Ñîâðåìåííûå èíôîðìàöèîííûå
òåõíîëîãèè/1. Êîìïüþòåðíàÿ èíæåíåðèÿ
cand. tech.
sci. Semakhin A.M.
Kurgan State University, Russia
THE OPTIMUM DECISION OF INTEGER MODEL OF INFORMATION
SYSTEM BY THE BRANCH AND BOUND METHOD
The branch and
bound method (BB method) is applied to the decision in full or in part integer
problems of linear programming. A. Land and A. G. Doig have offered BB-method
in to 1960 /1/.
In the beginning of
![]() iteration of the BB
method it is necessary to have:
iteration of the BB
method it is necessary to have:
1. The problem list
of linear programming, each of which should be solved in the subsequent
iterations.
2. The bottom bound
of optimum value of the linear form of a problem ![]() .
.
On the first
iteration as ![]() value of criterion
function
value of criterion
function ![]() in any integer point
undertakes
in any integer point
undertakes ![]() . If a point to specify it is impossible, accept
. If a point to specify it is impossible, accept ![]() .
.
Let as a result ![]() iterations of a
method have received the list from
iterations of a
method have received the list from ![]() problems:
problems: ![]() and also exists
and also exists ![]() . The algorithm of a BB method contains stages:
. The algorithm of a BB method contains stages:
1 Stage. The
problem ![]() for the decision gets
out of the problem list of linear programming,
for the decision gets
out of the problem list of linear programming, ![]() . The problem
. The problem ![]() is solved.
is solved.
2 Stage. If problem
![]() has the decision
has the decision ![]() we pass to a stage 3.
Otherwise - we exclude problem
we pass to a stage 3.
Otherwise - we exclude problem ![]() from the list
from the list ![]() =
=![]() . Transition to a stage 1. At
. Transition to a stage 1. At ![]() we do a conclusion,
that the initial problem has no decision and process of the decision comes to
an end.
we do a conclusion,
that the initial problem has no decision and process of the decision comes to
an end.
3 Stage. If ![]() we pass to a stage 4.
Otherwise problem
we pass to a stage 4.
Otherwise problem ![]() is excluded from the
list. Transition to a stage 1.
is excluded from the
list. Transition to a stage 1.
4 Stage. If
components of vector ![]() satisfy all to a
integrity condition we pass to a stage 5. Otherwise problem R is excluded from
the list. Plan
satisfy all to a
integrity condition we pass to a stage 5. Otherwise problem R is excluded from
the list. Plan ![]() is remembered.
Transition
to a stage 1. At
is remembered.
Transition
to a stage 1. At ![]() vector
vector ![]() is the decision of an
initial problem and process of the decision comes to an end.
is the decision of an
initial problem and process of the decision comes to an end.
5 Stage. The
problem ![]() is excluded from the
list. The list joins two new problems of linear programming - the problem
is excluded from the
list. The list joins two new problems of linear programming - the problem ![]() and the problem
and the problem ![]() ,
, ![]() =
=![]() . Transition to a stage 1. Process of splitting of problem
. Transition to a stage 1. Process of splitting of problem ![]() on two new problems
of linear programming is carried out as follows.
on two new problems
of linear programming is carried out as follows.
Let ![]() - fractional a
component in received optimum plan
- fractional a
component in received optimum plan ![]() and
and ![]() the whole part. Then
problem
the whole part. Then
problem ![]() looks like:
looks like:
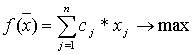
subject to
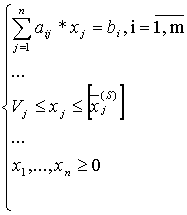 (1)
(1)
Then problem ![]() looks like:
looks like:
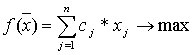
subject to
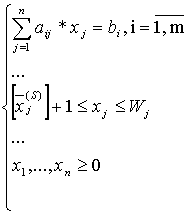 (2)
(2)
Process of the
decision proceeds will not be solved yet all of a problem of linear programming
from the list. The decision of a problem will be ![]() on last iteration
/2/.
on last iteration
/2/.
Let's develop
integer mathematical model of information system and we shall define the
optimum decision by BB method.
The mathematical
model is formulated as follows: from among the firms, rendering services satellite
Internet in territory of the Russian Federation, it is required to choose the
provider satellite Internet with the maximal size of the pure resulted effect
(NPV) and satisfying to financial restrictions /3/.
Let ![]() - share of financing
of the project NTV-plus,
- share of financing
of the project NTV-plus, ![]() - share of financing
of project Europe On Line,
- share of financing
of project Europe On Line, ![]() - share of financing
of project Astra Network,
- share of financing
of project Astra Network, ![]() - share of financing
of project Satpro,
- share of financing
of project Satpro, ![]() - share of financing
of project Network Service.
- share of financing
of project Network Service. ![]() - binary variables.
- binary variables.
The integer
mathematical model looks like.
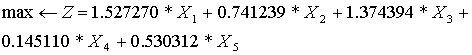
subject to (3)
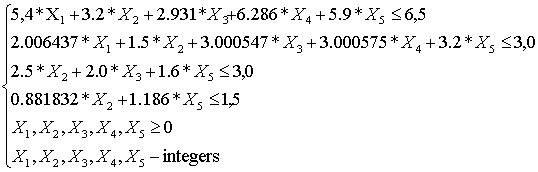
Let's solve a
continuous problem. We shall lead to the standard form and we shall make the
initial Jordan’s table (table 1).
