТРАЦИИ ГИДРОДИНАМИЧЕСКИ-
АКТИВНОЙ ДОБАВКИ ПРИ СОВМЕСТНОЙ РАБОТЕ
НАСОСА И ТРУБОПРОВОДА
Ф.А.Амиров, С.А.Агаммедова
Азербайджанская Государственная Нефтяная
Академия
ВЫВОДЫ
1. На основании баланса напоров насоса и трубопровода получена формула для определения объемной концентрации гидродинамически-активной добавки.
2. Уравнение баланса напоров можно решить с использовании современных математических пакетов (MathCAD Maple, Mathematic), а также графоаналитическим методом.
Авторы:
1. Фикрет Алибаба оглы Амиров, (кандидат
технических наук)
2. Севда Алипаша кызы Агаммедова. (доктор философии по технике)
Название статьи:
«Определение концентрации гидродинамически-активной добавки
при совместной работе насоса и трубопровода»
Адрес:
г. Баку, AZ 1010, Проспект Азадлыг 20
Азербайджанская Государственная Нефтяная Академия (кафедра № 43)