Strusovskaya O. G., Baykin P. I.
Northen State Medical University, Arkhangelsk
Chronic toxity determination of Cochlearia officinalis infusion
Actual
task of modern pharmacy is creation of drugs on vegetable base, having a low
threshold of undesirable effects beginning. Cochlearia
officinalis is a plant, which potentially has a hypoglycemic activity.
Plant extract’s hypoglycemic activity connected with availability in its
chemical composition of calystegines – polyhydroxylated unesterified nortropan
alkaloids, which are able to competitively inhibit activity of glucosidases [1]. C. officinalis chronic toxity studying is necessary because of long
drug use necessity, influencing on postprandial conditions.
«Wistar» line adult rats
weighing 180-200 grams were held in quarantine for 14 days before experiment and
used for toxicological research. Experimental animals maintenance was
corresponded to «Health rules on the device, equipment and maintenance of
experimental biological vivariums» and to order of The Russian Federation
Ministry of Health ¹267 of 19.06.2003 «Laboratory practicies rules adoption»
[2,3]. Animals were kept with continuous access to water on a standard diet.
Feeding was carried out in fixed time. Experiment was conducted according to
guidance for preclinical research of new drugs [4]. C. officinalis infusion was prepared in accordance with requirement
of State Pharmacopoeia XI [5].
The toxic doses of C. officinalis infusion six animals in each of four experimental
and control groups were used in this study. Determination of chronic toxity was
conducted by giving infusion to animals of experimental groups during 60 days.
Parallely groups of intact animals were given 0,9 % solution of sodium chloridi
in the same quantity. Observation of
the animals was carried out daily. Basic fixed parameters were: animal weight,
general state of health, frequency of eating, defecation and urination.
Dynamics of animals’ body mass change
presents in table 1.
Thus,
these studies are the base of conclusion, that using of C. officinalis
Table 1
Dynamics of animal’s body mass change
|
Days of
experiment |
Average mass of
animals in control groups, grams |
Average mass of
animals in experimental groups, grams |
||
|
Female |
Male |
Female |
Male |
|
|
1 |
197,1±3,5 |
200,2±1,4 |
197,6±3,5 |
200,2±5,4 |
|
7 |
197,9±2,3 |
200,4±4,6 |
197,5±2,3 |
200,4±4,5 |
|
14 |
197,6±3,6 |
200,6±3,4 |
196,6±3,6 |
200,6±3,4 |
|
21 |
197,0±2,9 |
200,4±5,6 |
197,4±2,9 |
200,4±5,6 |
|
28 |
197,2±8,7 |
202,1±1,8 |
197,2±3,7 |
200,1±2,8 |
|
35 |
197,4±2,9 |
200,0±2,7 |
197,4±2,9 |
200,0±4,7 |
|
42 |
197,2±3,7 |
200,9±1,9 |
197,2±3,7 |
200,9±1,9 |
|
49 |
197,3±2,4 |
200,8±1,3 |
197,4±1,7 |
200,8±2,3 |
|
56 |
197,2±3,5 |
200,9±1,9 |
197,3±3,5 |
200,9±2,9 |
|
61 |
199,5±4,8 |
200,7±1,9 |
197,6±4,2 |
201,9±2,4 |
infusion
doesn’t influence on behavioral responses, general state of health and
frequency of eating, defecation and urination of experimental animals.
After
60 days animals were removed from the experiment by decollation under espneic
anesthesia by ether vapor in accordance with rules for experimental animals
[6]. Visual inspection of dead animals doesn’t identify any significant
distinction from animals of control groups.
All animals had normal build and
average state of nourishment. Oral mucosa and tongue were pale and clean. Teeth
were preserved. Excretions from natural foramen didn’t present. Fur was shining
and clean. There are no centers of alopecia, skin irritation and erosion were
noticed.
Thus toxity measurement and animal
observation data during 60 days let to relate C. officinalis infusion to the
fourth class of low hazard substances [7].
