Современные информационные
технологии/3. Программное обеспечение
Zhuaspaev T.A
A.Baitursynov Kostanai State
University, Kazakhstan
DEVELOPMENT MODEL OF BEHAVIOR
Interaction diagrams are models that
describe the behavior of groups of interacting objects. Typically, an
interaction diagram covers the behavior of only one use case. On this chart
displays the number of objects and the messages they exchange with each other
within a given use.
There are two types of interaction
diagrams: sequence diagrams and charts cooperative.
Developing a model of behavior in
Rational Rose through the sequence diagram.
This type of chart allows us to
describe the interaction of objects, abstracting from the message sequence. On
this type of diagrams in a compact form displays all messages received and
transmitted on the subject and types of messages.
On the sequence diagram depicted
objects that are directly involved in the interaction and do not show the
possibility of static association with other objects. Sequence diagram for the
key point is it is the dynamics of interaction of objects in time. In this
sequence diagram is as if the two measurements. One - from left to right as
vertical lines, each of which depicts the life of a line object participating
in an interaction. The second - a vertical time axis pointing downwards. In
this case the interaction of objects implemented by messages that are sent to a
single object and also form another order in the time of the occurrence.
Lifeline object - is used to denote the period of time during
which the object exists in the system and hence can participate in all its
interactions. System objects can be created as needed, significantly saving
system resources and increasing productivity.
Focus control - serves to highlight
objects in the active state.
Each interaction is described by a
set of messages that are involved in it the objects exchanged between.
Message - finished piece of
information that is sent by one entity to another. While receiving a message
initiates specific actions aimed at solving a particular task by the object to
which the message was sent.
The UML can meet several varieties of
posts:
1. The first kind of message is the
most common and is used to call procedures, operations or designate individual
nested threads.
2. The second kind of message is used
to indicate a simple control flow. Each such arrow indicates the flow advances
one step. The corresponding messages are usually asynchronous.
On Figure 1 is a sequence diagram
modeling the user authentication.
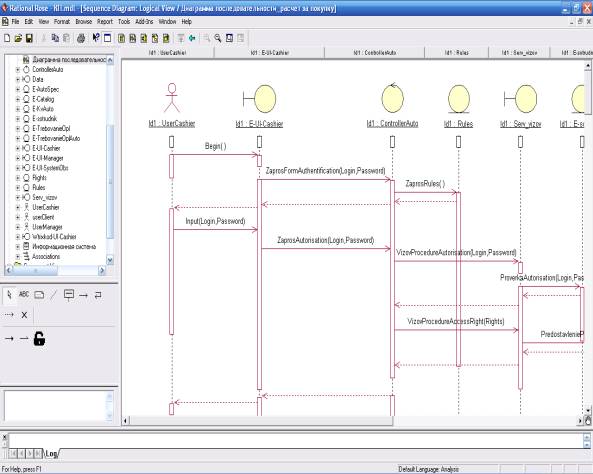
Picture 1. Example development behaviors.
Each type of interaction diagrams has
its advantages, the choice is usually carried out based on the developer's. On
sequence diagrams is the emphasis on the sequence of messages, while easier to
observe the order in which various events occur. In the case of cooperative
charts, you can use the spatial location of the object in order to show them
the static interaction.
One of the main properties of any
interaction diagram is its simplicity. Looking at the chart, you can easily see
all the messages.
But when trying to portray something
more complex than a single sequential process without a lot of conditional
branches or loops, this approach may not work.
To display conditional behavior on interaction diagrams there are two
approaches. One of them consists in using separate graphs for each scenario. The
second is that the messages are accompanied by conditions, showing the behavior
of objects.
Literature:
1. Калянов
Г.Н. CASE-технологии: Консалтинг
в автоматизации бизнес-процессов. 2-е изд. перераб. и доп. -
М.-Горячая линия – Телеком, 2000.-320 с.
2. Вендров
А.М. Проектирование программного обеспечения экономических
информационных систем. Учебник. М.: Финансы и статистика, 2000. – 352 с.: ил.
3. Уэнди Боггс, Майкл Боггс. UML и Rational
Rose 2002. Издательство “Лори”, 2004. -
509 с.