Table 1
The initial Jordan’s table
|
ÁÏ |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
6.5 |
5.4 |
3.2 |
2.931 |
6.286 |
5.9 |
|
|
3.0 |
2.006437 |
1.5 |
3.000547 |
3.000575 |
3.2 |
|
|
3.0 |
0.0 |
2.5 |
2.0 |
0.0 |
1.6 |
|
|
1.5 |
0.0 |
0.881832 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
1.186 |
|
Z= |
0 |
-1.52727 |
-0.741239 |
-1.374394 |
-0.14511 |
-0.530312 |
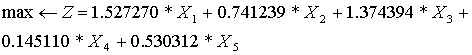
subject to (4)
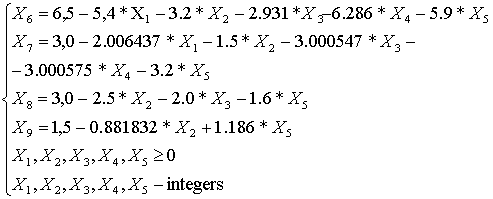
Iteration 1.
Preliminary conditions: 1. The problem 1. 2. The bottom bound
![]() .
.
Stage 1. We choose
the task 1 and it is solved it. We receive the optimum plan ![]() (1,037635, 0, 0.305961, 0, 0),
(1,037635, 0, 0.305961, 0, 0), ![]() =2,00526.
=2,00526.
Stage 2. The task 1
has the decision. Transition to 3 stage.
Stage 3. ![]() =2,00526>
=2,00526>![]() . Transition to 4 stage.
. Transition to 4 stage.
Stage 4. Variables
have fractional values. Transition to 5 stage.
Stage 5. The task 1
is excluded from the list. The list joins two new problems: 2 and 3.
The admissible decision
is resulted in table 2.
Table 2
The admissible decision
|
ÁÏ |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0,58484 |
-0,371563 |
0,311 |
1,911498 |
0,664934 |
1,007782 |
|
|
3,0 |
0 |
2,5 |
2,0 |
0 |
1,6 |
|
|
1,5 |
0 |
0,881832 |
0 |
0 |
1,186 |
|
Z= |
1,83838 |
0,282827 |
0,16381 |
-0,545426 |
1,632745 |
1,138371 |
The optimum
decision of the continuous problem is resulted in table 3.
Table 3
The optimum decision of the continuous problem.
|
ÁÏ |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
1,037635 |
0,290692 |
0,504283 |
-0,283954 |
0,975263 |
0,806429 |
|
|
0,305961 |
-0,194383 |
0,1627 |
0,52315 |
0,34786 |
0,527221 |
|
|
2,388078 |
0,388766 |
2,174601 |
-1,0463 |
-0,69572 |
0,545558 |
|
|
1,5 |
0 |
0,881832 |
0 |
0 |
1,186 |
|
Z= |
2,00526 |
0,176807 |
0,252551 |
0,28534 |
1,822477 |
1,425931 |
The problem 2.
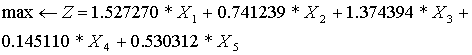
subject to (5)
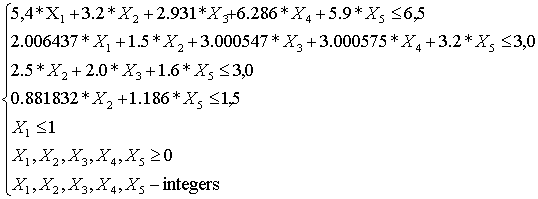
The problem 3.
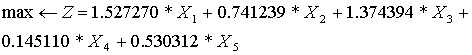
subject to (6)
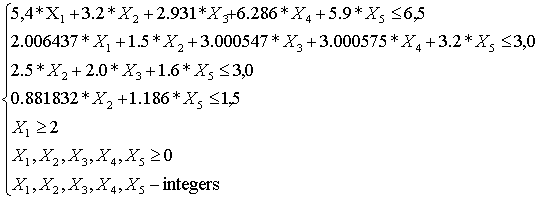
Optimum decision ![]() (1, 0, 0, 0, 0),
(1, 0, 0, 0, 0), ![]() =1,527270.
=1,527270.
Results of the lead
researches have allowed to draw following conclusions.
1. The integer
mathematical model of optimization of the information system is developed,
allowing to reduce expenses and terms of designing of information systems and
to raise validity of accepted decisions.
2. The optimum
decision of an integer problem of optimization of information system is found
by the branch and bound method.
References:
1. Hamdy A Taha
Operations Research: An Introduction. Seven Edition - Ì.: Publishing house "Williams", 2005 - 912
p.
2. Mastyaeva I.N.,
Gorbovtsov G.Y., Semenikhin O.N. Operations Research in economy: the Manual /
the Moscow state university of economy, statistics and computer science. - Ì.: ÌSUESC, 2003. - 119
p.
3. Semakhin A.M.
The analysis of mathematical model of information system. In the collection of
materials X of the All-Russia scientifically-practical conference with the
international participation (on November, 25-26th, 2011). - Tomsk: Publishing
house of Tomsk university . Part 2 - 206 p.