Histological research of experimental
animals internal organs in comparison with control animals internal organs were
also held. Animals’ hearts, livers,
kidneys and stomachs were fixed in Carnoy’s fluid, neutral formalin and flooded
by paraffin for these purposes. Sections were coloured by hematoxylin and eosin
by Van Gieson. In the course of researches was established:
-
endothelial cells of aortha inner membrane have clear nuclea; there are
no destruction of tunica media elastic fibers; myofibrills’ transverse
striation is clear in all heart sections, cardiomyocites’ nuclea contain
sufficient quantity of chromatin, nuclear membrane is thin. There are no
centers of cytoplasm tinctorial properties violation and cardiofibrosis; slight
swelling of heart’s stroma was fixed, which was associated with anesthesia
(picture 1);
-
trabecular liver structure on cuts from different liver lobes doesn’t
detect violations. Hepatocytes’ borders are clear, cytoplasm is granular. There
are no local tinctorial properties disorders of cytoplasm. Nuclea contain clear
nucleola and sufficient quantity of chromatin. Nuclear membrane is thin.
Liver’s sinusoids are plethoric (picture 2);
Picture 1
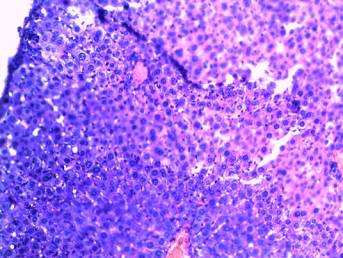
Histological
research results
(heart’s stroma slight swelling)
Picture 2
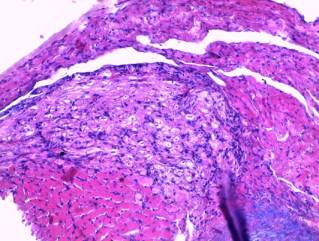
Histological research
results
(liver’s sinusoids
plethora)
-
capillaries of nephrons and intersticial tissue in kidneys are
plethoric, cytoplasm of kidney proximal tubule epithelium is oxyphilic, cell’s
borders are distinguishable, nuclea are bright and clear (picture 3);
Picture 3
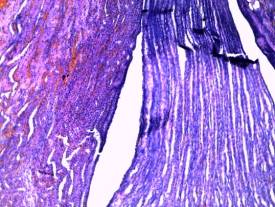
Histological
research results
(plethora of kidney
tissue)
-integumentary epithelium of stomach mucosa is formed
by mucous cylindrical cells. Epithelial lining defects were not noticed
(picture 4). Principal and parietal cells of stomach glands are not changed.
Picture 4
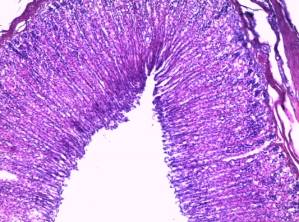
Histological
research results
(integumentary
epithelium of stomach mucosa)
There were
no clear differences between microscopic sections of experimental and control
groups of animals were detected as result of histological research. Daily
intragastric giving of C. officinalis to experimental animals of both sexes
during 60 days didn’t cause irritation, inflammation and destruction of
tissues. Dystrophic, destructive, local sclerotic changes in parenchymal cells
and stroma of internal organs didn’t occur.
References:
1.
Brock A. Brassicaceae contain nortropane alkaloids/ A. Brock, Ò. Herzfeld, R. Paschke, M. Koch et all//
Phytochemistry.- 2006. -Vol. 67. -Iss. 18.- Pp. 2050-2057.
2. M. G. Irapetyanz, I. P. Levshyna, L. V. Nozdracheva, N.
N. Shuikyn, Correction of behavioral and physiological indexes of white rats
neurosis-like state by giving the succinic acid, J. Higher nervous activity, V.
51, ¹3 (2001), p. 360–367.
3. RF
Ministry of Health order ¹ 267 from 19.06.2003 «Adoption of the rules of
laboratory practices».
4. R. U. Habriev, O. L. Verstakova, E. V. Arzamastzev,
E. A. Babayan
Guidance for experimental (preclinical) research of
new pharmacological agents, (2005), p. 832.
5. State
Pharmacopoeia XI, V. 2, (1990), p. 400.
6. RF
Ministry of Health order ¹ 755 from 12.08.1977 «Improvement steps of work’s
organizational forms with use of experimental animals».
7. State industry standard 12.1.007-76 from
01.01.1977, System of safety standards. Harmful substances. Classification and
safety requirements.